00007640652021FYfalseImplemented236648508516031295http://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitieshttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitieshttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent00007640652021-01-012021-12-3100007640652021-06-30iso4217:USD00007640652022-02-10xbrli:shares00007640652021-12-3100007640652020-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares00007640652020-01-012020-12-3100007640652019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-3100007640652019-12-3100007640652018-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-31clf:employee0000764065clf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-11-18clf:segment0000764065clf:HibbingMember2019-12-31xbrli:pure0000764065clf:HibbingMember2020-12-090000764065clf:HibbingMember2021-12-310000764065clf:HibbingMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentAssetsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentAssetsMember2020-12-310000764065srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:LandImprovementsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:LandImprovementsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:BuildingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:BuildingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:EquipmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:EquipmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:WorkforceSubjectToCollectiveBargainingArrangementsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMemberus-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMemberus-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMemberus-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMemberclf:AKSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-11-182021-12-310000764065clf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-11-182021-11-180000764065us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMemberclf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-11-182021-11-180000764065clf:SupplierRelationshipsMemberclf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-11-182021-11-180000764065us-gaap:TrademarksAndTradeNamesMemberclf:FerrousProcessingAndTradingMember2021-11-182021-11-180000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-12-092020-12-090000764065us-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2020-12-092020-12-090000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-12-092020-12-0900007640652020-12-092020-12-090000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-12-090000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMemberus-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2020-12-092020-12-090000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMemberus-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2020-12-090000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-12-090000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-12-092021-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2021-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-130000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:AKSteelMember2020-03-130000764065us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:A75002023AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:AKSteelMember2020-03-142021-03-310000764065clf:AKSteelMember2021-03-3100007640652020-03-142021-03-310000764065us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:AKSteelMemberus-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065us-gaap:TrademarksAndTradeNamesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMemberus-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMemberus-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMemberus-gaap:FairValueAdjustmentToInventoryMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMemberus-gaap:FairValueAdjustmentToInventoryMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMemberus-gaap:AcquisitionRelatedCostsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMemberus-gaap:AcquisitionRelatedCostsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:RestructuringCostsMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FranchiseMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FranchiseMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAAndAKSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:SalesMemberclf:CustomerSupplyAgreementMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:SalesMemberclf:CustomerSupplyAgreementMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:AutomotiveMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:AutomotiveMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:AutomotiveMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:InfrastructureAndManufacturingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:InfrastructureAndManufacturingMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:InfrastructureAndManufacturingMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:DistributorsAndConvertersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:DistributorsAndConvertersMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:DistributorsAndConvertersMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:SteelProducersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:SteelProducersMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:SteelProducersMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMemberclf:AutomotiveMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMemberclf:AutomotiveMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMemberclf:AutomotiveMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:InfrastructureAndManufacturingMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:InfrastructureAndManufacturingMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:InfrastructureAndManufacturingMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:DistributorsAndConvertersMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:DistributorsAndConvertersMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:DistributorsAndConvertersMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:HotRolledSteelMember2021-01-012021-12-31utr:T0000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:HotRolledSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:HotRolledSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:ColdRolledSteelMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:ColdRolledSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:ColdRolledSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:CoatedSteelMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:CoatedSteelMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:CoatedSteelMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:StainlessAndElectricalSteelMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:StainlessAndElectricalSteelMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:StainlessAndElectricalSteelMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:PlateMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:PlateMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:PlateMemberclf:SteelmakingMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:OtherSteelProductsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:OtherSteelProductsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:OtherSteelProductsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:OtherMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:OtherMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberclf:OtherMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:OtherMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:OtherMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:OtherMemberclf:OtherBusinessesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCurrentLiabilitiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCurrentLiabilitiesMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCurrentLiabilitiesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCurrentLiabilitiesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCurrentLiabilitiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherNoncurrentLiabilitiesMember2021-12-310000764065clf:CorporateandOtherSegmentsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:CorporateandOtherSegmentsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:CorporateandOtherSegmentsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:EBITDACalculationMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:EBITDACalculationMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:EBITDACalculationMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:AdjustedEBITDACalculationMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AdjustedEBITDACalculationMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:AdjustedEBITDACalculationMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberus-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMemberus-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2020-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMemberus-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2021-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMemberus-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2020-12-310000764065clf:CorporateandOtherSegmentsMember2021-12-310000764065clf:CorporateandOtherSegmentsMember2020-12-310000764065country:US2021-01-012021-12-310000764065country:US2020-01-012020-12-310000764065country:US2019-01-012019-12-310000764065country:CA2021-01-012021-12-310000764065country:CA2020-01-012020-12-310000764065country:CA2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:OtherCountriesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:OtherCountriesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:OtherCountriesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065country:US2021-12-310000764065country:US2020-12-310000764065country:US2019-12-310000764065country:CA2021-12-310000764065country:CA2020-12-310000764065country:CA2019-12-310000764065clf:OtherCountriesMember2021-12-310000764065clf:OtherCountriesMember2020-12-310000764065clf:OtherCountriesMember2019-12-310000764065clf:LandlandimprovementsandmineralrightsMember2021-12-310000764065clf:LandlandimprovementsandmineralrightsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:BuildingMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:BuildingMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:MachineryAndEquipmentMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:MachineryAndEquipmentMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCapitalizedPropertyPlantAndEquipmentMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherCapitalizedPropertyPlantAndEquipmentMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2020-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMember2021-12-310000764065clf:SteelmakingMember2020-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMember2021-12-310000764065clf:OtherBusinessesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CustomerRelationshipsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:TradeNamesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:TradeNamesMember2020-12-310000764065clf:MiningPermitsMember2021-12-310000764065clf:MiningPermitsMember2020-12-310000764065clf:SupplierRelationshipsMember2021-12-310000764065clf:SupplierRelationshipsMember2020-12-310000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A67502026SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A70002027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A70002027AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-12-310000764065clf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A62502040SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-12-310000764065clf:A48752024SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A67502026SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A76252021AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-12-310000764065clf:A75002023AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-12-310000764065clf:A6.3752025SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A63752025AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-12-310000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A57502025SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A70002027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A70002027AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-12-310000764065clf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:A62502040SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065clf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-12-310000764065clf:EDCRevolvingCreditFacilityMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneUponEquityIssuanceMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMember2021-03-112021-03-1100007640652021-02-110000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A67502026SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A67502026SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneUponEquityIssuanceMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:A67502026SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-02-170000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-02-170000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberclf:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneUponEquityIssuanceMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A46252029SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberclf:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneUponEquityIssuanceMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752031SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFiveMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MinimumMemberclf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberclf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2022-01-182022-01-180000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A70002027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:A70002027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneUponEquityIssuanceMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A62502040SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A57502025SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A62502040SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberclf:A70002027AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberclf:A70002027AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2020-03-130000764065us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2020-03-130000764065us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2020-03-270000764065us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2020-12-090000764065us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-12-170000764065us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2021-12-310000764065clf:EDCRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-10-012021-12-310000764065clf:A70002027AKSeniorNotesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-09-300000764065clf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMember2021-10-152021-10-150000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2021-07-012021-09-300000764065clf:A57502025SeniorNotesMember2021-04-012021-06-300000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMember2021-04-012021-06-300000764065us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-03-122021-03-120000764065clf:A98752025SeniorSecuredNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A48752024SeniorSecuredNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A76252021AKSeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A75002023AKSeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A6.3752025SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A63752025AKSeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:A57502025SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMember2021-01-012021-12-3100007640652020-04-242020-04-240000764065us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A76252021AKSeniorNotesMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:A75002023AKSeniorNotesMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:A76252021AKSeniorNotesMember2020-03-272020-03-270000764065clf:A75002023AKSeniorNotesMember2020-03-272020-03-270000764065clf:A76252021AKSeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A75002023AKSeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A48752024SeniorSecuredNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A6.3752025SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A15002025ConvertibleSeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A57502025SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A70002027SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A62502040SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A63752025AKSeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:A5.8752027SeniorNotesMemberclf:ClevelandCliffsInc.Member2019-12-310000764065clf:A57502025SeniorNotesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:A48752021SeniorNotesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberclf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberclf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberclf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberclf:IndustrialRevenueBondsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberclf:EDCRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberclf:EDCRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberclf:EDCRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberclf:EDCRevolvingCreditFacilityMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDiscountRatesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDiscountRatesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDiscountRatesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDiscountRatesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDemographicMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDemographicMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDemographicMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ChangeinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansDemographicMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansMortalityMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansMortalityMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansMortalityMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansMortalityMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansPerCapitaClaimsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansPerCapitaClaimsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansPerCapitaClaimsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansPerCapitaClaimsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansOtherActuarialGainLossMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansOtherActuarialGainLossMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansOtherActuarialGainLossMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansOtherActuarialGainLossMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansActuarialGainLossMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansActuarialGainLossMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansActuarialGainLossMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:ChangesinAssumptionsforDefinedBenefitPlansActuarialGainLossMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:VebaTrustMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:DirectPaymentsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:VebaTrustMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:DirectPaymentsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:VebaTrustMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065clf:DirectPaymentsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FixedIncomeInvestmentsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FixedIncomeInvestmentsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FixedIncomeInvestmentsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FixedIncomeInvestmentsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:StructuredFinanceMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:StructuredFinanceMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:StructuredFinanceMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:StructuredFinanceMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:NonUSAndOtherBondsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DefinedBenefitPlanEquitySecuritiesNonUsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:USGovernmentAgenciesDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:DomesticCorporateDebtSecuritiesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:HedgeFundsMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PrivateEquityFundsMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberclf:StructuredCreditMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:RealEstateMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:TrustForBenefitOfEmployeesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:TrustForBenefitOfEmployeesMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:TrustForBenefitOfEmployeesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:TrustForBenefitOfEmployeesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:TrustForBenefitOfEmployeesMember2021-12-310000764065clf:SteelworkersPensionTrustMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SteelworkersPensionTrustMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SteelworkersPensionTrustMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelworkersPensionTrustMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MaximumMemberclf:SteelworkersPensionTrustMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:IAMNationalPensionFundsNationalPensionPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:IAMNationalPensionFundsNationalPensionPlanMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:IAMNationalPensionFundsNationalPensionPlanMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065srt:MinimumMemberclf:IAMNationalPensionFundsNationalPensionPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MaximumMemberclf:IAMNationalPensionFundsNationalPensionPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AmericanMaritimeOfficersPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AmericanMaritimeOfficersPlanMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:AmericanMaritimeOfficersPlanMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:SteelworkersPensionTrustMember2020-12-310000764065clf:A2021EquityPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AR2015EquityPlanMember2021-12-310000764065clf:A2021EquityPlanMember2021-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMemberclf:AR2015EquityPlanMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:LongTermPerformancePlanMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065clf:AKSteelMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2020-03-132020-03-130000764065us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:SellingGeneralAndAdministrativeExpensesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AcquisitionRelatedCostsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AcquisitionRelatedCostsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AcquisitionRelatedCostsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-12-310000764065clf:LongTermPerformancePlanMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMemberclf:AKSteelMember2021-12-310000764065srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:AKSteelMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-12-310000764065clf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2021-12-310000764065clf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2020-12-310000764065clf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2019-12-310000764065clf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:DeferredCompensationShareBasedPaymentsMemberclf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:DeferredCompensationShareBasedPaymentsMemberclf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:DeferredCompensationShareBasedPaymentsMemberclf:DirectorsPlanMembersrt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:ShareBasedPaymentArrangementNonemployeeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:DissolutionofentitiesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:DissolutionofentitiesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:DissolutionofentitiesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:IncludedinincometaxexpensebenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:IncludedinincometaxexpensebenefitMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:IncludedinincometaxexpensebenefitMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:IncreaseDecreaseFromAcquisitionsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:IncreaseDecreaseFromAcquisitionsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:IncreaseDecreaseFromAcquisitionsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:DissolutionofentitiesMembercountry:LU2019-01-012019-12-310000764065country:LUclf:IntercompanynotesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:OtherLiabilitiesMember2021-12-310000764065clf:ArcelorMittalMember2021-02-110000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2021-07-012021-09-3000007640652021-03-3100007640652021-04-290000764065us-gaap:SeriesAPreferredStockMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2021-12-3100007640652021-04-012021-06-3000007640652021-01-012021-03-310000764065us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2018-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedDefinedBenefitPlansAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedForeignCurrencyAdjustmentIncludingPortionAttributableToNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:AccumulatedGainLossCashFlowHedgeIncludingNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:ReclassificationOutOfAccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:ReclassificationOutOfAccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065us-gaap:ReclassificationOutOfAccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000764065clf:HibbingMemberclf:USSteelCanadaMember2021-12-310000764065clf:HibbingMemberclf:ArcelorMittalUSAMember2020-12-090000764065clf:SunCokeMiddletownMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065clf:SunCokeMiddletownMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2020-01-012020-12-310000764065clf:SunCokeMiddletownMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-12-310000764065clf:SunCokeMiddletownMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2020-12-310000764065us-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:ConvertibleDebtSecuritiesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000764065us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-182022-01-180000764065us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2022-02-10
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021
OR
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 1-8944
CLEVELAND-CLIFFS INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ohio | | 34-1464672 | |
| (State or Other Jurisdiction of
Incorporation or Organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) | |
| | | | | | |
| 200 Public Square, | Cleveland, | Ohio | | 44114-2315 | |
| (Address of Principal Executive Offices) | | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (216) 694-5700
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | | Trading Symbol(s) | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Shares, par value $0.125 per share | | CLF | | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(g) of the Act: NONE
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ NO ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of June 30, 2021, the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common shares held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based on the closing price of $21.56 per share as reported on the New York Stock Exchange — Composite Index, was $10,636,421,962 (excluded from this figure are the voting shares beneficially owned by the registrant’s officers and directors).
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s common shares, par value $0.125 per share, was 525,409,705 as of February 10, 2022.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s proxy statement for its 2022 annual meeting of shareholders are incorporated by reference into Part III.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | Page Number |
| | | | | |
| DEFINITIONS | | | |
| | | |
| PART I | | | |
| Item 1. | Business | | | |
| | Information About Our Executive Officers | | | |
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | | | |
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | | | |
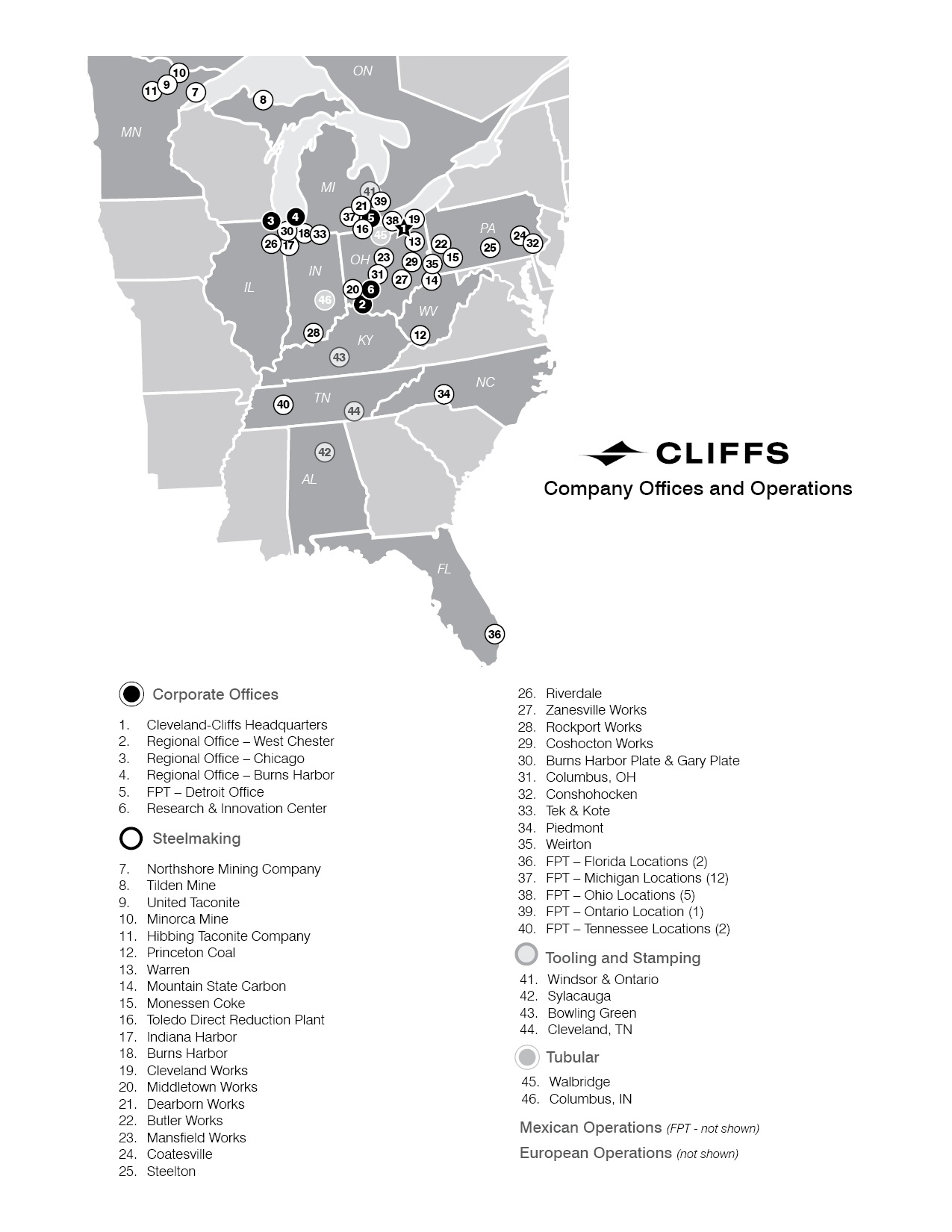
| Item 2. | Properties | | | |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | | | |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | | | |
| | | | | |
| PART II | | | |
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | | | |
| Item 6. | [Reserved] | | | |
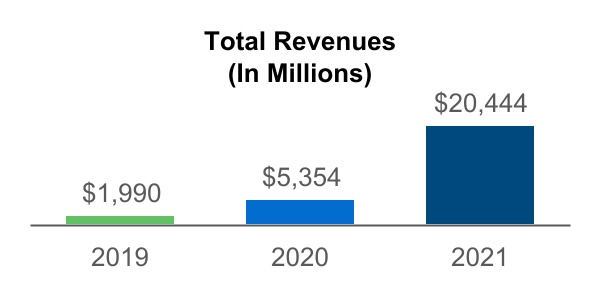
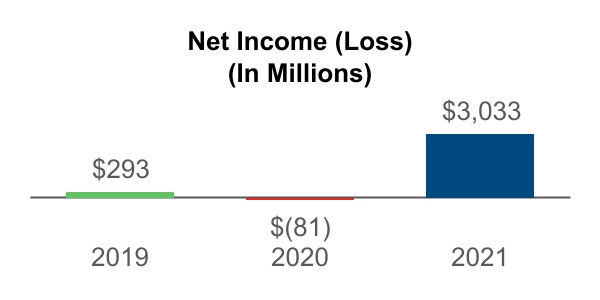
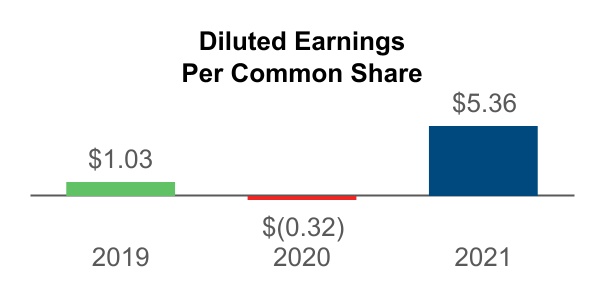
| Item 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | | | |
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | | | |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | | | |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | | | |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | | | |
| Item 9B. | Other Information | | | |
| Item 9C. | Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections | | | |
| | | |
PART III | | | |
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | | | |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation | | | |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | | | |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | | | |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services | | | |
| | | | | |
| PART IV | | | |
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | | | |
| Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary | | | |
| | | |
| SIGNATURES | | | |
DEFINITIONS
The following abbreviations or acronyms are used in the text. References in this report to the “Company,” “we,” “us,” “our” and “Cliffs” are to Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and subsidiaries, collectively. References to “$” is to United States currency.
| | | | | | | | |
| Abbreviation or acronym | | Term |
| 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes | | 4.625% Senior Guaranteed Notes due 2029 issued by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. on February 17, 2021 in an aggregate principal amount of $500 million |
| 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes | | 4.875% Senior Guaranteed Notes due 2031 issued by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. on February 17, 2021 in an aggregate principal amount of $500 million |
| 2012 Amended Equity Plan | | Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. 2012 Incentive Equity Plan, as amended or amended and restated from time to time |
| 2020 Acquisitions | | The AK Steel Merger and AM USA Transaction, collectively |
| 2021 Equity Plan | | Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. 2021 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan |
| A&R 2015 Equity Plan | | Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. Amended and Restated 2015 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan |
| ABL Facility | | Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of March 13, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, as amended as of March 27, 2020, December 9, 2020 and December 17, 2021, and as may be further amended from time to time |
| Adjusted EBITDA | | EBITDA, excluding certain items such as EBITDA of noncontrolling interests, extinguishment of debt, severance, acquisition-related costs, acquisition-related loss on equity method investment, amortization of inventory step-up, impacts of discontinued operations and intersegment corporate allocations of selling, general and administrative costs |
| AG | | Autogenous grinding |
| AHSS | | Advanced high-strength steel |
| | |
| AK Steel | | AK Steel Holding Corporation (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Steel Holding Corporation) and its consolidated subsidiaries, including AK Steel Corporation (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Steel Corporation), its direct, wholly owned subsidiary, collectively, unless stated otherwise or the context indicates otherwise |
| AK Steel Merger | | The merger of Merger Sub with and into AK Steel, with AK Steel surviving the merger as a wholly owned subsidiary of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the Merger Agreement, consummated on March 13, 2020 |
| AK Steel Merger Agreement | | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of December 2, 2019, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., AK Steel and Merger Sub |
| AM USA Transaction | | The acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA, consummated on December 9, 2020 |
| AM USA Transaction Agreement | | Transaction Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2020, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and ArcelorMittal |
| | |
| ANSI | | American National Standards Institute |
| AOCI | | Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
| APBO | | Accumulated postretirement benefit obligation |
| ArcelorMittal | | ArcelorMittal S.A., a company organized under the laws of Luxembourg and the former ultimate parent company of ArcelorMittal USA |
| ArcelorMittal USA | | Substantially all of the operations of the former ArcelorMittal USA LLC, its subsidiaries and certain affiliates, and Kote and Tek, collectively |
| ASC | | Accounting Standards Codification |
| ASTM | | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| ASU | | Accounting Standards Update |
| BART | | Best available retrofit technology |
| BNSF | | Burlington Northern Santa Fe, LLC |
| Board | | The Board of Directors of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. |
| BOF | | Basic Oxygen Furnace |
| CAFE | | Corporate Average Fuel Economy |
| CARES Act | | Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act |
| CECL | | Current expected credit losses |
| CERCLA | | Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act of 1980 |
| CFR | | Cost and freight |
| Clean Water Act | | Federal Water Pollution Control Act |
| CN | | Canadian National Railway Company |
| Compensation Committee | | Compensation and Organization Committee of the Board |
| COVID-19 | | A novel strain of coronavirus that the World Health Organization declared a global pandemic in March 2020 |
| Directors’ Plan | | Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. 2021 Nonemployee Directors’ Compensation Plan |
| Dodd-Frank Act | | Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act |
| DOE | | U.S. Department of Energy |
| DR-grade | | Direct reduction-grade |
| EAF | | Electric arc furnace |
| EBITDA | | Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization |
| | | | | | | | |
| Abbreviation or acronym | | Term |
| EDC | | Export Development Canada |
| EGLE | | Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes and Energy |
| Empire | | Iron ore mining property owned by Empire Iron Mining Partnership, an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs |
| EPA | | U.S. Environmental Protection Agency |
| EPS | | Earnings per share |
| ERISA | | Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended |
| EV | | Electric vehicle |
| Exchange Act | | Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended |
| FASB | | Financial Accounting Standards Board |
| FCA | | Financial Conduct Authority (the authority that regulates LIBOR) |
| Fe | | Iron |
| FeT | | Total iron |
| FILO | | First-in, last-out |
| FIP | | Federal implementation plan |
| | |
| Former ABL Facility | | Amended and Restated Syndicated Facility Agreement, dated as of March 30, 2015, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the subsidiary borrowers party thereto, the lenders party thereto and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, as amended and restated as of February 28, 2018, and as further amended, which was terminated on March 13, 2020 in connection with entering into the ABL Facility |
| FPT | | Ferrous Processing and Trading Company, including certain related entities |
| FPT Acquisition | | The purchase of FPT, subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the FPT Acquisition Agreement |
| FPT Acquisition Agreement | | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 8, 2021, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Anthony Soave Revocable Trust u/a/d January 14, 1987, as amended and restated |
| GAAP | | Accounting principles generally accepted in the United States |
| GHG | | Greenhouse gas |
| GOES | | Grain oriented electrical steel |
| HBI | | Hot briquetted iron |
| Hibbing | | Iron ore mining property owned by Hibbing Taconite Company, an unincorporated joint venture between subsidiaries of Cliffs and U.S. Steel |
| HRC | | Hot-rolled coil steel |
| HVAC | | Heating, ventilation and air conditioning equipment |
| IAM | | International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers |
| IBA | | ICE Benchmark Administration Limited (the entity that calculates and publishes LIBOR) |
| IRB | | Industrial Revenue Bond |
| IRC | | U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended |
| ISO | | International Organization for Standardization |
| IT | | Information technology |
| JSW Steel | | JSW Steel (USA) Inc. and JSW Steel USA Ohio, Inc., collectively |
| Kote and Tek | | Cleveland-Cliffs Kote L.P. and Cleveland-Cliffs Tek L.P., collectively |
| LIBOR | | London Interbank Offered Rate |
| LIFO | | Last-in, first-out |
| LoM | | Life-of-mine |
| Long ton | | 2,240 pounds |
| LS&I | | Lake Superior & Ishpeming Railroad Company |
| Merger Sub | | Pepper Merger Sub Inc., a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs prior to the AK Steel Merger |
| Metric ton | | 2,205 pounds |
| Minorca | | Iron ore mining property owned by Cleveland-Cliffs Minorca Mine Inc. (f/k/a ArcelorMittal Minorca Mine Inc.), an
indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs acquired in connection with the AM USA Transaction |
| MMBtu | | Million British Thermal Units |
| MPCA | | Minnesota Pollution Control Agency |
| MSHA | | Mine Safety and Health Administration of the U.S. Department of Labor |
| NAV | | Net asset value |
| Net ton | | 2,000 pounds |
| NOL | | Net operating loss |
| NOVs | | Notices of violations |
NOx | | Nitrogen oxide |
| NOES | | Non-oriented electrical steel |
| | | | | | | | |
| Abbreviation or acronym | | Term |
| Northshore | | Iron ore mining property owned by Northshore Mining Company, a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs |
| NPDES | | National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System, authorized by the Clean Water Act |
| NWPR | | Navigable Waters Protection Rule |
| NYSE | | New York Stock Exchange |
| OPEB | | Other postretirement benefits |
| OSHA | | Occupational Safety and Health Administration of the U.S. Department of Labor |
| PBO | | Projected benefit obligation |
| PHS | | Press-hardened steel |
| Platts 62% price | | Platts IODEX 62% Fe Fines CFR North China |
| PPI | | Producer Price Indices |
| | |
| QA/QC | | Quality assurance/quality control |
| QP | | Qualified person, within the meaning set forth in Item 1300 of Regulation S-K |
| RCRA | | Resource Conservation and Recovery Act |
| RI/FS | | Remedial Investigation/Feasibility Study |
| | |
| S&P | | Standard & Poor's |
| SEC | | U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission |
| Second ABL Amendment | | Second Amendment to Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of December 9, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent |
| Section 232 | | Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962 (as amended by the Trade Act of 1974) |
| Securities Act | | Securities Act of 1933, as amended |
| SIP | | State Implementation Plan |
| SLR | | SLR International Corporation |
| SOFR | | Secured Overnight Financing Rate |
| STRIPS | | Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal of Securities |
| SunCoke Middletown | | Middletown Coke Company, LLC, a subsidiary of SunCoke Energy, Inc. |
| Third ABL Amendment | | Third Amendment to Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of December 17, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent |
| Tilden | | Iron ore mining property owned by Tilden Mining Company L.C., an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs |
| TMDL | | Total maximum daily load |
| Tooling and Stamping | | Cleveland-Cliffs Tooling and Stamping Holdings LLC (f/k/a PPHC Holdings, LLC), an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs, together with its subsidiaries |
| Topic 805 | | ASC Topic 805, Business Combinations |
| Topic 815 | | ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging |
| TSR | | Total shareholder return |
| Tubular Components | | Cleveland-Cliffs Tubular Components LLC (f/k/a AK Tube LLC), an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs |
| United Taconite | | Iron ore mining property owned by United Taconite LLC, an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs |
| U.S. | | United States of America |
| U.S. Steel | | United States Steel Corporation and its subsidiaries, collectively, unless stated otherwise or the context indicates otherwise |
| UAW | | United Auto Workers |
| USMCA | | United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement |
| USW | | United Steelworkers |
| VEBA | | Voluntary employee benefit association trusts |
| VIE | | Variable interest entity |
| WLT | | Wet long ton |
PART I
Introduction
Cliffs is the largest flat-rolled steel producer in North America. Founded in 1847 as a mine operator, we are also the largest manufacturer of iron ore pellets in North America. We are vertically integrated from mined raw materials, direct reduced iron and ferrous scrap to primary steelmaking and downstream finishing, stamping, tooling and tubing. We are the largest supplier of steel to the automotive industry in North America and serve a diverse range of other markets due to our comprehensive offering of flat-rolled steel products. Headquartered in Cleveland, Ohio, we employ approximately 26,000 people across our operations in the United States and Canada.
On November 18, 2021, we completed the acquisition of FPT, a leading prime ferrous scrap processor in the U.S. These operations consist of 22 scrap processing facilities, primarily in the Midwest region of the United States. The FPT Acquisition bolsters our raw materials position by securing access to prime scrap, which will allow us to optimize productivity at our existing EAFs and BOFs.
Competitive Strengths
As the largest flat-rolled steel producer in North America, we benefit from having the size and scale necessary in a competitive, capital intensive business. Our sizeable operating footprint provides us with the operational leverage, flexibility and cost performance to achieve competitive margins throughout the business cycle. We also have a unique vertically integrated profile from mined raw materials, direct reduced iron, and ferrous scrap to primary steelmaking and downstream finishing, stamping, tooling and tubing. This positioning gives us both lower and more predictable costs throughout the supply chain and more control over both our manufacturing inputs and our end product destination.
Our legacy business of producing iron ore pellets, which is our primary steelmaking raw material input, is another competitive advantage. By controlling our iron ore pellet supply, our primary steelmaking raw material feedstock can be secured at a stable and predictable cost and not be subject to as many factors outside of our control.
The FPT Acquisition gives us a competitive advantage in sourcing prime scrap, as we expect to leverage our long-standing flat-rolled automotive and other customer relationships into recycling partnerships to further grow our prime scrap presence. Additionally, FPT has 22 facilities located primarily in the Midwest near our steel facilities, which gives us an increased advantage in logistics.
We are also the largest supplier of automotive-grade steel in the U.S. Compared to other steel end markets, automotive steel is generally higher quality and more operationally and technologically intensive to produce. As such, it often generates higher through-the-cycle margins, making it a desirable end market for the steel industry. Given the strong demand and market environment in 2021, we were able to significantly improve our fixed price contracts, which should benefit us throughout 2022. Demand for our automotive-grade steel is expected to increase with pent-up automotive demand as a result of the semiconductor shortage. Automotive customers have requested higher volumes in contract negotiations compared to the prior year, which we believe is a sign of the semiconductor shortage easing. With our continued technological innovation, as well as leading delivery performance, we expect to remain the leader in supplying this industry.
We are the only producers of both GOES and NOES in the U.S. The recently passed Infrastructure and Jobs Act of 2021 in the U.S. provides funding to be used for the modernization of the electrical grid and the infrastructure needed to allow for increased EV adoption, both of which require our electrical steels. As a result, with increased demand for both transformers and motors for EVs, we expect to benefit from this position in what is currently a rapidly growing market.
We believe we offer the most comprehensive flat-rolled steel product selection in the industry, along with several complementary products and services. A sampling of our offering includes AHSS, hot-dipped galvanized, aluminized, galvalume, electrogalvanized, galvanneal, HRC, cold-rolled coil, plate, tinplate, GOES, NOES, stainless steels, tool and die, stamped components, rail, slab and cast ingot. Across the quality spectrum and the supply chain, our customers can frequently find the solutions they need from our product selection.
We are the first and the only producer of HBI in the Great Lakes region. Construction of our Toledo direct reduction plant was completed in the fourth quarter of 2020 and reached full run-rate nameplate annual capacity of 1.9 million metric tons during the middle of 2021. From this modern plant, we produce a high-quality, low-cost and low-carbon intensive HBI product that can be used in our blast furnaces and as a productivity enhancer in our BOFs and EAFs as a scrap alternative. We can use HBI to stretch our hot metal production, lowering carbon intensity and reliance on coke. As a result of our internal usage of HBI, coupled with our ongoing evaluation of coke use strategies, we idled our coke facility at Middletown Works during the third quarter of 2021 and we intend to permanently idle our Mountain State Carbon coke plant in the second quarter of 2022. With increasing tightness in the scrap market and our own internal needs for scrap and metallics, we expect our Toledo direct reduction plant to support healthy margins for us going forward.
Strategy
Maximize Our Commercial Strengths
We offer a full suite of flat steel products encompassing all steps of the steel manufacturing process. We have an industry-leading market share in the automotive sector, where our portfolio of high-end products delivers a broad range of differentiated solutions for this highly sought after customer base.
As a result of our exposure to these high-end markets, we have the highest fixed price contractual volumes in our industry. Approximately 45% of our volumes are sold under these contracts. These contracts reduce volatility and allow for more predictable through-cycle margins. Our fixed contract values are expected to dramatically improve in 2022 compared to 2021.
We are also proponents of the “value over volume” approach in terms of steel supply. We take our leadership role in the industry very seriously and intend to manage our steel output in a responsible manner. In the fourth quarter of 2021, we elected to pull forward repairs and maintenance to match automotive demand that was negatively impacted by the semiconductor shortage. Going forward, we will continue to use our operational flexibility to align with our “value over volume” approach in terms of steel supply.
Optimize Our Fully Integrated Steelmaking Footprint
We are a fully-integrated steel enterprise with the size and scale to achieve margins above industry averages for flat-rolled steel. Our focus remains on both maintaining and enhancing our cost advantage while also lowering carbon emissions. The combination of our ferrous raw materials, including iron ore, scrap, and HBI, allows us to do so relative to peers who must rely on more unpredictable and unreliable raw material sourcing strategies.
In 2022, we intend to use more scrap and HBI in our melting processes to stretch our production of liquid pig iron from traditional inputs. The use of higher amounts of these raw materials in our blast furnaces ultimately boosts liquid steel output, which will reduce coke needs and lower carbon emissions from our operations. With our acquisition of FPT, we have ample access to scrap along with internally sourced HBI.
Expand our Ferrous Scrap Recycling Presence
Throughout our entire footprint, we consume a very significant amount of scrap in our EAFs and BOFs, more than half of which can now be obtained through internal sources. Prime scrap is a byproduct of industrial manufacturing. As manufacturing in the U.S. has moved offshore and yields have improved, prime scrap supply has been shrinking for the last 50 years. As the steel industry continues to increase its focus on decarbonization and brings new flat-rolled EAF capacity online over the next five years, securing additional access to prime scrap will continue to be an important strategic initiative.
Our expansion in this area began with the FPT Acquisition and will continue to grow by pairing FPT's processing capabilities with our long-standing customer relationships. As the largest supplier of flat-rolled steel in North America, we are the largest source of the steel that generates prime scrap in manufacturing facilities. Based on this, we seek to leverage our long-standing flat-rolled automotive and other customer relationships into recycling partnerships to grow our prime scrap presence. The FPT Acquisition allows us to optimize productivity at our existing EAFs and BOFs, as we have no current plans to add additional steelmaking capacity.
Advance our Participation in the Green Economy
We are seeking to expand our customer base with the rapidly growing and desirable electric vehicle market. At this time, we believe the North American automotive industry is approaching a structural inflection point, with the adoption of electrical motors in passenger vehicles. As this market grows, it will require more advanced steel
applications to meet the needs of electric vehicle producers and consumers. With our unique technical capabilities and leadership in the automotive industry, we believe we are positioned better than any other North American steelmaker to supply the steel and parts necessary to fill these needs.
We also have the right products to meet the growing demand for renewable energy as well as for the modernization of the U.S. electrical grid. We offer plate products that can be used in windmills, which we estimate contain 130 tons of steel per megawatt of electricity. In addition, panels for solar power are heavy consumers of galvanized steel, where we are a leading producer. We estimate solar panels consume 40 tons of steel per megawatt of electricity.
We are currently the sole producer of electrical steel in the U.S., which can facilitate the modernization of the U.S. electrical grid. Along with charging networks, electrical steels are also needed in the motors of electric vehicles.
Enhance our Environmental Sustainability
Our commitment to operating our business in a more environmentally responsible manner remains constant. One of the most important issues impacting our industry, our stakeholders and our planet is climate change. In early 2021, we announced our commitment to reduce GHG emissions 25% from 2017 levels by 2030. This goal represents combined Scope 1 (direct) and Scope 2 (indirect) GHG emission reductions across all of our operations.
Prior to setting this goal with our newly acquired steel assets, we exceeded our previous GHG reduction target at our legacy facilities six years ahead of our 2025 goal. In 2019, we reduced our combined Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions by 42% on a mass basis from 2005 baseline levels. Our goal is to further reduce those emissions in coming years.
Additionally, many of our steel assets have improved plant and energy efficiency through participation in programs like the U.S. Department of Energy’s Better Plants program, including their Better Climate Challenge and the EPA’s Energy Star program. With our longstanding focus on plant and energy efficiency, we aim to build on our previous successes across our newly integrated enterprise.
Our GHG reduction commitment is based on executing the following five strategic priorities:
•Developing domestically sourced, high quality iron ore feedstock and utilizing natural gas in the production of HBI;
•Implementing energy efficiency and clean energy projects;
•Investing in the development of carbon capture technology;
•Enhancing our GHG emissions transparency and sustainability focus; and
•Supporting public policies that facilitate GHG reduction in the domestic steel industry.
Improve Financial Flexibility
Given the cyclicality of our business, it is important to us to be in the financial position to easily withstand any negative demand or pricing pressure we may encounter. During the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, we were able to issue secured debt to provide insurance capital through the uncertain industry conditions caused by the pandemic. Now that business conditions have improved, allowing us to generate a healthy free cash flow during 2021 that is expected to continue into 2022, we have the ability to reduce debt, return capital to shareholders through our share repurchase program and make investments to both improve and grow our business. We have also been able to reduce our diluted share count and effectively return capital to shareholders via the cash redemption of our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock during the third quarter of 2021.
We anticipate that a strong market environment and significantly improved fixed price contracts will provide us ample opportunities to reduce our debt with our own free cash flow generation in the coming years. We will also continue to review the composition of our debt, as we are interested in both extending our average maturity profile and increasing our ratio of unsecured debt to secured debt, which we demonstrated by executing a series of favorable debt and equity capital markets transactions during February 2021. In addition, in June 2021, we redeemed all $396 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of our 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes. In December 2021, we increased our liquidity by amending our ABL Facility to increase the aggregate revolver commitments from $3.5 billion to $4.5 billion. These actions give us additional financial flexibility and will better prepare us to navigate more easily through
potentially volatile industry conditions in the future. In January 2022, we redeemed all $294 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of our 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes.
Business Operations
We have a vertically integrated portfolio, which begins at the mining stage and goes all the way through the manufacturing of steel products, including stamping, tooling and tubing. We have the unique advantage as a steel producer of being fully or partially self-sufficient with our production of raw materials for steel manufacturing, which includes iron ore pellets, HBI, scrap and coking coal. We operate iron ore mines in Michigan and Minnesota, which produce iron ore pellets, and a direct reduction plant in Ohio that produces HBI. Additionally, with our recently completed FPT Acquisition, we now operate scrap facilities in Michigan, Ohio, Tennessee, Florida and Ontario. We also operate a coal mining complex in West Virginia and produce coke from our facilities in Ohio, Pennsylvania, Indiana and West Virginia.
We believe such vertical integration represents a sustainable business model that is in the best interest of all stakeholders and the surest way to secure a long-term competitive advantage. We are focused on securing additional access to prime scrap as the steel industry continues to increase its focus on decarbonization and with demand coming from new flat-rolled EAF capacity set to come online over the next five years. We continue to strive to operate responsibly and produce cleaner steel, which is the most recycled material on the planet. Additionally, our investment in the Toledo direct reduction plant, which was completed in the fourth quarter of 2020, also helps to support environmental stewardship, as the increased use of HBI in our blast furnaces stretches liquid steel output, which reduces coke needs and emissions. From a focus on key environmental processes, such as steel recycling and reduction of carbon emissions, to corporate and social responsibility, sustainability is central to our values and operations.
The following table lists our steel producing and finishing properties, their location and their products and services:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property | | Segment | | State/ Province | | Products and Services |
| Burns Harbor | | Steelmaking | | Indiana | | Hot-rolled, cold-rolled, and hot-dipped galvanized sheet and coke |
| Burns Harbor Plate and Gary Plate | | Steelmaking | | Indiana | | Carbon steel plate, high-strength low alloy steel plate, ASTM grades steel plate |
| Butler Works | | Steelmaking | | Pennsylvania | | Flat-rolled electrical and stainless steel, stainless and carbon semi-finished slabs |
| Cleveland | | Steelmaking | | Ohio | | Hot-rolled and hot-dipped galvanized sheet |
| Coatesville | | Steelmaking | | Pennsylvania | | Steel plate - carbon, high-strength low-alloy, commercial allow, military alloy, flame-cut |
| Columbus | | Steelmaking | | Ohio | | Hot-dipped galvanized steel |
| Conshohocken | | Steelmaking | | Pennsylvania | | Coiled and discrete plate, military alloy, commercial alloy, heat-treated carbon |
| Coshocton Works | | Steelmaking | | Ohio | | Flat-rolled stainless steel |
| Dearborn Works | | Steelmaking | | Michigan | | Carbon semi-finished slabs, hot-dipped galvanized, AHSS |
| Indiana Harbor | | Steelmaking | | Indiana | | Carbon semi-finished slabs, hot-rolled, cold-rolled and hot-dipped galvanized sheet |
| Kote and Tek | | Steelmaking | | Indiana | | Cold-rolled, hot-dipped galvanized and galvannealed, electrogalvanized coil |
| Mansfield Works | | Steelmaking | | Ohio | | Semi-finished hot bands, high chrome ferritic and martensitic stainless steels |
| Middletown Works | | Steelmaking | | Ohio | | Hot-rolled, cold-rolled, hot-dipped galvanized, aluminized sheet and coke |
| Piedmont | | Steelmaking | | North Carolina | | Plasma - cuts plate steel products into blanks |
| Riverdale | | Steelmaking | | Illinois | | Hot-rolled sheet |
| Rockport Works | | Steelmaking | | Indiana | | Cold-rolled carbon, coated and stainless steels |
| Steelton | | Steelmaking | | Pennsylvania | | Railroad rails, specialty blooms, flat bars and cast ingots |
| Weirton | | Steelmaking | | West Virginia | | Tinplate, cold-rolled sheet |
| Zanesville Works | | Steelmaking | | Ohio | | Electrical steels |
Our Other Businesses primarily includes the Tubular Components and Tooling and Stamping properties that provide customer solutions with carbon and stainless steel tubing products, advanced-engineered solutions, tool design and build, hot- and cold-stamped steel components, and complex assemblies.
Refer to Part I - Item 2. Properties for additional information.
Customers and Markets
We primarily sell our products to customers in four broad market categories: automotive; infrastructure and manufacturing, which includes electrical power; distributors and converters; and steel producers, which consume iron ore and metallics and further process semi-finished materials. The following table presents the percentage of our net revenues to each of these markets during the year:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Market | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Automotive | | 25 | % | | 45 | % |
| Infrastructure and manufacturing | | 27 | % | | 15 | % |
| Distributors and converters | | 38 | % | | 13 | % |
| Steel producers | | 10 | % | | 27 | % |
The change in percentages of net revenues to each market in 2021 compared to 2020 was driven primarily by the AM USA Transaction, which increased overall sales to automotive customers, but reduced the total percentage exposure, increased exposure to infrastructure and manufacturing and distributors and converters customers, and drove more in-house iron ore sales, which reduced the percentage of sales to steel producers.
Approximately 45% of our flat-rolled steel shipments are sold under fixed base price contracts. These contracts are typically one year in duration and expire at various times throughout the year. Some of these contracts have a surcharge mechanism that passes through certain changes in input costs. A certain portion of our flat-rolled steel shipments are sold based on the spot market at prevailing market prices or under contracts that involve variable pricing that is tied to an independently published steel index.
We sell our steel products principally to customers in North America. For the vast majority of international sales, we are not the importer of record and do not bear the responsibility for paying any applicable tariffs.
Automotive Market
We specialize in manufacturing difficult-to-produce, high-quality steel products, combined with demanding delivery performance, customer technical support and collaborative relationships, to develop breakthrough steel solutions that help our customers meet their product requirements. In addition, many of our competitors do not have the capability to supply the full portfolio of products that we make for our automotive customers, such as steel for exposed automotive applications, the most sophisticated grades of AHSS and value-added stainless steel products. The exacting requirements for servicing the automotive market generally allows for higher selling prices for products sold to that market than for the commodity types of carbon and stainless steels sold to other markets.
The largest end user for our steel products is the automotive industry in North America, which makes light vehicle production a key driver of demand. During 2021, North American light vehicle production was 13 million units, the same as the prior year. Production each of the past two years was down 3 million units compared to the prior ten-year average primarily due to the global semiconductor shortage, as well as other material shortages and supply chain disruptions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic. This has caused several outages amongst light vehicle manufacturers despite strong consumer demand. In light of these production outages, we have been able to redirect certain volumes originally intended for this end market to the spot market, where demand has been strong and pricing has reached all-time highs.
Furthermore, during 2021, consumer demand for sport utility vehicles, trucks and crossovers continued to increase while demand for smaller sedans and compact cars declined. We benefit from intentionally targeting larger vehicle platforms to take advantage of consumer preferences, and we have focused on and have been successful in getting sourced on numerous sport utility vehicle, truck, crossover and larger vehicle platforms. As a result, a significant portion of the carbon automotive steel that we sell is used to produce these popular larger vehicles. In addition to benefiting from our exposure to consumers’ strong demand for larger vehicles, these vehicles also typically contain a higher volume of steel than smaller sedans and compact cars, providing us the opportunity to sell a greater proportion of our steel products to our automotive customers.
Automotive manufacturers are under pressure to achieve heightened federally mandated CAFE standards. The CAFE standards generally require automobile manufacturers to meet an average fuel economy goal across the fleet of vehicles they produce with certain milestone dates. As a result, our automotive customers continue to explore various avenues for achieving the standards, including light weighting components and developing more fuel-efficient engines. Light weighting efforts include the use of alternatives to traditional carbon steels, such as AHSS and other materials. While this could reduce the aggregate volume of steel consumed by the automotive industry, we expect
that demand will increase for current and next-generation AHSS and that our AHSS and other innovative steels will command higher margins. We are collaborating with our automotive customers and their suppliers to develop innovative solutions using our developments in light weighting, efficiency, and material strength and formability across our extensive product portfolio, in combination with our automotive stamping and tube-making capabilities. We are also working with our customers to develop steels with greater heat resistance for exhaust systems that support new, fuel-efficient engines that run at higher temperatures.
Automotive manufacturers have also been increasing their development of EVs and battery electric vehicles in order to meet the CAFE standards and growing customer adoption of EVs. Many motors used in EVs being sold in the U.S. today are imported from foreign suppliers, but more local sourcing and manufacturing of motors is expected to occur in the future. As the only North American producer of high-efficiency NOES, which is a critical component of EV motors, we are positioned to potentially benefit from the growth of EVs going forward. We believe our strong foundation in electrical steels and long-standing relationships with automotive manufacturers and their suppliers will provide us with an advantage in this market as it continues to grow and mature. Likewise, the growing customer adoption of EVs may also increase demand for improvements in the electric grid to support higher demand for more extensive battery charging, which our GOES could support.
The majority of our sales to the automotive market are under annual fixed price contracts. In 2022, our selling prices to this end market will be substantially higher as a result of favorable renewals. The improved prices in our fixed price contracts were driven by stronger market conditions and our unique product offering of automotive grade steel.
Infrastructure and Manufacturing Market
We sell a variety of our steel products, including plate, carbon, stainless, electrical, tinplate and rail, to the infrastructure and manufacturing market. This market includes sales to manufacturers of HVAC, appliances, power transmission and distribution transformers, storage tanks, ships and railcars, wind towers, machinery parts, heavy equipment, military armor, food preservation, and railway lines. Domestic construction activity and the replacement of aging infrastructure directly affects sales of steel to this market. Residential construction spending surged in 2021 due to overwhelming demand for new houses. Nonresidential construction spending was slightly down in 2021; however, the sector saw a surge in spending in the second half of the year and will likely continue into 2022 with the passing of the Infrastructure and Jobs Act of 2021. The Infrastructure and Jobs Act of 2021 will likely also increase demand for steel products related to renewable energy, as well as the modernization of the U.S. electrical grid. Our plate products can be used in windmills, which we estimate contain 130 metric tons of steel per megawatt of electrical generating capacity. Additionally, we estimate solar panels consume 40 metric tons of steel per megawatt of electrical generating capacity. We also expect to see an increase in charging stations for EVs which we will benefit from as we are the sole producer of electrical steel in the U.S.
Sales to this end market are made under a combination of annual fixed price contracts and index-linked pricing arrangements. Our selling prices under our annual fixed price contracts will be substantially higher in 2022 as a result of favorable renewals.
Distributors and Converters Market
Virtually all of the grades of steel we produce are sold to the steel distributors and converters market. This market generally represents downstream steel service centers, which source various types of steel from us and fabricate it according to their customers' needs. Our steel is typically sold to this market on a spot basis or under short-term contracts linked to steel pricing indices. Demand and pricing for this market can be highly dependent on a variety of factors outside our control, including global and domestic commodity steel production capacity, the relative health of countries’ economies and whether they are consuming or exporting excess steel production, the provisions of international trade agreements and fluctuations in international currencies and, therefore, are subject to market changes in steel prices.
The price for domestic HRC, the most significant index in driving our revenues and profitability of our Steelmaking segment, averaged $1,573 per net ton for 2021, a record year that was also 174% higher than 2020. The record prices for steel products in 2021 was a result of both supply and demand factors, each driven by a rapid recovery since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
Steel Producers Market
The steel producers market represents third-party sales to other steel producers, including those who operate blast furnaces and EAFs. It includes sales of raw materials and semi-finished and finished goods, including iron ore pellets, coal, coke, HBI, scrap and steel products.
The largest component of sales to this market during the year ended December 31, 2021 was third-party slab sales, which are primarily made under a long-term supply agreement that was initiated in connection with the closing of the AM USA Transaction.
Following the 2020 Acquisitions, production from our iron ore mines is predominantly consumed by our steelmaking operations. On a full-year basis, we would expect between 22 million and 24 million long tons of our iron ore pellets to be consumed by our steelmaking operations. During 2021, 2020 and 2019, we sold 4 million, 12 million and 19 million long tons of iron ore product, respectively, to third parties from our share of production from our iron ore mines. The merchant portion of our iron ore pellet production is sold pursuant to long-term supply agreements and through spot contracts.
We also entered into the scrap business with the FPT Acquisition in 2021. FPT is one of the largest processors of prime scrap in the country, representing approximately 15% of the entire U.S. merchant market. We believe this acquisition is a complementary addition to our footprint as prime scrap demand is expected to grow as new flat-rolled EAF capacity is set to come online over the next five years, and the worldwide focus on decarbonization continues. We expect to be able to leverage our long-standing flat-rolled automotive and other customer relationships into recycling partnerships to further grow our prime scrap presence.
The price of busheling scrap, a necessary input for flat-rolled steel production in EAFs in the U.S., averaged $602 per long ton during 2021, a 97% increase from the prior year. We expect the price of busheling scrap to remain elevated throughout 2022 due to decreasing prime scrap generation from original equipment manufacturers and the growth of EAF capacity in the U.S., along with a push for expanded scrap use globally. The expected rising price of busheling scrap was a key strategic rationale for the FPT Acquisition.
Applied Technology, Research and Development
We have an extensive history of being an innovator dating back more than a century. From upstream research and development, to downstream applications, we have dedicated technical and engineering resources that begin with improving customers' production and manufacturing performance to applications for their end product use.
We have a world-class research and development team expanding our capabilities to bring new steel products to the marketplace. Rapidly evolving and highly competitive markets for our steel products require our customers to seek new, comprehensive steel solutions, and we believe we are well positioned to deliver the most robust solutions through our broad portfolio of offerings. Collaboration across our research groups and operations generates innovative and comprehensive solutions for our customers, which we believe enhances our competitive advantage.
Our ongoing efforts to enhance technical collaboration at our state-of-the-art Research and Innovation Center in Middletown, Ohio, have increased the introduction of new steel solutions to the marketplace. Creating innovative products and breakthrough solutions is a strategic priority, as we believe differentiation through producing higher value steels to meet challenging requirements enables us to maintain and enhance our margins. We conduct a broad range of research and development activities aimed at improving existing products and processes and developing new ones. Our innovation of steel has produced a highly diversified steel product portfolio. As part of our underlying strategy to focus on higher-value materials and minimize exposure to commodity products, we have invested in research and innovation totaling $17 million and $15 million in 2021 and 2020, respectively.
We have also been a leader in iron ore mining and processing technology through the application of new technology to the centuries-old business of mineral extraction. We have also been a pioneer in iron ore pelletizing with over 60 years of experience. We are able to produce customized, environmentally-friendly pellets to meet blast furnace specifications and produce standard, fluxed and DR-grade pellets.
HBI
We are a pioneer in the development of emerging reduction technologies, a leader in the extraction of value from challenging resources and a front-runner in the implementation of safe and sustainable technology. We are also devoted to promoting environmental sustainability, evidenced with the development of our direct reduction plant in Toledo, Ohio. Construction of our Toledo direct reduction plant was completed in the fourth quarter of 2020, and the
plant reached full run-rate nameplate annual capacity of 1.9 million metric tons of HBI per year in 2021. From this modern plant, we produce a high-quality, low-cost and low-carbon intensive HBI product that can be used throughout our footprint. We intend to use more HBI in our melting process to stretch our production of liquid pig iron from traditional inputs. The use of higher amounts of HBI in our blast furnaces ultimately stretches liquid steel output, which reduces coke needs and lowers carbon intensity.
Carbon Steel
We focus much of our research and innovation efforts on carbon steel applications for automotive manufacturers and their suppliers. We are particularly focused on AHSS for the automotive market, and we produce virtually every AHSS grade currently used by our customers. Our AHSS grades, such as Dual Phase 590, 780, 980 and 1180, have been adopted by our customers for both stamped and roll-formed parts, and our TRIP and NEXMET® products have demonstrated enhanced strength, formability and opportunities for automotive light weighting in cold-stamped applications. We are also pursuing application of NEXMET 490EX in surface-critical, exposed auto body panels as an alternative to aluminum.
Third Generation Advanced High-Strength Steel
Our third generation NEXMET AHSS products enable our customers to achieve significant light weighting in the unexposed structural components of their vehicles. NEXMET 1200, for example, offers superior formability similar to conventional Dual Phase 600 steel, but at twice the strength level. We have expanded the application of the NEXMET technology to our tubular products and stamped components businesses. These AHSS products allow automotive engineers to design lightweight parts that meet rigorous service and safety requirements. The NEXMET family of steels helps our customers achieve vehicle weight savings for ambitious fuel efficiency standards while avoiding significant capital costs required to re-design production facilities to use alternative materials.
Both galvanized and cold-rolled NEXMET AHSS are progressing through product qualification with several original equipment manufacturer customers. A number of stamping and component assembly trials have been completed successfully, with more planned and underway. Because the timing of automotive design and production cycles spans several years, widespread automotive customer adoption of revolutionary new material such as NEXMET AHSS may also extend over several years. We expect that other automotive vehicle platforms will incorporate NEXMET AHSS in their designs and that NEXMET AHSS will become a strong differentiator for us going forward.
Downstream Steel Applications
Our portfolio of steel solutions includes the operations of Tooling and Stamping, which provides advanced-engineered solutions, tool design and build, hot and cold-stamped components and complex assemblies for the automotive market. In addition to Tooling and Stamping, our downstream operations include Tubular Components, which manufactures advanced tubular products for automotive and other applications using carbon and stainless steels. We believe that collaboration among our steelmaking operations and our downstream businesses can accelerate the adoption of our innovative steel products by automotive manufacturers and their first tier suppliers.
Our research and technical experts have undertaken numerous collaborative projects that are generating robust solutions for our customers. Our expertise in tool design and stamping capabilities has allowed us to create prototype components using our innovative new sheet materials and present customers with new potential steel solutions. This approach has and, we expect, will continue to demonstrate to customers that they can significantly light weight automotive parts on an accelerated timeline and in a cost-effective manner by using our highly formable grades of AHSS in place of traditional material types.
In addition, our collaborative projects are enhancing our collective knowledge and experience in the stamping of new, advanced grades of steel, advanced engineered solutions, and tool design and build. For example, our Tooling and Stamping segment specializes in hot-stamping PHS for automotive applications. Our experience as a leader in PHS and expertise in hot-stamping has enabled us to have greater insight into these high-growth areas and has accelerated product development and customer adoption of these automotive light weighting solutions. Likewise, collaboration with the Tubular segment strategically advances our mission to innovate in AHSS for the automotive industry, as we have been at the forefront of producing tubular products from PHS and third-generation AHSS. We believe the combination of our stamping and advanced die-making capabilities, leading tube making capabilities and breakthrough material introductions will enhance our ability to deliver innovative, steel solutions to our customers.
We have recently been awarded contracts with several customers to supply complex assemblies and stamped automotive parts. In winning these contracts, we have been able to leverage our hot-stamping tooling
leadership, in addition to our innovative hot-stamping process, to capture new strategic opportunities and demonstrate that we are one of the few businesses in North America that has the technical capabilities to produce a major complex assembly and stamping work of this nature.
Competition
Our Steelmaking segment principally competes with domestic and foreign producers of flat-rolled carbon, plate, tinplate, stainless, rail and electrical steel, carbon and stainless tubular products, aluminum, carbon fiber, concrete and other materials that may be used as a substitute for flat-rolled steels in manufactured products. Our Tooling and Stamping and Tubular Components businesses both compete against other niche companies in highly fragmented markets.
Price, quality, on-time delivery, customer service and product innovation are the primary competitive factors in the steel industry and vary in importance according to the product category and customer requirements. Steel producers that sell to the automotive market face competition from aluminum manufacturers (and, to a lesser extent, other materials) as automotive manufacturers attempt to develop vehicles that will enable them to satisfy more stringent, government-imposed fuel efficiency standards. To address automotive manufacturers’ light weighting needs that the aluminum industry is targeting, we and others in the steel industry have developed AHSS grades that we believe provide weight savings similar to aluminum, while being stronger, less costly, easier to repair, more sustainable and more environmentally friendly. Aluminum penetration has been primarily limited to specific automotive applications, such as outer panels and closures, rather than entire body designs. In addition, our automotive customers who continue to use steel, as opposed to aluminum and other alternative materials, are able to avoid the significant capital expenditures required to re-tool their manufacturing processes to accommodate the use of non-steel materials.
Mini-mills (producers using EAFs) comprise about 70% of steel production and 42% of flat-rolled steel production in the U.S. Their primary raw material is scrap metal, which has unpredictable and often volatile pricing. Due to the announced flat-rolled mini-mill capacity additions in the U.S. and increasing focus on industry decarbonization, we expect the price of scrap to remain elevated over historical averages, providing our integrated footprint a competitive advantage. Mini-mills also generally offer a narrower range of products than integrated steel mills, but the increasing use of pig iron and direct reduced iron have enabled them to modestly expand their product capabilities in recent years. However, we believe mini-mills often do not have the equipment capabilities to produce the product range that integrated facilities offer, nor do we believe they possess our depth of customer service, technical support, and research and innovation.
Domestic steel producers, including us, face significant competition from foreign producers. For many reasons, these foreign producers often are able to sell products in the U.S. at prices substantially lower than domestic producers. Depending on the country of origin, these reasons may include government subsidies; lower labor, raw material, energy and regulatory costs; less stringent environmental regulations; less stringent safety requirements; the maintenance of artificially low exchange rates against the U.S. dollar; and preferential trade practices in their home countries. In 2021, finished steel imports increased 48% compared to the prior year, as a result of a larger disparity between foreign and domestic prices, but still remain below levels seen between 2013 and 2018. We believe this is at least partially attributable to the implementation of certain trade restrictions on imported steel over the past five years, including both targeted trade cases and the more broad Section 232 tariffs. Modifications to these trade restrictions by government authorities could directly or indirectly impact import levels in the future. Import levels are also affected to varying degrees by the relative level of steel production in China and other countries, the strength of demand for steel outside the U.S., and the relative strength or weakness of the U.S. dollar against various foreign currencies. Imports of finished steel into the U.S. accounted for approximately 22% of domestic steel market consumption in 2021.
We continue to provide significant pension and healthcare benefits to a greater number of our retirees compared to certain other domestic and foreign steel producers that do not provide such benefits to any or most of their retirees, which increases our overall cost of production relative to certain other steelmakers. However, we have taken a number of actions to reduce pension and healthcare benefits costs, including negotiating progressive labor agreements that have significantly reduced total employment costs at our union-represented facilities, transferring all responsibility for healthcare benefits for various groups of retirees to VEBAs, offering voluntary lump-sum settlements to pension plan participants, lowering retiree benefit costs for salaried employees, and transferring pension obligations to highly rated insurance companies. These actions have not only reduced some of the risks associated with our pension funding obligations, but more importantly have reduced our risk exposure to performance of the financial markets, which are a principal driver of pension funding requirements. We continue to actively seek opportunities to reduce pension and healthcare benefits costs.
Environmental Matters
Our operations are subject to various laws and regulations governing the protection of the environment. We monitor these laws and regulations, which change over time, to assess whether the changes affect our operations. We conduct our operations in a manner that is protective of public health and the environment.
Environmental matters and their management continue to be an important focus at each of our operations. From 2017 to 2021, we invested approximately $1 billion into our Toledo direct reduction plant, which provides a low carbon intensity raw material to our steelmaking operations. The HBI produced from the plant requires less energy to produce compared to traditional feedstock and can be used in blast furnaces to reduce emissions by improving energy efficiency and reducing the amount of coke required for steel production.
In the construction and operation of our facilities, substantial costs have been and will continue to be incurred to comply with regulatory requirements and avoid undue effect on the environment. In 2021, 2020, and 2019, our capital expenditures relating to environmental matters totaled $62 million, $34 million and $9 million, respectively. Our current estimate for capital expenditures for environmental improvements in 2022 is approximately $120 million for various water treatment, air quality, dust control, tailings management and other miscellaneous environmental projects. Additionally, we expect capital expenditures for environmental improvements for each of 2023 and 2024 to be generally in line with 2022's estimated spending.
Regulatory Developments
Various governmental bodies continually promulgate new or amended laws and regulations that affect us, our customers, and our suppliers in many areas, including air and water discharges, waste management and disposal, the classification of materials and products and other environmental, health, and safety matters. Although we believe that our environmental policies and practices are sound and do not expect that the application of any current laws, regulations or permits would reasonably be expected to result in a material adverse effect on our business or financial condition, we cannot predict the collective potential adverse impact of the expanding body of laws and regulations. Moreover, because all domestic steel, scrap and mining producers operate under the same federal environmental regulations, we do not believe that we are more disadvantaged than our domestic competitors by our need to comply with these regulations. Some foreign competitors may benefit from less stringent environmental requirements in the countries where they produce, resulting in lower compliance costs for them and providing those foreign competitors with a cost advantage on their products.
Specifically, there are several notable proposed or potential rulemakings or activities that could have a material adverse impact on our facilities in the future depending on their ultimate outcome: climate change and GHG regulation; selenium discharge regulation; Minnesota's sulfate wild rice water quality standard; Minnesota's mercury TMDL and mercury reduction rules; and the regulation of discharges to groundwater.
Climate Change and GHG Regulation
With the complexities and uncertainties associated with the U.S. and global navigation of the climate change issue as a whole, one of our potentially significant risks for the future is mandatory carbon pricing obligations, whether it be in the form of additional costs for emission allowances or restriction of production, as examples. Policymakers are in the design process of carbon regulation at the state, regional, national and international levels. The current regulatory variety of carbon compliance schemes presents a challenge for multi-facility entities to identify their near-term risks. Amplifying the uncertainty, the dynamic forward outlook for carbon pricing obligations presents a challenge to large industrial companies to assess the long-term net impacts of carbon compliance costs on their operations. Our exposure on this issue includes both the direct and indirect financial risks associated with the regulation of GHG emissions, as well as potential physical risks associated with climate change adaptation. We are continuing to review the physical risks related to climate change. As an energy-intensive business, we have a broad range of GHG emissions sources, such as iron ore furnaces and kilns, diesel mining equipment and integrated steelmaking facilities, among others. As such, among our most significant regulatory risks are: (1) the costs associated with on-site emissions levels (direct impacts); and (2) indirect costs passed through to us from power and fuel suppliers (indirect impacts).
Internationally, mechanisms to reduce emissions are being implemented in various countries, with differing designs and stringency, according to resources, economic structure and politics. The Paris Agreement to reduce global GHG emissions and limit global temperature increases to 2 degrees Celsius compared to pre-industrial temperatures became effective in November 2016 with 196 signatory countries. The U.S. became a signatory to the Paris Agreement with a pledge to reduce its GHG emissions by 26% to 28% from 2005 levels by 2025. The U.S. withdrew from the treaty in November 2020 and then subsequently rejoined the Paris Agreement in February 2021.
Continued attention to issues concerning climate change, the role of human activity in it and potential mitigation through regulation may have a material impact on our customer base, operations and financial results in the future.
In the U.S., future federal and/or state carbon regulation potentially presents a significantly greater impact to our operations. To date, the U.S. Congress has not legislated carbon constraints. In the absence of comprehensive federal carbon legislation, numerous state, regional and federal regulatory initiatives are under development or are becoming effective, thereby creating a disjointed approach to GHG emissions control and potential carbon pricing impacts. We intend to remain active in the discussions related to legislative and regulatory changes at the federal and state levels.
Due to the potential variety of federal, state or regional carbon restriction schemes, our business and customer base could suffer negative financial impacts over time as a result of increased energy, environmental and other costs to comply with the limitations that would be imposed on GHG emissions. We believe our exposure can be reduced substantially by numerous factors, including currently contemplated regulatory flexibility mechanisms, such as allowance allocations, fixed process emissions exemptions, offsets and international provisions; emissions reduction opportunities, including energy efficiency, biofuels and fuel flexibility; and business opportunities associated with pursuing combined heat and power partnerships and new products, including DR-grade pellets, HBI, fluxed pellets and other efficiency-improving technologies.
Selenium Discharge Regulation
In Michigan, the Empire and Tilden mines have implemented compliance plans to manage selenium according to applicable permit conditions. A water treatment system for both facilities is anticipated sometime before 2028. As of December 31, 2021, included within our Empire asset retirement obligation is a discounted liability of approximately $100 million, which includes the estimated costs associated with the construction of Empire's portion of the required infrastructure and expected future operating costs of the treatment facilities. Additionally, included within our Tilden future capital plan is approximately $20 million for the construction of Tilden's portion of the required infrastructure. We are continuing to assess and develop cost effective and sustainable selenium treatment technologies.
In July 2016, the EPA published new selenium fish tissue limits and lower lentic and lotic water column concentration criteria, which may someday increase the cost for treatment should EGLE adopt these new standards in lieu of the existing limits required by the Great Lakes Water Quality Initiative. Accordingly, we cannot reasonably estimate the timing or long-term impact of these water quality criteria on our business.
Minnesota’s Sulfate Wild Rice Water Quality Standard
The Minnesota Governor established a Wild Rice Task Force by Executive Order in May 2018 that provided recommendations on wild rice restoration and regulation. The existing sulfate water quality standard for lakes and streams that contain wild rice has not been applied to any of our discharge permits or enforced historically by Minnesota. Further, the standard may be unenforceable because of legislation that prohibits the MPCA from enforcing it until the obsolete standard is updated based on modern science.
Minnesota submitted a list of impaired water revisions to the EPA in 2020. In 2021, the EPA disapproved of Minnesota’s draft impaired waters list and subsequently announced its proposed list of wild rice water bodies that were impaired due to sulfate under the Clean Water Act’s Section 303(d) process, which resulted in the addition of 32 waters in November 2021. At this time, it is unknown how the MPCA intends to implement requirements to address sulfate impaired waters.
For these reasons, the impact of potential obligations to address sulfate concentrations in certain water discharges from our Minnesota iron ore mining and pelletizing operations is not estimable at this time, but it could have a material adverse impact if we are required to significantly reduce sulfate in certain discharges.
Minnesota's Mercury TMDL and Mercury Reduction Rules
In September 2014, Minnesota promulgated the Mercury Air Emissions Reporting and Reduction Rules, mandating mercury air emissions reporting and reductions from certain sources, including taconite facilities. The rules apply to all of our Minnesota iron ore mining and pelletizing operations and required submittal of a Mercury Reduction Plan to the MPCA in 2018 with plan implementation requirements becoming effective on January 1, 2025. In the Mercury Reduction Plan, facilities evaluated if available control technologies can technically achieve a 72% mercury reduction rate. If available control technologies cannot technically achieve a 72% mercury reduction rate, the facilities must propose alternative mercury reduction measures. One of the main tenets agreed upon for evaluating potential
mercury reduction technologies during TMDL implementation and 2014 rule development proceedings was that the selected technology must meet the following “Adaptive Management Criteria”: the technology must be technically feasible; must be economically feasible; must not impact pellet quality; and must not cause excessive corrosion in the indurating furnaces or air pollution control equipment.
The Mercury Reduction Plans for our Minnesota facilities were submitted to the MPCA in December 2018. In 2020, the MPCA requested additional information on certain plans, and we responded in a timely manner. There is currently no proven technology to cost effectively reduce mercury emissions from taconite furnaces to achieve the targeted 72% reduction rate, while satisfying all four Adaptive Management Criteria. The Mercury Reduction Plans that were submitted to the MPCA include documentation that describes the results of detailed engineering analysis and research testing on potential technologies to support this determination. The results of this analysis will continue to guide dialogue with the MPCA. Potential impacts to us are not estimable at this time because the revised Mercury Reduction Plans and additional technical information are currently being reviewed by the MPCA.
Regulation of Discharges to Groundwater
In general, states traditionally have regulated discharges of pollutants to groundwater through various programs such as wellhead protection programs and regulations related to remediation. In April 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court held in County of Maui v. Hawaiʻi Wildlife Fund that the EPA (and delegated states) have jurisdiction under the NPDES program if a point source discharges to groundwater and is the “functional equivalent” of a discharge to Waters of the United States. Until now, the NPDES program in the states we operate in has regulated only direct discharges to surface waters that constitute Waters of the United States from point sources. Although we do not anticipate that broadening EPA jurisdiction over groundwater discharges will materially adversely affect our operations, the impact to our operations is not reasonably estimable at this time.
Other Government Laws and Regulations
In addition to environmental laws and regulations, we are subject to various laws and regulations around the world. For example, changes in trade regulations, including tariffs or other import or export restrictions, could lead to lower or more volatile global steel prices, impacting our profitability. In addition, health and safety regulations, including laws or regulations promulgated in response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, and OSHA and MSHA regulations, have necessitated, and may continue to necessitate, increased operating costs or capital investments to promote a safe working environment. We are also required to comply with complex foreign and U.S. laws and regulations, which may include the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other anti-bribery laws, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation and other U.S. and foreign privacy regulations, and transportation and logistics regulations. The laws and regulations noted above, as well as other applicable laws and regulations, or the manner in which they are interpreted or enforced, may require us to make material investments in the form of additional processes, training and capital, among other things. For a discussion of the risks associated with certain applicable laws and regulations, see Part I – Item 1A, Risk Factors.
Raw Materials and Energy
Our steelmaking operations require iron ore, HBI, coke, coal, ferrous and carbon and stainless scrap, chrome, nickel and zinc as primary raw materials. We also consume natural gas, electricity, industrial gases and diesel fuel at our operations. As a vertically integrated steel company, we are able to internally supply a majority of our raw materials needed for our steelmaking operations. We also attempt to reduce the risk of future supply shortages and price volatility in other ways. If multi-year contracts are available in the marketplace for those raw materials that we cannot supply internally, we may use these contracts to secure sufficient supply to satisfy our key raw material needs. When multi-year contracts are not available, or are not available on acceptable terms, we purchase the remainder of our raw materials needs under annual contracts or conduct spot purchases. We also regularly evaluate alternative sources and substitute materials. Additionally, we may hedge portions of our energy and raw materials purchases to reduce volatility and risk. We believe that we have secured, or will be able to secure, adequate supply to fulfill our raw materials and energy requirements for 2022.
The raw materials needed to produce a ton of steel will fluctuate based upon the specifications of the final steel products, the quality of raw materials and, to a lesser extent, differences among steel production equipment. For example, generally, in our integrated steelmaking facilities, we consume approximately 1.4 net tons of coal to produce one net ton of coke. The process to produce one ton of raw steel generally requires approximately 1.4 net tons of iron ore pellets, 0.4 net tons of coke and 0.3 net tons of steel scrap. At normal operating levels, we also consume approximately 6 MMBtu’s of natural gas per net ton of raw steel produced. Additionally, on average, our EAFs require 1.1 net tons of ferrous or stainless scrap to produce one net ton of high quality steel. We consume approximately 420 kilowatt-hours of electricity per net ton of steel produced. While these estimated consumption amounts are presented
to give a general sense of raw material and energy consumption used in our steel production, substantial variations may occur.
Our investment into HBI production provides us access, when needed, to clean iron units in order to make advanced steel and stainless products. This access to our own production provides us flexibility and allows us to avoid the risks and carbon footprints of imported iron substitutes. Iron substitutes imported into the U.S. are traditionally sourced from regions of the world that have historically experienced greater political turmoil and have lower pollution standards than the U.S. Our investment demonstrates our raw material and company strategy in responsibly managing the risks of pricing, availability and overall carbon footprint of our critical inputs.
Our acquisition of FPT provides us sourcing and processing capabilities for both prime and obsolete scrap. This access is critical as prime scrap demand is expected to grow as new flat-rolled EAF capacity is set to come online over the next five years. The FPT Acquisition included 22 facilities that are primarily located in the Midwest near our steel facilities. We plan to pair the operational footprint of FPT with our long-standing flat-rolled automotive and other customer relationships to develop recycling partnerships that will further grow our prime scrap presence. Additionally, the FPT Acquisition furthers our commitment to being an environmentally-friendly, low-carbon intensity steelmaker with a cleaner materials mix as we are able to better optimize productivity at our existing EAFs and BOFs. Our investment in FPT further demonstrates our commitment to a vertically integrated business model.
Iron Ore
We own or co-own five active iron ore mines in Minnesota and Michigan. Based on our ownership in these mines, our share of annual rated iron ore production capacity is approximately 28 million long tons, which supplies all of the iron ore needed for our steelmaking operations. Refer to Part I - Item 2. Properties for additional information.
Coke and Coal
We own five cokemaking facilities, including two coke batteries located within our steelmaking facilities, one of which is temporarily idled. These facilities currently provide over half of the coke requirements for our steelmaking operations and have an annual rated capacity of 3.9 million net tons. Additionally, we have coke supply agreements with suppliers that provide our remaining requirements. Our purchases of coke are made under annual or multi-year agreements with periodic price adjustments. We typically purchase most of our metallurgical coal under annual fixed-price agreements. We have annual rated metallurgical coal production capacity of 2.3 million net tons from our Princeton mine, which supplies a portion of our metallurgical coal needs. We believe there are adequate external supplies of coke and coal available at competitive market prices to meet our needs. Refer to Part I - Item 2. Properties for additional information.
Steel Scrap and Other Materials
Following the FPT Acquisition, the majority of our scrap requirements are generated or processed from internal sources, including scrap generated at our steel production facilities. We believe that supplies of additional steel scrap, chrome, nickel and zinc adequate to meet the needs of our steelmaking operations are readily available from outside sources at competitive market prices.
Energy
We consume a large amount of natural gas, electricity, industrial gases and diesel fuel, which are significant costs to our operations. The majority of our energy requirements are purchased from outside sources. Access to long-term, low-cost sources of energy in various forms is critically important to our operations.
Natural gas is procured for our operations utilizing a combination of long-term, annual, quarterly, monthly and spot contracts from various suppliers at market-based pricing. We believe access to low-cost and reliable sources of natural gas is available to meet our operations’ requirements.
We purchase electricity for all of our operations in either regulated or deregulated markets. Due to the distinct nature of these markets, we procure electricity through either long-term or annual contracts. Some of our operations also use self-generated coke oven gas and/or blast furnace gas to produce electricity, which is an environmentally-friendly practice that also reduces our need to purchase electricity from external sources. We also closely monitor developments at the state and federal levels that could impact electricity availability or cost and incorporate such changes into our electricity supply strategy in order to maintain reliable, low-cost supply. We are currently evaluating the use of renewable energy to complement our existing supply. We believe there is an adequate supply of competitively priced electricity to fulfill our requirements.
We purchase industrial gases under long-term contracts with various suppliers. We believe we have access to adequate supplies of industrial gases to meet our needs.
We predominantly purchase diesel fuel for our mining operations under long-term contracts with various suppliers. We believe we have access to adequate supplies of diesel fuel to meet our needs.
Human Capital
Cliffs has a long, proven history of attracting and retaining exceptional talent. We believe our employee-centric management philosophy is the key to our success. Even though many other employers are facing unprecedented labor shortages, we continued to grow during 2021.
As of December 31, 2021, we employed approximately 26,000 people. Approximately 25,500 were employed in the U.S. Approximately 24,000 employees were employed at production facilities, with the balance employed in corporate support roles. The vast majority of our approximately 21,000 hourly employees were subject to collective bargaining agreements (approximately 18,500) with various labor unions.
Labor Relations
Our labor relations philosophy is a cornerstone of our talent strategy. At Cliffs, we know that maintaining strong, positive relationships with labor unions is key to our long-term growth. We recognize and respect the right of our employees to freely associate and collectively bargain, and we do not engage in harassment, intimidation or retaliation for their efforts to bargain collectively.
More than three-quarters of Cliffs’ workforce are represented by three prominent unions—USW, UAW and IAM. The hardworking men and women of Cliffs are the lifeblood of our Company. Our employees operate and maintain our facilities and are, ultimately, responsible for safely delivering a quality product to our customers. Therefore, we engage with our unions as business partners, and together, we have achieved a number of successes that benefit our business and our people alike.
In 2021, labor contracts for workers represented at our Rockport, Dearborn, Mansfield and Monessen facilities were successfully ratified. We are proud to report we did not experience any strikes or lockouts last year. We expect to continue productive dialogue with our labor partners into 2022 as a number of other site agreements reach expiration and will be renegotiated. This positive partnership with our unions helps us remain competitive for talent and protects our customers and their supply chains from disruptions due to labor disagreements.
Talent Retention
We believe that our future success largely depends upon our continued ability to attract and retain a highly skilled workforce. We provide our employees with competitive salaries, incentive-based bonus programs that provide above-market compensation opportunities when our Company performs well, development programs that enable continued learning and growth, and a robust benefit package that promotes well-being across all aspects of their lives, including health care, retirement planning and paid time off. In addition to these programs, we have used targeted, equity-based grants with vesting conditions to facilitate retention of key personnel. These tools have enabled us to increase the retention of key personnel, including our corporate and site leadership teams and critical technical talent.
Robust Employee Benefits Programs
The success of our business is fundamentally connected to the well-being of our people. Accordingly, we are committed to the health, safety and wellness of our employees. We provide our employees and their families with access to a variety of innovative, flexible and convenient health and wellness programs, including benefits that provide protection and security so they can have peace of mind concerning events that may require time away from work or that impact their financial well-being; that support their physical and mental health by providing tools and resources to help them improve or maintain their health and encourage engagement in healthy behaviors; and that offer choice where possible so they can customize their benefits to meet their needs and the needs of their families.
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
We continue to foster a culture of diversity, equity and inclusion at Cliffs. Through our OneCliffs Way of Doing Business (our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics), we outline our Core Values, which include Trust, Respect and Open Communication. To us, this means encouraging and accepting different views, and supporting and advancing gender and racial diversity. Further, our OneCliffs Way of Doing Business provides that we will not make employment-related decisions nor will we discriminate based on race, color, national origin, gender, age, religion, mental or
physical disability, veteran status, sexual orientation or any other characteristic protected by applicable law. We strive to make Cliffs a safe place to work for all. Harassment and/or intimidation are not tolerated anywhere in our Company, and we hope our people make a career at Cliffs doing meaningful and challenging work.
COVID-19
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, we implemented significant changes in our operations and workplaces in the best interest of our employees, as well as the communities in which we operate, which exceeded government regulations. This includes having all employees who could perform their work remotely work from home when necessary, while implementing numerous safety measures for employees continuing critical on-site work at our operations.
Additionally, in an effort to best protect our workforce and the Company, we launched a vaccine incentive program in July 2021 that was developed in partnership with our labor unions. Throughout the 45 days the program was in place, the vaccination rate more than doubled and we achieved a vaccination rate of over 75% throughout our workforce. The initiative resulted in a payout of $45 million in total cash incentive to our vaccinated workforce. The successful vaccination program allowed us to operate efficiently and safely throughout the remainder of 2021 and into 2022.
Safety
Safe production is our primary core value as we continue toward achieving a zero injury culture at our facilities. We constantly monitor our safety performance and make continuous improvements to affect change. Best practices and incident learnings are shared globally to ensure each facility can administer the most effective policies and procedures for enhanced workplace safety. Progress toward achieving our objectives is accomplished through a focus on proactive sustainable safety initiatives, and results are measured against established industry and Company benchmarks, including our Company-wide Total Reportable Incident Rate. During 2021, our Total Reportable Incident Rate (including contractors) was 1.37 per 200,000 hours worked.
Refer to Exhibit 95 Mine Safety Disclosures (filed herewith) for mine safety information required in accordance with Section 1503(a) of the Dodd-Frank Act.
Available Information
Our headquarters are located at 200 Public Square, Suite 3300, Cleveland, Ohio 44114-2315, and our telephone number is (216) 694-5700. We are subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and its rules and regulations. The Exchange Act requires us to file reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC.
The SEC maintains a website that contains reports, proxy statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. These materials may be obtained electronically by accessing the SEC’s home page at www.sec.gov.
We use our website, www.clevelandcliffs.com, as a channel for routine distribution of important information, including news releases, investor presentations and financial information. We also make available, free of charge on our website, our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file these documents with, or furnish them to, the SEC. In addition, our website allows investors and other interested persons to sign up to receive automatic email alerts when we post news releases and financial information on our website.
We also make available, free of charge, the charters of the Audit Committee, Strategy and Sustainability Committee, Governance and Nominating Committee, and Compensation and Organization Committee, as well as the Corporate Governance Guidelines, and the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics adopted by our Board of Directors. These documents are available through our investor relations page on our website at www.clevelandcliffs.com. The SEC filings are available by selecting “Investors” and then “SEC Filings,” and corporate governance materials are available by selecting "Investors" and then “Governance” for the Board Committee Charters, the Corporate Governance Guidelines, and the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics.
References to our website or the SEC’s website do not constitute incorporation by reference of the information contained on such websites, and such information is not part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Copies of the above-referenced information are also available, free of charge, by calling (216) 694-5700 or upon written request to:
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.
Investor Relations
200 Public Square, Suite 3300
Cleveland, OH 44114-2315
INFORMATION ABOUT OUR EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
Following are the names, ages and positions of the executive officers of the Company as of February 11, 2022. Unless otherwise noted, all positions indicated are or were held with Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.
| | | | | | | | |
| Name | Age | Position(s) Held |
| Lourenco Goncalves | 64 | Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer (August 2014 – present); and Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer of Metals USA Holdings Corp., an American manufacturer and processor of steel and other metals (May 2006 – April 2013). |
| Clifford Smith | 62 | Executive Vice President & President, Cleveland-Cliffs Steel (September 2021 – present); Executive Vice President, Chief Operating Officer (January 2019 – September 2021); and Executive Vice President, Business Development (April 2015 – January 2019). |
| Keith Koci | 57 | Executive Vice President & President, Cleveland-Cliffs Services (September 2021 – present); Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer (February 2019 – September 2021); and Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, Metals USA Holdings Corp. (2013 – February 2019). |
| Celso Goncalves | 34 | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer (September 2021 – present); Senior Vice President, Finance & Treasurer (March 2020 – September 2021); Vice President, Treasurer (January 2018 – March 2020); and Assistant Treasurer (September 2016 – January 2018). |
| Terry Fedor | 57 | Executive Vice President, Operations, East (September 2021 – present); Executive Vice President, Chief Operating Officer, Steel Mills (March 2020 – September 2021); Executive Vice President, Operations (February 2019 – March 2020); and Executive Vice President, U.S. Iron Ore (January 2014 – February 2019). |
| Traci Forrester | 50 | Executive Vice President, Environmental & Sustainability (May 2021 – present); Executive Vice President, Business Development (May 2019 – May 2021); Vice President, Deputy General Counsel & Assistant Secretary (January 2018 – May 2019); and Deputy General Counsel & Assistant Secretary (January 2017 – May 2019). |
| James Graham | 56 | Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer & Secretary (November 2014 – present). |
| Maurice Harapiak | 60 | Executive Vice President, Human Resources & Chief Administration Officer (January 2018 – present); and Executive Vice President, Human Resources (March 2014 – January 2018). |
| Kimberly Floriani | 39 | Senior Vice President, Controller & Chief Accounting Officer (August 2021 – present); Vice President, Corporate Controller & Chief Accounting Officer (April 2020 – August 2021); and Director, Accounting & Reporting (August 2015 – April 2020). |
All executive officers serve at the pleasure of the Board. There are no arrangements or understandings between any executive officer and any other person pursuant to which an executive officer was selected to be an officer of the Company. Celso Goncalves, our Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, is the son of Lourenco Goncalves, our Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer. There is no other family relationship between any of our executive officers, or between any of our executive officers and any of our directors.
An investment in our common shares or other securities is subject to risks inherent in our businesses and the industries in which we operate. Described below are certain risks and uncertainties, the occurrences of which could have a material adverse effect on us. The risks and uncertainties described below include known material risks that we face currently, but our material risks are constantly evolving and the below descriptions may not include future risks that are not presently known, that are not currently believed to be material or that are common to all businesses. Investors should not interpret the disclosure of any risk to imply that such risk has not already materialized. Although we have extensive risk management policies, practices and procedures in place that are aimed to mitigate these risks, the occurrence of these uncertainties may nevertheless impair our business operations and adversely affect the actual outcome of matters as to which forward-looking statements are made. This report is qualified in its entirety by these risk factors. Before making an investment decision, investors should consider carefully all of the risks described below together with the other information included in this report and the other reports we file with the SEC.
Management has identified several categories of material risks that we are subject to, including: (I) economic and market, (II) regulatory, (III) financial, (IV) operational, (V) sustainability and development and (VI) human capital. Although the risks are organized by these headings, and each risk is discussed separately, many are interrelated.
I. ECONOMIC AND MARKET RISKS
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and the resulting economic volatility has had, and is expected to continue to have, an adverse impact on our businesses.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is continuing to impact countries, communities, supply chains and markets. Responses by individuals, governments and businesses to ever-changing developments in the COVID-19 pandemic and efforts to reduce its spread, including quarantines, travel restrictions, business closures, and mandatory stay-at-home or work-from-home orders, have led to significant disruptions to overall business and economic activity. While vaccines are now widely available and the economy experienced a partial recovery during 2021, due to the number of unvaccinated individuals and the novel strains and multiple variants of the COVID-19 virus periodically being encountered on a global basis that may be more resistant to existing vaccines, it is currently unknown for how long and to what extent consumer and business activity will continue to be impacted by the volatility caused by the pandemic.
Among other things, the COVID-19 pandemic adversely affected our businesses by temporarily curtailing certain of our end markets, and certain of our mining and production facilities were idled for various periods during 2020 in response to the decrease in customer demand. While we were able to resume operations at our temporarily idled facilities later in 2020 or 2021, we cannot predict whether any of our production facilities or mines will experience disruptions in the future as a result of adverse impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. We are also subject to risks arising out of the turbulence of the economic recovery associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, including inflationary pressures, which may increase the costs of our labor, raw materials, energy supplies and other production inputs, which could have an adverse impact on our results of operations and profitability.
In addition, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has heightened the risk that a significant portion of our workforce and on-site contractors will suffer illness or otherwise be unable to perform their ordinary work functions. While we have periodically instituted remote work policies where practical across our footprint, the safe and responsible operation of our production facilities often requires that workers be on-site. Accordingly, during 2021, we experienced direct and indirect workforce impacts from COVID-19 at many of our operations. We also may need to reduce our workforce as a result of declines in our business caused by any further adverse developments in the COVID-19 pandemic leading to a downturn in the economy, and there can be no assurance that we will be able to rehire our workforce once our business has recovered. We have experienced, and may continue to experience, supply chain disruptions or operational issues with our vendors or logistics providers, as our suppliers and contractors face similar challenges related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Because the prolonged COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve, we cannot predict the full extent to which our businesses, results of operations, financial condition or liquidity will ultimately be impacted. To the extent the COVID‑19 pandemic adversely affects our businesses, it may also have the effect of exacerbating many of the other risks described in this ‘‘Risk Factors’’ section, any of which could have a material adverse effect on us.
The volatility of commodity prices, including steel, iron ore and scrap metal, directly and indirectly affects our ability to generate revenue, maintain stable cash flows and fund our operations.
Our profitability is dependent upon the prices of the steel, iron ore and scrap metal that we sell to our customers. As an integrated producer of steel, iron ore and scrap metal, we experience direct impacts of steel price fluctuations through customer sales, as well as direct and indirect impacts of iron ore and scrap metal price fluctuations through third-party sales and the impacts that fluctuations in iron ore and scrap metal prices have on steel prices. The prices of steel, iron ore and scrap metal have fluctuated significantly in the past and are unpredictable and affected by factors beyond our control, including: international demand for raw materials used in steel production; availability of scrap metal substitutes such as pig iron; commodity price speculation; rates of global economic growth, especially construction and infrastructure activity that requires significant amounts of steel; changes in the levels of economic activity in the U.S., China, India, Europe and other industrialized or developing economies; changes in China’s emissions policies and environmental compliance enforcement practices; changes in the production capacity, production rate and inventory levels of other steel producers, iron ore suppliers and scrap metal processors and traders; changes in trade laws; volumes of unfairly traded imports; imposition or termination of duties, tariffs, import and export controls and other trade barriers impacting the steel and iron ore markets; climate change and other weather-related disruptions, infectious disease outbreaks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, or natural disasters that may impact the global supply of steel, iron ore or scrap metal; and the proximity, capacity and cost of infrastructure and transportation.
Our earnings, therefore, fluctuate with the prices of the products we sell. Although we experienced generally higher prices for our products during 2021 as compared to 2020, to the extent that commodity prices, including the HRC price, coated and other specialty steel prices, international steel prices and scrap metal prices, significantly decline for an extended period of time, whether due to the COVID-19 pandemic or otherwise, we may have to further revise our operating plans, including curtailing production, reducing operating costs and deferring capital expenditures. We also may have to record impairments on our goodwill, intangible assets, long-lived assets and/or inventory. Sustained lower prices also could cause us to further reduce existing mineral reserves if certain reserves no longer can be economically mined or processed at prevailing prices. We may be unable to decrease our costs in an amount sufficient to offset reductions in revenues and may incur losses. These events could have a material adverse effect on us.
We sell a significant portion of our steel products to the automotive market and fluctuations or changes in the automotive market could adversely affect our business operations and financial performance.
The largest end user for our steel products is the automotive industry in North America. Beyond these direct sales to the automotive industry, we make additional sales to distributors and converters, which may ultimately resell some of that volume to the automotive market. In addition to the size of our exposure to the automotive industry, we face risks arising from our relative concentration of sales to certain specific automotive manufacturers, including several significant customers that previously idled certain automotive production facilities for varying lengths of time in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, automotive production and sales are cyclical and sensitive to general economic conditions and other factors, including interest rates, consumer credit, spending and preferences, and supply chain disruptions, such as the current semiconductor shortage. If automotive production and sales decline, our sales and shipments to the automotive market are likely to decline in a corresponding manner. Similarly, while certain market and industry experts are predicting an increase in new vehicle builds during 2022 as compared to 2020 and 2021, if this increase fails to materialize, our sales to the automotive market could be adversely affected. Adverse impacts that we may sustain as a result include, without limitation, lower margins because of the need to sell our steel to less profitable customers and markets, higher fixed costs from lower steel production if we are unable to sell the same amount of steel to other customers and markets, and lower sales, shipments, pricing and margins generally as our competitors face similar challenges and compete vigorously in other markets that we serve. These adverse impacts would negatively affect our sales, financial results and cash flows. Additionally, the trend toward light weighting in the automotive industry, which requires lighter gauges of steel at higher strengths, could result in lower steel volumes required by that industry over time.
Moreover, despite our newly acquired position as the largest flat-rolled steel producer in North America, competition for automotive business has intensified in recent years, as steel producers and companies producing alternative materials have focused their efforts on capturing and/or expanding their market share of automotive business because of less favorable conditions in other markets for steel and other metals, including commodity products. As a result, the potential exists that we may lose market share to existing or new entrants or that automotive manufacturers will take advantage of the intense competition among potential suppliers during periodic contract renewal negotiations to pressure our pricing and margins in order to maintain or expand our market share with them, which could negatively affect our sales, financial results and cash flows.
Global steelmaking overcapacity, steel imports and oversupply of iron ore could lead to lower or more volatile global steel and iron ore prices, directly or indirectly impacting our profitability.
Significant existing global steel capacity and new or expanded production capacity in recent years could potentially cause capacity to exceed demand globally. Although certain of our U.S. competitors temporarily shut down production capacity during the COVID-19 pandemic, much of the previously idled capacity has been restarted, and certain of our competitors have announced and are moving ahead with plans to develop new steelmaking capacity in the near term. In addition, certain foreign competitors, which may have cost advantages due to being owned, controlled or subsidized by foreign governments, have substantially increased their steel production capacity in the last few years and in some instances appear to have targeted the U.S. market for imports. The risk of even greater levels of imports may continue, depending upon foreign market and economic conditions, changes in trade agreements and treaties, laws, regulations or government policies affecting trade, the ability of foreign producers to circumvent U.S. trade sanctions and policy (including in the market for electrical steels), the value of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies and other variables beyond our control. In addition, higher sustained market prices of steel and iron ore products could cause new producers to enter the market or existing producers to further expand productive capacity, which could in turn lead to lower steel prices and increasing prices of steelmaking inputs, such as scrap metal. Excess steel and iron ore supply combined with reduced global steel demand, including in China, and increased foreign imports could also lead to lower steel and iron ore prices. Downward pressure on steel and/or iron ore prices could have an adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and profitability.
Severe financial hardship or bankruptcy of one or more of our major customers or key suppliers could adversely affect our business operations and financial performance.
Sales and operations of a majority of our customers are sensitive to general economic conditions, especially, with respect to our steel customers, as they affect the North American automotive, housing, construction, appliance, energy, defense and other industries. Some of our customers are highly leveraged. If there is a significant weakening of current economic conditions, whether because of operational, cyclical, supply chain or other issues, including further adverse developments in the COVID-19 pandemic, it could cause customers to reduce, delay or cancel their orders with us, impact significantly the creditworthiness of our customers and lead to other financial difficulties or even bankruptcy filings by our customers. Failure to receive payment from our customers for products that we have delivered could adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity. The concentration of customers in a specific industry, such as the automotive industry, may increase our risk because of the likelihood that circumstances may affect multiple customers at the same time. Such events could cause us to experience lost sales or losses associated with the potential inability to collect all outstanding accounts receivable and reduced liquidity. Similarly, if our key suppliers face financial hardship or need to operate in bankruptcy, such suppliers could experience operational disruption or even face liquidation, which could result in our inability to secure replacement raw materials on a timely basis, or at all, or cause us to incur increased costs to do so. Such events could adversely impact our operations, financial results and cash flows.
II. REGULATORY RISKS
U.S. government actions on trade agreements and treaties, laws, regulations or policies affecting trade could lead to lower or more volatile global steel prices, impacting our profitability.
In recent years, the U.S. government has altered its approach to international trade policy, both generally and with respect to matters directly and indirectly affecting the steel industry, including by undertaking certain unilateral actions affecting trade, renegotiating existing bilateral or multilateral trade agreements, and entering into new agreements or treaties with foreign countries. For example, in March 2018, the U.S. government issued a proclamation pursuant to Section 232 imposing a 25% tariff on imported steel. These Section 232 tariffs were imposed on the basis of national security and addressed imported steel that was being unfairly traded by certain foreign competitors at artificially low prices. In retaliation against the Section 232 tariffs, the European Union subsequently imposed its own tariffs against certain steel products and other goods imported from the U.S. Moreover, in light of the U.S. government leadership changes resulting from the November 2020 federal congressional and presidential elections, further changes in U.S. international trade policy may be forthcoming. For example, the U.S. government and the European Union recently agreed to a tariff rate quota system that will allow more European Union imports to enter the U.S. market free of Section 232 tariffs. The U.S. government may also negotiate reductions or eliminations of Section 232 duties with other trading partners. If the Section 232 tariffs are further removed or substantially lessened, whether through legal challenge, legislation, executive action or otherwise, imports of foreign steel would likely increase and steel prices in the U.S. would likely fall, which could materially adversely affect our revenues, financial results and cash flows.
In addition, during 2020, the USMCA was implemented among the U.S., Mexico and Canada in place of the North American Free Trade Agreement. Because all of our steel manufacturing facilities are located in North America and one of our principal markets is automotive manufacturing in North America, we believe that the USMCA has the potential to positively impact our business by incentivizing automakers and other manufacturers to increase manufacturing production in North America and to use North American steel. However, it is difficult to predict the short- and long-term implications of changes in trade policy and, therefore, whether the USMCA or other new or renegotiated trade agreements, treaties, laws, regulations or policies that may be implemented by the U.S. government, or otherwise, will have a beneficial or detrimental impact on our business and our customers’ and suppliers’ businesses. Adverse effects could occur directly from a disruption to trade and commercial transactions and/or indirectly by adversely affecting the U.S. economy or certain sectors of the economy, impacting demand for our customers’ products and, in turn, negatively affecting demand for our products. Important links of the supply chain for some of our key customers, including automotive manufacturers, could be negatively impacted by the USMCA or other new or renegotiated trade agreements, treaties, laws, regulations or policies. Any of these actions and their direct and indirect impacts could materially adversely affect our revenues, financial results and cash flows.
Although we may currently benefit from certain antidumping and countervailing duty orders, any such relief is subject to periodic reviews and challenges, which can result in revocation of the orders or reduction of the duties. For example, during 2022, the U.S. government is scheduled to review antidumping and countervailing duty orders on some of our key products, including corrosion-resistant steel, cold-rolled steel, hot-rolled steel and cut-to-length plate. In addition, previously granted and future petitions for trade relief may not be successful or fully effective at preventing harm. Even if received, it is uncertain if any relief will be continued in the future or will be adequate to counteract completely the harmful effects of unfairly traded imports.
We are subject to extensive governmental regulation, which imposes potential significant costs and liabilities on us. Future laws and regulations or the manner in which they are interpreted and enforced could increase these costs and liabilities or limit our ability to produce our raw materials and products.
New laws or regulations, or changes in existing laws or regulations, or the manner of their interpretation or enforcement, could increase our cost of doing business and restrict our ability to operate our businesses or execute our strategies. This includes, among other things: changes in MSHA regulations, such as respirable silica standards; reevaluation of the National Ambient Air Quality Standards, such as revised nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, lead, ozone and particulate matter criteria; changes in the interpretation of OSHA regulations, such as standards for occupational exposure to noise, certain chemicals or hazardous substances and infectious diseases; and the possible taxation under U.S. law of certain income from foreign operations.
In addition, we and our operations are subject to various international, foreign, federal, state, provincial and local laws and regulations relating to protection of the environment and human health and safety, including those relating to air quality, water pollution, plant, wetlands, natural resources and wildlife protection (including endangered or threatened species), reclamation, remediation and restoration of properties and related surety bonds or other financial assurances, land use, the discharge of materials into the environment, the effects that industrial operations and mining have on groundwater quality and availability, the management of electrical equipment containing polychlorinated biphenyls, and other related matters. Despite implementation of rigorous environmental protocols and management systems, we cannot be certain that we have been or will be at all times in complete compliance with such laws and regulations. If we violate or fail to comply with these laws or regulations, we could be fined, required to cease operations, subject to criminal or civil liability, or otherwise sanctioned by regulators or barred from participating in government contracts. In addition, federal or state regulatory agencies have the authority, under certain circumstances following significant health and safety incidents, such as fatalities, to order a mine or production facility to be temporarily or permanently closed. Compliance with the complex and extensive laws and regulations to which we are subject imposes substantial costs on us, which could increase over time because of heightened regulatory oversight, adoption of more stringent environmental, health and safety standards and greater demand for remediation services leading to shortages of equipment, supplies and labor, as well as other factors.
Specifically, there are several notable proposed or recently enacted rulemakings or activities to which we would be subject or that would further regulate and/or tax us and our customers, which may also require us or our customers to reduce or otherwise change operations significantly or incur significant additional costs, depending on their ultimate outcome. These emerging or recently enacted rules, regulations and policy guidance include, but are not limited to: governmental regulations imposed, modified or rescinded in response to developments in the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic; trade regulations, such as the USMCA and/or other trade agreements, treaties or policies; changes in tariff policy, including with respect to the 25% tariff on certain imported steel imposed under Section 232; climate change mitigation strategies and GHG regulation; selenium discharge regulation; revisions to the sulfate wild rice water quality standard and its implementation; Minnesota’s Mercury TMDL and associated federal rules governing mercury air emission reductions; evolving water quality standards and the regulation of discharges to groundwater;
the Regional Haze FIP Rule; and revised National Ambient Air Quality Standards, particularly for ozone and particulate matter. In addition, the Biden Administration has indicated via executive orders and in public statements that it will propose more stringent environmental regulation, in particular related to climate change. Any new or more stringent legislation, regulations, rules, interpretations or orders, when enacted and enforced, including any related to required reductions in, or taxes on, levels of carbon emissions, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition or profitability.
Our operations may be impacted by the recent enactment, and ongoing consideration, of significant federal and state laws and regulations relating to certain mine-related issues, such as the stability of tailings basins, mine drainage and fill activities, reclamation and safety in underground and surface mines. With respect to underground mines, for example, these laws and regulations include requirements for constructing and maintaining caches for the storage of additional self-contained self-rescuers throughout the mines; installing rescue chambers in the mines; continuous tracking of and communication with personnel in the mines; installing cable lifelines from the mine portal to all sections of the mine to assist in emergency escape; submission and approval of emergency response plans; and additional safety training. Additionally, there are requirements for the prompt reporting of accidents and increased fines and penalties for violations of these and existing regulations. These laws and regulations may cause us to incur substantial additional costs.
In addition, certain of our operations are subject to the risks of doing business abroad and we must comply with complex foreign and U.S. laws and regulations, which may include, but are not limited to, the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other anti-bribery laws, regulations related to import/export and trade controls, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation and other U.S. and foreign privacy regulations, and transportation and logistics regulations. These laws and regulations may increase our costs of doing business in international jurisdictions and expose our operations and our employees to elevated risk. We require our employees, contractors and agents to comply with these and all other applicable laws and regulations, but failure to do so could result in possible administrative, civil or criminal liability and reputational harm to us and our employees.
As a supplier on federal, state and local public procurement projects, including projects that may arise out of proposed or recently enacted governmental legislation regarding infrastructure investments, we may be subject to certain stringent procurement regulations that may present compliance challenges or may increase the costs of securing certain business. We may also be indirectly affected through regulatory changes that impact our customers, which in turn could reduce the quantity of our products they demand, adversely impact the terms upon which they purchase or the prices for our products they are willing to pay. Regulatory changes that impact our suppliers could decrease the availability of products or services they sell to us or could increase the price they demand for products or services they sell to us.
Our operations use hazardous materials and inadvertently may impact the environment, which could result in material liabilities to us.
Our operations currently use, and have in the past used, hazardous materials and substances, and we have generated, and expect to continue to generate, solid and hazardous waste. We have been, and may in the future be, subject to claims under international, foreign, federal, state, provincial and local laws and regulations for toxic torts, natural resource damages and other damages as well as for the investigation and clean-up of soil, surface water, sediments, groundwater and other natural resources and reclamation of properties. Such claims for damages, as well as investigation, remediation and reclamation requirements, have arisen and may arise in the future out of current, future or former conditions at sites that we or our acquired companies own, lease or operate, as well as sites that we or our acquired companies formerly owned, leased or operated, and at contaminated sites that are or have been owned, leased or operated by our joint venture partners. We may also have liability for contamination at third-party sites where we have sent hazardous wastes. Our liability for these claims may be strict and/or joint and several, such that we may be held responsible for more than our share of the contamination or other damages, or even for entire claims regardless of fault. We may be named as a potentially responsible party at other third-party sites in the future, and we cannot be certain that the costs associated with these additional sites will not exceed any reserves we have established or otherwise be material.
We may be unable to obtain, maintain, renew or comply with permits necessary for our operations or be required to provide additional financial assurances, which could reduce our production, cash flows, profitability and available liquidity.
We must obtain, maintain and comply with numerous permits that require approval of operational plans and impose strict conditions on various environmental, health and safety matters in connection with our steel production and processing and mining and other operations. These include permits and approvals issued by various federal,
state, provincial, foreign and local agencies and regulatory bodies, with which we may not always be able to comply. The permitting rules are complex and may change over time, making our ability to comply with the applicable requirements more difficult or potentially impractical and costly, possibly precluding the continuance of ongoing operations or the development of future operations. Interpretations of rules may also change over time and may lead to requirements, such as additional financial assurances, making it costlier to comply. Moreover, despite our ongoing efforts to reduce our environmental footprint and improve the resiliency of our business model, heightened levels of regulatory oversight focused on addressing climate change and industrial activities that generate GHG emissions, such as our steelmaking, cokemaking and mining operations, could impact, delay or disrupt our ability to obtain new or renewed permits or modifications to existing permits.
In addition, the public, including special interest groups and individuals, have certain rights under various statutes to comment upon, submit objections to, and otherwise engage in the permitting process, including bringing citizens’ lawsuits to challenge such permits or activities. Accordingly, required permits may not be issued or renewed in a timely fashion (or at all), or permits issued or renewed may include conditions that we cannot meet or otherwise be conditioned in ways that may restrict our ability to conduct our production, mining and processing activities efficiently or include requirements for additional financial assurances that we may not be able to provide on commercially reasonable terms (or at all), which could reduce available borrowing capacity under our ABL Facility. Such conditions, restrictions or requirements could also reduce our production, cash flows or profitability.
III. FINANCIAL RISKS
Our existing and future indebtedness may limit cash flow available to invest in the ongoing needs of our businesses, which could prevent us from fulfilling our obligations under our senior notes, ABL Facility and other debt, and we may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our debt, which may not be successful.
As of December 31, 2021, we had $5,369 million aggregate principal amount of long-term debt outstanding, $1,452 million of which was secured (excluding $175 million of outstanding letters of credit and $291 million of finance leases), and $48 million of cash on our balance sheet. On December 17, 2021, we amended our ABL Facility to, among other things, increase the tranche A revolver commitments available under the ABL Facility by an additional $1,000 million and exchange $150 million of tranche B revolver commitments available thereunder for tranche A revolver commitments. After giving effect to this amendment, the aggregate principal amount of tranche A revolver commitments under our ABL Facility is $4,500 million, and there are no longer any tranche B commitments under our ABL Facility. As of December 31, 2021, $1,609 million was outstanding under our ABL Facility, and the principal amount of letters of credit obligations and other commitments totaled $175 million. As of December 31, 2021, the available borrowing capacity on our ABL Facility was $2,716 million.
We dedicate a portion of our cash flow from operations to the payment of debt service, reducing the availability of our cash flow to fund capital expenditures, acquisitions or strategic development initiatives, and other general corporate purposes. Our ability to make scheduled payments on or to refinance our debt obligations depends on our ability to generate cash in the future and our financial condition and operating performance, which are subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business and other factors beyond our control, including the impact of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. There can be no assurance that we will maintain a level of cash flows from operating activities sufficient to permit us to pay the principal, premium, if any, and interest on our debt. In addition, any failure to comply with covenants in the instruments governing our debt could result in an event of default that, if not cured or waived, would have a material adverse effect on us.
Our level of indebtedness could have further consequences, including, but not limited to, increasing our vulnerability to adverse economic or industry conditions, placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to other businesses in the industries in which we operate that are not as leveraged and that may be better positioned to withstand economic downturns, limiting our flexibility to plan for, or react to, changes in our businesses and the industries in which we operate, and requiring us to refinance all or a portion of our existing debt. We may not be able to refinance on commercially reasonable terms or at all, and any refinancing of our debt could be at higher interest rates and may require us to comply with more onerous covenants, making it more difficult to obtain surety bonds, letters of credit or other financial assurances that may be demanded by our vendors or regulatory agencies, particularly during periods in which credit markets are weak.
A portion of our borrowing capacity and outstanding indebtedness bears interest at a variable rate based on LIBOR. According to the FCA, the IBA will permanently cease to publish each of the LIBOR settings by June 2023. It is unclear whether new methods of calculating LIBOR will be established such that it continues to exist after such end date, and there is considerable uncertainty regarding the publication or representativeness of LIBOR beyond such
end date. The U.S. Federal Reserve, in conjunction with the Alternative Reference Rates Committee, is seeking to replace U.S. dollar LIBOR with a newly created index, SOFR. Our ABL Facility provides a mechanism to automatically transition to a SOFR-based benchmark when all USD LIBOR settings are no longer provided or are no longer representative. In addition, our ABL Facility includes an option for us and the agent to jointly elect to transition early to a SOFR-based benchmark, or in certain circumstances, an alternative benchmark replacement. It is not possible to predict the effect of these changes, other reforms or the establishment of alternative reference rates. To the extent these interest rates increase, our interest expense will increase. If sources of capital for us are reduced, capital costs could increase materially. Restricted access to capital markets and/or increased borrowing costs could have an adverse effect on our results of operations, cash flows, financial condition and liquidity.
If we are unable to service our debt obligations, we could face substantial liquidity problems and we may be forced to reduce or delay investments and capital expenditures, or to sell assets, seek additional capital, including additional secured or unsecured debt, or restructure or refinance our debt, and we may be unable to continue as a going concern. We may be unable to consummate any proposed asset sales or recover the carrying value of these assets, and any proceeds may not be adequate to meet any debt service obligations then due. Any of these examples potentially could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, profitability, shareholders’ equity and capital structure.
Changes in credit ratings issued by nationally recognized statistical rating organizations could adversely affect our cost of financing and the market price of our securities.
Credit rating agencies could downgrade our ratings due to various developments, including incurring additional indebtedness and other factors specific to our businesses, a prolonged cyclical downturn in the steel, scrap metal and mining industries or macroeconomic trends (such as global or regional recessions), increases in pension and OPEB obligations, and trends in credit and capital markets more generally. Any decline in our credit ratings may result in an increase to our cost of future financing or limit our access to the capital markets, which could harm our financial condition, hinder our ability to refinance existing indebtedness on acceptable terms, or have an adverse effect on the market price of our securities and the terms under which we purchase goods and services.
Our actual operating results may differ significantly from our guidance.
From time to time, we release guidance, including that set forth under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations–Outlook” in our Annual Reports on Form 10-K and our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, regarding our future performance. This guidance, which consists of forward-looking statements, is prepared by our management and is qualified by, and subject to, the assumptions and the other information included in our Annual Reports on Form 10-K and our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q. Our guidance is not prepared with a view toward compliance with published guidelines of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, and neither our independent registered public accounting firm nor any other independent or outside party compiles or examines the guidance and, accordingly, no such person expresses any opinion or any other form of assurance with respect thereto.
Guidance is based upon a number of assumptions and estimates that, while presented with numerical specificity, are inherently subject to business, economic, regulatory and competitive uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond our control and are based upon specific assumptions with respect to future business decisions, some of which will change. The principal reason that we release such data is to provide a basis for our management to discuss our business outlook with analysts and investors. We do not accept any responsibility for any projections or reports published by any such third parties.
Guidance is necessarily speculative in nature, and it can be expected that some or all of the assumptions of the guidance furnished by us will not materialize or will vary significantly from actual results. Accordingly, our guidance is only an estimate of what management believes is realizable as of the date of release. Actual results will vary from the guidance. Investors should also recognize that the reliability of any forecasted financial data diminishes the further in the future that the data are forecast. In light of the foregoing, investors are urged to put the guidance in context and not to place undue reliance on it.
Any failure to successfully implement our operating strategy or the occurrence of any of the risks described in our Annual Reports on Form 10-K or our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q could cause actual operating results to differ from the guidance, and such differences may be adverse and material.
We may be subject to various lawsuits, claims, arbitrations or governmental proceedings that could result in significant expenditures.
We are from time to time subject to various lawsuits, claims, arbitrations or governmental proceedings relating to commercial and business disputes, environmental matters, government investigations, occupational or personal injury claims, property damage, labor and employment matters, or suits involving legacy operations and other matters. For example, certain of our subsidiaries have been named in lawsuits claiming exposure to asbestos, many of which have been dismissed and/or settled for non-material amounts. Nevertheless, it is likely that similar types of claims will continue to be filed in the future, and we could experience material adverse judgments or incur significant costs to defend such claims or any other existing and future lawsuits, claims, arbitrations or governmental proceedings. The insurance we maintain may not be adequate to protect us in the event of significant claims.
IV. OPERATIONAL RISKS
Our operating expenses could increase significantly if the prices of raw materials, electrical power, fuel or other energy sources increase.
Our operations require significant use of energy and raw materials. Although we are fully self-sufficient in iron ore and partially self-sufficient in coke, metallurgical coal and scrap metal, we are wholly or partially dependent on third-party suppliers for certain critical raw materials and production inputs, including industrial gases, graphite electrodes, chrome, zinc, coke, metallurgical coal and scrap metal. Prices for electricity, natural gas, diesel fuel, oils and raw materials can fluctuate widely with availability and demand levels from other users, including fluctuations caused by the impact of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. For example, increased electricity demand to the grid in response to physical climate-related risks and electrification of the economy could adversely impact energy prices. During periods of peak usage, although some operations have contractual arrangements in place whereby they receive certain offsetting payments in exchange for electricity load reduction, supplies of energy and raw materials in general may be curtailed and we may not be able to purchase them at historical rates. A disruption in the transmission of energy, inadequate energy transmission infrastructure, or the termination of any of our energy supply contracts could interrupt our energy supply and adversely affect our operations. While we have some long-term contracts with electrical, natural gas and raw material suppliers, we are exposed to fluctuations in energy, natural gas and raw material costs that can affect our production costs. We enter into many market-based pricing supply contracts for electricity, natural gas and diesel fuel for use in our operations. Those contracts expose us to price increases in energy costs, which could cause our profitability to decrease significantly. As an example, our Toledo direct reduction plant is subject to changes in the market price of natural gas, which is a key input in the direct reduction of iron ore pellets to produce HBI, and natural gas experienced a substantial market price increase during the fourth quarter of 2021. In addition, U.S. public utilities may impose rate increases and pass through additional capital and operating cost increases to their customers related to new or pending U.S. environmental regulations or other charges that may require significant capital investment and use of cleaner fuels in the future. In particular, the recent decision of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia vacating and remanding the Affordable Clean Energy Rule, as well as recent executive orders from President Biden regarding the environment and climate change, indicate that new or revised regulations under the Biden Administration could result in rate increases from U.S. utilities.
The majority of our steel shipments are sold under contracts that do not allow us to pass through all increases in raw materials, supplies and energy costs. Some of our customer contracts include variable-pricing mechanisms allowing us to adjust the total sales price based on changes in specified raw materials, supplies and energy costs. Those adjustments, however, rarely reflect all of our underlying raw materials, supplies and energy cost changes. The scope of the adjustment may also be limited by the terms of the negotiated language, including limitations on when the adjustment occurs. Our need to consume existing inventories may also delay the impact of a change in prices of raw materials or supplies. Significant changes in raw material costs may also increase the potential for inventory value write-downs in the event of a reduction in selling prices and our inability to realize the cost of the inventory. In addition, even though we are partially self-sufficient in scrap metal, if the market price of scrap metal were to experience a sustained price increase, our cost to produce steel would be adversely affected due to the higher prices we would need to pay to acquire third-party scrap metal for consumption in our operations.
Our sales and competitive position depend on transporting our products to customers at competitive rates and in a timely manner, and our ability to optimize our operational footprint depends on predictably and cost effectively moving products and raw materials internally among our facilities.
Disruption of the rail, trucking, lake and other waterway transportation services because of weather-related problems, including ice and winter weather conditions on the Great Lakes or St. Lawrence Seaway, climate change,
strikes, lock-outs, driver shortages and other disruptions in the trucking industry, train crew shortages or other rail network constraints, global or domestic pandemics or epidemics (such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic) or other infectious disease outbreaks, in each case causing a business disruption, or other events and lack of alternative transportation options could impair our ability to move products internally among our facilities and to supply products to our customers at competitive rates or in a timely manner and, thus, could adversely affect our operations, revenues, margins and profitability. Further, dredging issues and environmental changes, particularly at Great Lakes ports, could impact adversely our ability to move certain of our products or result in higher freight rates. Similarly, we depend on third-party transportation services for delivery of raw materials and other production inputs to us, and failures or delays in delivery would have an adverse effect on our ability to maintain steady-state production and processing operations to meet customer obligations.
Natural or human-caused disasters, weather conditions, disruption of energy, unanticipated geological conditions, equipment failures, infectious disease outbreaks, and other unexpected events may lead our customers, our suppliers or our facilities to curtail production or shut down operations.
Operating levels within our industry and the industries of our customers and suppliers are subject to unexpected conditions and events that are beyond the industries’ control. Those events, including the occurrence of an infectious disease, widespread illness or public health emergency, such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, could cause industry members or their suppliers to curtail production or shut down a portion or all of their operations, which could reduce the demand for our products and adversely affect our revenues, margins and profitability. For example, the temporary production shutdowns in the automotive industry that occurred during 2020 as a result of the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic and associated reduction in demand for our products led to our decision to temporarily idle certain steelmaking facilities and iron ore mines.
Our operating levels are subject to conditions beyond our control that can delay deliveries or increase the cost of production for varying lengths of time. Factors that could cause production disruptions could include adverse weather conditions due to climate change or otherwise (such as extreme winter weather, tornadoes, floods, and the lack of availability of process water due to drought) and natural and human-caused disasters, lack of adequate raw materials, energy or other supplies, and infectious disease outbreaks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. During 2021, for example, while it did not result in material financial consequences, we experienced a severe weather event involving a tornado that damaged one of our Tooling and Stamping production facilities and a third-party warehouse located in Kentucky, which adversely impacted our operations, destroyed some of our finished goods inventory and disrupted certain scheduled deliveries to customers. In addition, factors that could adversely impact production and operations at our mining operations include tailings dam failures, pit wall failures, unanticipated geological conditions, including variations in the amount of rock and soil overlying deposits of iron ore and metallurgical coal, and processing changes.
Our mining operations, processing facilities, steelmaking and logistics operations depend on critical pieces of equipment. This equipment may, on occasion, be out of service because of unanticipated failures or unplanned outages. In addition, most of our mines and production and processing facilities have been in operation for several decades, and the equipment is aged. In the future, we may experience additional lengthy shutdowns or periods of reduced production because of equipment failures. Further, remediation of any interruption in production capability may require us to make large capital expenditures that could have a negative impact on our profitability and cash flows. Our business interruption insurance would not cover all of the lost revenues associated with equipment failures. Longer-term business disruptions could result in a loss of customers, which could adversely affect our future sales levels and revenues.
Many of our production facilities and mines are dependent on one source for electric power, natural gas, industrial gases and/or certain other raw materials or supplies. A significant interruption in service from our suppliers due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, terrorism or sabotage, weather conditions such as heat waves that may be attributable to climate change, natural disasters, equipment failure or any other cause could result in substantial losses that may not be fully recoverable, either from our business interruption insurance or responsible third parties.
A disruption in or failure of our IT systems, including those related to cybersecurity, could adversely affect our business operations, reputation and financial performance.
We rely on the accuracy, capacity, integrity and security of our IT systems for the operation of many of our business processes and to comply with regulatory, legal and tax requirements. While we maintain some of our critical IT systems, we are also dependent on third parties to provide important IT services relating to, among other things, off-site content hosting, operational process technology at our facilities, human resources, electronic communications and certain finance functions. Further, in connection with our recent acquisitions, we inherited certain legacy
hardware and software IT systems that can be supported only by a very limited number of specialists in the market, and our increased reliance on these legacy IT systems may increase the risk of IT system disruption or failure, which could adversely affect our operations.
Despite the security measures that we have implemented, including those related to cybersecurity, our IT systems could be breached or damaged by computer viruses, natural or human-caused incidents or disasters, or unauthorized physical or electronic access or intrusions. Though we have controls in place, we cannot provide assurance that a cyberattack will not occur. Furthermore, despite our efforts to audit certain critical vendors’ information security controls, we may have little or no oversight with respect to security measures employed by third-party service providers, which may ultimately prove to be ineffective at countering threats. We may also experience increased risk of IT system failures or cyberattacks as many of our employees continue to work from home on a periodic basis as part of our response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Failures of our IT systems, whether caused maliciously or inadvertently, may result in the disruption of our business processes, or in the unauthorized release of sensitive, confidential, personally identifiable or otherwise protected information, or result in the corruption of data, each of which could adversely affect our businesses. For example, cybersecurity vulnerabilities could result in an interruption of the functionality of our automated manufacturing operating or health and safety systems, which, if compromised, could cease, threaten, delay or slow down our ability to produce or process steel or any of our other products for the duration of such interruption or lead to unanticipated health or safety incidents, which could result in reputational harm and may adversely affect our employees, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. In addition, any compromise of the security of our IT systems could result in a loss of confidence in our security measures and subject us to litigation, regulatory investigations and negative publicity that could adversely affect our reputation and financial condition. Our customers, suppliers and vendors may also access or store certain of our sensitive information on their IT systems, which, if breached, attacked or accessed by unauthorized persons, could likewise expose our sensitive information and adversely impact our businesses. Furthermore, as cybersecurity threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, we may be required to incur significant costs and invest additional resources to protect against and, if required, remediate the damage caused by such disruptions or system failures in the future. The amount of insurance coverage we maintain may be inadequate to cover claims or liabilities resulting from cybersecurity attacks.
The closure of an operating facility or mine entails substantial costs. If our assumptions underlying our accruals for closure costs prove to be inaccurate or we prematurely close one or more of our facilities or mines, our results of operations and financial condition would likely be adversely affected.
If faced with overcapacity in the market or other adverse conditions, including as a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, we may seek to rationalize assets through asset sales, temporary shutdowns, indefinite idles or facility closures. If we indefinitely idle or permanently close any of our facilities or mines, our production and revenues would be reduced unless we were able to increase production at our other facilities or mines in an offsetting amount, which may not be possible, and could result in customers responding negatively by taking current or future business away from us if we seek to transition production to a different facility. Alternatively, we could fail to meet customer specifications at the facilities to which products are transitioned, resulting in customer dissatisfaction or claims.
The closure of a steelmaking or other operating facility or mining operation involves significant closure costs, including reclamation and other environmental costs, the costs of terminating long-term obligations, including customer, energy and transportation contracts and equipment and real property leases, and certain accounting charges, including asset impairment and accelerated depreciation. In addition, a permanent facility or mine closure could accelerate and significantly increase employment legacy costs, including our expense and funding costs for pension and OPEB obligations and multiemployer pension withdrawal liabilities. For example, a number of employees would be eligible for immediate retirement under special eligibility rules that apply upon a steelmaking facility or mine closure. All employees eligible for immediate retirement under the pension plans at the time of the permanent closure also could be eligible for OPEB, thereby accelerating our obligation to provide these benefits. Certain closures would precipitate a pension closure liability significantly greater than an ongoing operation liability and may trigger certain severance liability obligations. In addition, we are party to several joint ventures relating to iron ore mining, downstream steel processing and scrap metal recycling, and if our joint venture partners experience financial hardships or fail to perform their obligations upon closure, we may be required to assume significant additional obligations on behalf of the joint venture, including costs of environmental remediation and pension and OPEB obligations.
We base our assumptions regarding the life of our mines on detailed studies we perform from time to time, but those studies and assumptions are subject to uncertainties and estimates that may not be accurate. We recognize the costs of reclaiming open pits, stockpiles, tailings ponds, roads and other mining support areas based on the
estimated mining life of our properties. If our assumptions underlying our accruals for closure costs, including reclamation and other environmental costs, prove to be inaccurate or insufficient, or our liability in any particular year is greater than currently anticipated, our results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected. In addition, if we were to significantly reduce the estimated life of any of our mines, the mine closure costs would be applied to a shorter period of production, which would increase costs per ton produced and could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We incur certain costs when production capacity is idled, as well as increased costs to resume production at previously idled facilities.
Our decisions concerning which facilities to operate and at what production levels are made based in part upon our customers’ orders for products, as well as the quality, performance capabilities and cost of our operations. During depressed market conditions, we may concentrate production at certain facilities and not operate others in response to customer demand, and as a result we may incur idle costs that could offset our anticipated savings from not operating the idled facility. For example, due to reduced demand arising out of the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, certain of our steelmaking facilities and iron ore mines were temporarily idled during portions of 2020 and we continued to incur certain fixed costs at those facilities. We cannot predict whether our operations will experience additional similar or dissimilar disruptions in the future.
When we restart idled facilities, we incur certain costs to replenish inventories, prepare the previously idled facilities for operation, perform the required repair and maintenance activities, and prepare employees to return to work safely and resume production responsibilities. The amount of any such costs could be significant, depending on a variety of factors, such as the period of idle time, necessary repairs and available employees, and is difficult to project.
We face ongoing risks relating to our recent mergers and acquisitions activities.
In recent years, we have completed several significant acquisition transactions, including the AK Steel Merger, the AM USA Transaction and the FPT Acquisition. These recent acquisitions have transformed our business and involve a number of significant risks and uncertainties that may adversely affect us over the short, medium and long terms, including the following:
•inability to realize anticipated synergies or other expected benefits or cost savings;
•additional debt incurred or assumed in connection with the acquisitions could limit our financial flexibility;
•diversion of financial resources to the new operations or acquired businesses;
•assumption of substantial additional environmental exposures, commitments, contingencies and remediation and reclamation projects;
•liabilities for acquired pension and OPEB obligations, which could require us to make significant cash expenditures and funding contributions in excess of current estimates and contribution rates;
•impairment of recorded tangible and intangible asset values, including goodwill, could result in material non-cash charges to our results of operations in the future;
•failure to successfully separate from legacy systems and to integrate acquired systems, business processes, policies and procedures;
•exposure to unknown liabilities and unforeseen costs that were not disclosed to us or discovered during due diligence;
•potential loss of key employees, suppliers or customers; and
•other challenges associated with managing the larger, more complex and integrated combined businesses.
If one or more of these risks and uncertainties were to materialize, we could experience reduced revenues, higher costs, lower profitability and other adverse impacts to our operations and businesses.
We may not have adequate insurance coverage for some business risks.
Our operations are generally subject to a number of hazards and risks that could result in personal injury or damage to, or destruction of, equipment, properties or facilities. Depending on the nature and extent of a loss, the insurance that we maintain to address risks that are typical in our businesses may not be adequate or available to fully protect or reimburse us, or our insurance coverage may be limited, canceled or otherwise terminated. Insurance against some risks, such as liabilities for environmental pollution, tailings basin breaches, or certain hazards or interruption of certain business activities, may not be available at an economically reasonable cost, or at all. Even if available, we may self-insure where we determine it is most cost effective to do so. As a result, despite the insurance coverage that we carry, accidents or other negative developments involving our production, mining, processing or transportation activities causing losses in excess of policy limits, or losses arising from events not covered under insurance policies, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and cash flows. In addition, the potential increase in extreme weather events due to climate change or otherwise may adversely impact our access to cost effective insurance in the future. The risk of increased insurance costs may have greater impact where the adverse event, such as the tornado we recently experienced at our Tooling and Stamping operations in Kentucky, results in us asserting an insurance claim, the cost of which our insurers may seek to recoup during a future insurance renewal through increased premiums or limitations on coverage.
V. SUSTAINABILITY AND DEVELOPMENT RISKS
As our customers, competitors and investors seek to reduce their carbon footprint, transition to carbon neutrality and enhance the sustainability of their respective businesses, we face increased financial, regulatory, legal and reputational risks and potential loss of business opportunities because our operations utilize carbon-based energy sources and produce GHG emissions.
As described in detail in Part I - Item 1, Business - Environment - Regulatory Developments - Climate Change and GHG Regulation above, because our operations use carbon-based energy and produce GHG emissions, we are subject to a number of risks relating to decarbonization initiatives being undertaken by regulators and other stakeholders as part of global efforts to address the potential impacts of climate change. For example, as part of climate change mitigation strategies, federal, state or local governmental authorities may introduce mandatory carbon pricing obligations, carbon emissions limitations, carbon taxes or carbon trading mechanisms, any of which could impose significant costs on our operations, including causing us to incur higher energy costs, invest in costly and potentially unproven emissions control or reduction technologies, and engage in more intensive environmental monitoring and reporting efforts. In addition, complying with current or future international treaties and federal, state or local laws or regulations concerning climate change and GHG emissions could negatively impact our ability, and that of our customers and suppliers, to compete with companies located in areas not subject to or not complying with such constraints. We may also face more limited access to, or increased costs of, capital to the extent financial institutions and investors increase expectations relating to lowering GHG emissions or reduce investments in carbon-intensive businesses. Further, increased pressure from customers or other business partners seeking to reduce their indirect carbon footprints could result in the potential loss of business opportunities if we are unable to meet their carbon, GHG emissions or sustainability expectations.
In order to maintain consistent operational performance and foster growth in our businesses, we must maintain our social license to operate with our stakeholders.
Maintaining a strong reputation and consistent operational, environmental and safety track records is vital in order to continue to foster business growth and maintain our permission to operate. As stakeholders’ sustainability expectations increase and regulatory requirements continue to evolve, maintaining our social license to operate becomes increasingly important. Our ability to maintain our reputation and strong operating track record could be threatened, including by challenges relating to the integration of our recent acquisitions or by circumstances outside of our control, such as disasters caused or suffered by other companies in the steel and mining industries. Our social license to operate could also be adversely affected and claims could be made against us to the extent that environmental factors negatively impact local communities, such as air emissions, discharges to water, dust, odors, noise and other factors that are inherent in industrial activities like our steelmaking, cokemaking, scrap metal processing and mining operations, even if such activities are conducted in accordance with legal, regulatory and permit requirements. If we are not able to respond effectively to these and other challenges to our social license to operate, our reputation could be damaged significantly. Damage to our reputation could adversely affect our operations, current and prospective business relationships, and ability to foster growth projects.
The cost and time to implement a strategic capital project may prove to be greater than originally anticipated.
From time to time, we undertake strategic capital projects, such as our recently-completed Toledo direct reduction plant, in order to enhance, expand or upgrade our production, mining and processing capabilities or to diversify our customer base. Our ability to achieve the anticipated production volumes, revenues or otherwise realize acceptable returns on strategic capital projects that we may undertake is subject to a number of risks, many of which are beyond our control, including a variety of market (such as a volatile pricing environment for our products), operational, permitting and labor-related factors. Further, the cost to implement any given strategic capital project ultimately may prove to be greater and may take more time than originally anticipated. Inability to achieve the anticipated results from the implementation of our strategic capital projects, incurring unanticipated implementation costs or penalties, or the inability to meet contractual obligations could adversely affect our results of operations and future earnings and cash flow generation.
We rely on estimates of our recoverable mineral reserves, which is complex due to geological characteristics of the properties and the number of assumptions made.
We regularly evaluate, and engage third-party QPs to review and validate, our mineral reserves based on revenues and costs and update them as required in accordance with SEC regulations. Estimates of mineral reserves and future net cash flows necessarily depend upon a number of variable factors and assumptions, some of which are beyond our control, such as production capacity, effects of regulations by governmental agencies, future prices for minerals we mine, future industry conditions and operating costs, severance and excise taxes, development costs, and costs of extraction and reclamation. Estimating the quantity and grade of mineral reserves requires us to determine the size, shape and depth of our mineralized bodies by analyzing geological data, such as samplings of drill holes, and a QP to review and validate our determinations. Estimated mineral reserves could be affected by future industry conditions, future changes in the SEC’s mining property disclosure requirements, variation in geological conditions and ongoing mine planning. Actual volume and grade of reserves recovered, production rates, revenues on third-party sales and expenditures with respect to our reserves will likely vary from estimates, and if such variances are material, our sales and profitability could be adversely affected.
Defects in title or loss of any leasehold interests in our mining properties could limit our ability to mine these properties or result in significant unanticipated costs.
Many of our operations are conducted on properties we lease, license or as to which we have easements or other possessory interests. We generally do not maintain title insurance on our properties. A title defect or the loss of any lease, license, easement or other possessory interest for any mining property could adversely affect our ability to mine any associated reserves. In addition, from time to time the rights of third parties for competing uses of adjacent, overlying or underlying lands, such as for roads, easements, public facilities or other mining activities, may affect our ability to operate as planned if our title is not superior or mutually acceptable arrangements cannot be negotiated. Any challenge to our title could delay the exploration and development of some reserves, resources, deposits or surface rights, cause us to incur unanticipated costs, and could ultimately result in the loss of some or all of our interest in those properties. In the event we lose reserves, resources, deposits or surface rights, we may be required to shut down or significantly alter impacted mining operations, thereby affecting future production, revenues and cash flows.
VI. HUMAN CAPITAL RISKS
We may encounter labor shortages for critical operational positions, which could adversely affect our ability to produce our products.
We are predicting a long-term shortage of skilled workers in heavy industry and in certain highly specialized IT roles, and competition for available workers limits our ability to attract and retain employees as well as engage third-party contractors. As our experienced employees retire and we lose their specialized institutional knowledge of our legacy businesses and systems, we have encountered challenges and may continue to have difficulty replacing them at competitive wages. In addition, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a number of workers resigning or retiring sooner than would typically be expected, and the pandemic may continue to result in increased government restrictions and regulation, including quarantines of our personnel and potential inability to access facilities, which has adversely affected and could continue to adversely affect our operations.
Our profitability could be adversely affected if we fail to maintain satisfactory labor relations.
Our production is dependent upon the efforts of our employees. We are party to labor agreements with various labor unions that represent employees at the majority of our operations. Such labor agreements are negotiated periodically, and, therefore, we are subject to the risk that these agreements may not be able to be renewed on reasonably satisfactory terms. It is difficult to predict what issues may arise as part of the collective bargaining process, and whether negotiations concerning these issues will be successful. Due to union activities or other employee actions, we could experience labor disputes, work stoppages or other disruptions in our production that could affect us adversely. While we successfully negotiated all of our labor agreements that expired in 2021, we have ten labor agreements that will expire in 2022 and three labor agreements that will expire in 2023, and the outcomes of those labor negotiations are uncertain. If we enter into a new labor agreement with any union that significantly increases our labor costs relative to our competitors or fail to come to an agreement upon expiry, our ability to compete or continuity of production may be materially and adversely affected.
We depend on our senior management team and other key employees, and the loss of these employees could adversely affect our businesses.
Our success depends in part on our ability to attract, retain, develop and motivate our senior management and key employees. Achieving this objective may be difficult due to a variety of factors, including fluctuations in the global economic and industry conditions, competitors’ hiring practices, cost reduction activities, and the effectiveness of our compensation programs. Competition for qualified personnel can be intense. We must continue to recruit, retain, develop and motivate our senior management and key personnel in order to maintain our businesses and support our projects. A loss of senior management and key personnel could prevent us from capitalizing on business opportunities, and our operating results could be adversely affected. We are also subject to the risk that the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic may impact the health or effectiveness of members of our senior management team or other key employees.
Our expenditures for pension and OPEB obligations could be materially higher than we have predicted if our underlying assumptions differ from actual outcomes, there are regulatory changes or other contributors fail to perform their obligations that relate to employee pension plans.
We provide defined benefit pension plans and OPEB to certain eligible union and non-union employees. Our pension and OPEB expenses and our required contributions to our pension and OPEB plans are affected directly by the value of plan assets, the projected and actual rate of return on plan assets, and the actuarial assumptions we use to measure our defined benefit pension plan obligations, including the rate at which future obligations are discounted. We cannot predict whether changing market or economic conditions, regulatory changes or other factors will increase our pension and OPEB expenses or our funding obligations, diverting funds we would otherwise apply to other uses.
We have calculated our unfunded pension and OPEB obligations based on a number of assumptions. If our assumptions do not materialize as expected, cash expenditures and costs that we incur could be materially higher. Moreover, we cannot be certain that regulatory changes will not increase our obligations to provide these or additional benefits. These obligations also may increase substantially in the event of adverse medical cost trends or unexpected rates of early retirement, particularly for bargaining unit retirees. In addition, changes in the laws governing pensions could also materially adversely affect our costs and ability to meet our pension obligations.
We also contribute to certain multiemployer pension plans, including the Steelworkers’ Pension Trust, for which we are one of the largest contributing employers. If other contributors were to default on their obligations to contribute to any such plans, we could become liable for additional unfunded contributions to the plans.
In addition, some of the transactions in which we previously sold or otherwise disposed of our non-core assets included provisions transferring certain pension and other liabilities to the purchasers or acquirers of those assets. While we believe that all such transfers were completed properly and are legally binding, if the purchaser fails to fulfill its obligations, we may be at risk that a court, arbitrator or regulatory body could disagree and determine that we remain responsible for pension and other liabilities that we intended to and did transfer.
| | | | | |
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
We have no unresolved comments from the SEC.
The following map shows the locations of our operations and offices as of December 31, 2021:
Corporate Offices
We lease our corporate headquarters in Cleveland, Ohio. We also have leased office space in West Chester, Ohio, Chicago, Illinois and Detroit, Michigan. We own our office space located in Burns Harbor, Indiana and our Research and Innovation Center located in Middletown, Ohio.
Steelmaking
Steelmaking and Finishing Facilities
Below is a listing and description of our principal steelmaking and finishing facilities:
Burns Harbor is a fully integrated steelmaking facility located on Lake Michigan in Northwest Indiana, 50 miles southeast of Chicago. The location allows for prime shipping access to the Port of Indiana, as well as excellent highway and railroad transport. Burns Harbor’s major production facilities include coke plant operations, iron producing, steel producing, hot rolling, pickling, cold rolling, annealing, galvanizing, finishing and plate rolling and heat treating. The plant operates two blast furnaces and is capable of producing hot-rolled sheet, cold-rolled sheet and hot dip galvanized sheet. Burns Harbor is capable of producing nearly 5 million net tons of raw steel annually. Burns Harbor serves key markets including the automotive, appliance, construction, converters, distribution and pipe and tube markets.
Burns Harbor Plate and Gary Plate are located in Burns Harbor and Gary, Indiana, respectively, and are heat treating and finishing operations producing carbon steel plate, high-strength low alloy steel plate and ASTM grades steel plate. These operations serve the construction, distribution, energy, heavy equipment, infrastructure, military, pipe and tube, rail car and shipbuilding markets.
Butler Works is located in Butler, Pennsylvania, and produces stainless, electrical and carbon steel. Melting takes place in an EAF that feeds an argon-oxygen decarburization unit for the specialty steels. A ladle metallurgy furnace feeds two double-strand continuous casters, which are capable of producing 1 million net tons of raw steel annually. Butler Works also includes a hot rolling mill, annealing and pickling units and one tandem cold rolling mill. It also has various intermediate and finishing operations for both stainless and electrical steels. Butler Works primarily serves the power and distribution transformers and stainless and carbon converters markets.
The Cleveland facility is an integrated steelmaking facility strategically located on the Cuyahoga River in Cleveland, Ohio, with access to the Port of Cleveland and Great Lakes shipping, as well as excellent highway and railroad transport. The Cleveland facility is supplied with coke from our cokemaking operations in Warren, Ohio. Cleveland's major production facilities include iron making, steel producing, hot rolling, pickle and cold rolling, and hot galvanizing. The plant is capable of producing more than 3 million net tons of raw steel annually. Products made at this location are hot-rolled, cold-rolled and hot-dipped galvanized sheet and semi-finished slabs. The Cleveland facility serves the automotive, construction, converters and distribution markets.
Coatesville is a steel plate production facility located in Coatesville, Pennsylvania, about 40 miles west of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and has access to highways and railroads. The facility produces steel from scrap in an EAF and is capable of producing 0.8 million net tons of raw steel annually. The facility also operates ingot teeming facilities, a slab caster, two plate mills, heat-treating facilities, quench and temper and flame-cut shape facilities. The Coatesville facility refines more than 450 different steel chemistries and, together with the Conshohocken facility, produces some of the widest, thickest and heaviest steel plates in the industry. Steel plate products made at this location include carbon, high-strength low-alloy, commercial alloy, military alloy and flame-cut steel. Coatesville serves the aircraft and aerospace, construction, distribution, energy, heavy equipment, military, mold and tool and shipbuilding markets.
Our Columbus operations include a hot-dip galvanizing facility in Columbus, Ohio, and a processing facility in nearby Obetz, Ohio. These operations were temporarily idled due to the COVID-19 pandemic and restarted during the second quarter of 2021. These central Ohio locations are able to utilize highway and rail transport shipping access. Two zinc pots enable the transition between coatings to be accomplished in a timely manner while allowing for longer exposed runs. The plant produces hot-dip galvanized sheet using cold-rolled coils supplied by other Cliffs facilities and is capable of coating 450,000 net tons annually. The Columbus operations serve the automotive and distribution markets.
Conshohocken is a plate finishing facility located on the Schuylkill River adjacent to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The area is surrounded by highway and railroad systems that provide shipping access. Coatesville and Burns Harbor supply steel plates to the Conshohocken plant, which operates heat treat, finishing and inspection
facilities for steel plate finishing. The Conshohocken plant has a steckel mill that is currently idled, which is capable of producing coil and discrete plates. Conshohocken plate products are used in construction and military applications.
Coshocton Works is located in Coshocton, Ohio, and consists of a stainless steel finishing plant containing two Sendzimer mills and two Z-high mills for cold reduction, four annealing and pickling lines, bell annealing furnaces, two bright annealing lines, two temper mills, and other processing equipment, including temper rolling, slitting and a packaging line. Coshocton Works produces various flat-rolled stainless steel products including austenitic (chrome nickel) stainless steel grades, martensitic (chrome) stainless steel grades and ferritic (chrome) stainless steel grades, serving the automotive, appliance, distribution and medical markets among others.
Dearborn Works is an integrated steelmaking facility located in Dearborn, Michigan. The facility is strategically located in close proximity to the automotive center of Michigan with access to highway, railroad and waterway transport. Dearborn's major production facilities include iron making, steel producing, a pickling line tandem cold mill and a hot-dipped galvanizing line. Dearborn Works is capable of producing 3 million net tons of raw steel annually. Products made at this location include carbon slabs, cold-rolled, and hot-dip galvanized and galvannealed sheet. Dearborn Works serves the automotive, HVAC, converters and distribution markets. During 2020, the Dearborn Works hot strip mill, anneal and temper operations were permanently idled as part of our cost reduction efforts.
Indiana Harbor is one of the largest integrated steelmaking facilities in North America and is located in East Chicago, Indiana, just 20 miles southeast of Chicago, Illinois. The major production facilities include iron making, a recycle plant, steel producing, hot rolling, cold rolling, annealing, and hot dip galvanizing lines. Indiana Harbor is currently capable of producing 5.5 million net tons of raw steel annually. Indiana Harbor is a leader in North American development of new automotive products and is a primary supplier of coils to Kote and Tek. Indiana Harbor serves the automotive, appliance, contractor applications, distribution, steel producers, strip converters and tubular markets.
The Kote and Tek operations are located in New Carlisle, Indiana, and receive substantially all of their feedstock from Indiana Harbor via daily unit trains. Kote has separate lines producing 0.5 million net tons of hot-dip galvanized and galvannealed and 0.5 million net tons of electrogalvanized sheet annually. Tek is a continuous cold-rolling plant that is capable of producing 1.7 million net tons of sheet steel annually through a continuous descale cold mill and 1.0 million net tons of sheet steel annually through a continuous annealing processing line. The principal customers of Kote and Tek are in the automotive and appliance markets.
Mansfield Works is located in Mansfield, Ohio, and produces high chrome ferritics and martensitic stainless steels and semi-finished hot bands. The major production facilities include a melt shop with two EAFs, an argon oxygen decarburization unit, a ladle metallurgy facility, a thin slab continuous caster, a walking beam slab furnace and a hot rolling mill. The thin slab caster uses an advanced technology production system to meet customer specifications. Mansfield Works is capable of producing 0.6 million net tons of raw steel annually. Mansfield Works serves the automotive and appliance for stainless products markets.
Middletown Works is an integrated steel operation located in Middletown, Ohio, just 30 miles north of Cincinnati, Ohio with access to railroad and highway transport. The major production facilities include a coke facility, iron making and steel producing, which is capable of producing nearly 3 million net tons of raw steel annually. Middletown Works facilities also include hot rolling, pickling, cold rolling, electrogalvanizing, hot dip carbon and stainless aluminizing, hot dip galvanizing, annealing, and finishing facilities. We temporarily idled the coke facility during the third quarter of 2021, as a result of our HBI use in our blast furnaces. Products made at this location include hot-rolled and cold-rolled carbon steels, electrogalvanized steels, hot-dip galvanized products and aluminized carbon and stainless steel sheets. Middletown Works serves the automotive, appliance, HVAC, culvert and distribution markets.
Piedmont is a finishing facility located in Newton, North Carolina, 50 miles northwest of Charlotte. The facility specializes in plasma cutting plate steel products into blanks for machinery and automotive manufacturers and primarily serves the truck axle blank business. Additionally, it provides services such as part leveling and just-in-time deliveries.
Riverdale is a compact strip mill that produces hot-rolled sheet located in Illinois, 14 miles west of our Indiana Harbor facility. The location allows for close shipping access to Lake Michigan and is surrounded by highway and railroad systems. The Riverdale facility operates two BOFs, a ladle metallurgy facility, continuous thin slab caster, tunnel furnace and hot strip mill, which are capable of producing 1 million net tons of thin-slab casting and rolling annually. The light gauge capabilities and tight gauge tolerances are desired characteristics for line pipe and structural and mechanical tubing producers. Principal products made at this plant include hot-rolled black bands in a
full range of grades, including high carbon and alloy. The Riverdale facility primarily serves cold-rolled strip producers who supply the automotive, saw blade and strapping markets.
Rockport Works is located near the Ohio River in southwest Indiana near Rockport, Indiana. Rockport Works consists of a carbon and stainless steel finishing plant containing a continuous cold rolling mill, a continuous hot-dip galvanizing and galvannealing line, a continuous carbon and stainless steel pickling line, a continuous stainless steel annealing and pickling line, hydrogen annealing facilities and a temper mill. Utilizing innovative manufacturing technologies, the plant incorporates automated guidance vehicles and automated cranes to move the steel through the various finishing operations. Steel produced at Rockport Works includes a full range of cold-rolled carbon, coated and stainless steels in either the annealed and pickled or temper rolled surface condition. Product offerings include a wide variety of AHSS. The Rockport Works hot-dip galvanizing and galvannealing line incorporates revolutionary proprietary technologies, including induction transition heating, which provides rapid, accurate annealing temperature control. In addition, the Rockport Works line produces 80-inch sheet steel. Rockport Works serves the automotive, appliance, HVAC and distribution for carbon and stainless markets.
Steelton is one of only three rail producers in North and South America and is located in Steelton, Pennsylvania, about 100 miles west of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Steelton consists of a 150 net ton direct current EAF with ladle refining and vacuum degassing, a three-strand continuous jumbo bloom caster and an ingot teeming facility. Steelton has an annual steelmaking capacity of 1 million net tons. Steelton produces railroad rails, specialty blooms, cast ingots and flat bars for use in railroad and forging markets.
Our Weirton facility is a tinplate facility located on the northern panhandle of West Virginia along the Ohio River in the city of Weirton, West Virginia. The location provides shipping access along the Ohio River, as well as highway and railroad shipping. Products made at this location include cold-rolled and tinplate products serving the distribution and packaging markets.
Zanesville Works is located on the Muskingum River in Zanesville, Ohio. The finishing facility's products include regular GOES and cold-rolled NOES. These specialty flat-rolled steels enable customers to create a variety of products, including generators, transformers and a host of other electrical devices. Zanesville Works primarily serves the power and distribution transformers markets.
In the aggregate, we have annual production capacity of approximately 23 million net tons of raw steel. Our steelmaking facilities produced a total of 18 million net tons of raw steel during the year ended December 31, 2021. Due to the timing of the 2020 Acquisitions and the idling of facilities in response to impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, our steelmaking facilities produced a total of 4 million net tons of raw steel during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Scrap Processing Facilities
Our scrap business consists of our subsidiary FPT, which has 22 locations in Michigan, Ohio, Tennessee, Florida and Ontario. These facilities are primarily located in Michigan and Ohio, which are in close proximity to our scrap consuming steel facilities. FPT processes approximately 3 million net tons of scrap metal annually, of which approximately 50% of total output is prime grade.
Direct Reduction Plant
Our direct reduction plant is located in Toledo, Ohio, and is near an existing dock, has rail access and heavy haul roads for operation logistics. We are leasing the property on which the plant is located. Our Toledo direct reduction plant, which began production in the fourth quarter of 2020, produces a specialized high quality iron alternative to scrap and pig iron. The Toledo direct reduction plant has annual capacity of 1.9 million metric tons of HBI per year, and we reached full nameplate capacity in 2021.
Iron Ore Mines and Pellet Plants
The following information concerning our mining properties has been prepared in accordance with the requirements of subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K, which first became applicable to us for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021. These requirements differ significantly from the previously applicable disclosure requirements of SEC Industry Guide 7. Among other differences, subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K requires us to disclose our mineral resources, in addition to our mineral reserves, as of the end of our most recently completed fiscal year both in the aggregate and for each of our individually material mining properties.
As used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the terms “mineral resource,” “measured mineral resource,” “indicated mineral resource,” “inferred mineral resource,” “mineral reserve,” “proven mineral reserve” and “probable mineral reserve” are defined and used in accordance with subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K. Under subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K, mineral resources may not be classified as “mineral reserves” unless the determination has been made by a QP that the mineral resources can be the basis of an economically viable project. You are specifically cautioned not to assume that any part or all of the mineral deposits (including any mineral resources) in these categories will ever be converted into mineral reserves, as defined by the SEC.
You are cautioned that, except for that portion of mineral resources classified as mineral reserves, mineral resources do not have demonstrated economic value. Estimates of inferred mineral resources have too high of a degree of uncertainty as to their existence and may not be converted to a mineral reserve. Therefore, you are cautioned not to assume that all or any part of an inferred mineral resource exists, that it can be the basis of an economically viable project, or that it will ever be upgraded to a higher category. Likewise, you are cautioned not to assume that all or any part of measured or indicated mineral resources will ever be converted to mineral reserves.
See Part I – Item 1A, Risk Factors – V. Sustainability and Development Risks - We rely on estimates of our recoverable mineral reserves, which estimation is complex due to geological characteristics of the properties and the number of assumptions made.
The information that follows relating to the Hibbing, Minorca, Northshore, Tilden and United Taconite iron ore mines is derived, for the most part, from, and in some instances is an extract from, the Technical Report Summaries relating to such properties prepared in compliance with Item 601(b)(96) and subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K. Portions of the following information are based on assumptions, qualifications and procedures that are not fully described herein. Reference should be made to the full text of the Technical Report Summaries, which are filed as Exhibits 96.1 through 96.5 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and are incorporated by reference herein.
All of our iron ore mining operations are open-pit mines. Additional development is underway as required by long-range mine plans. Drilling programs are conducted periodically to collect geologic modeling data and for refining ongoing operations.
Geologic models are developed for all mines to define the major ore and waste rock types. Computerized block models for iron ore are constructed that include all relevant geologic and metallurgical data. These are used to generate grade and tonnage estimates, followed by detailed mine design and LoM operating schedules.
We currently own or co-own and operate five production-stage iron ore mines in Michigan and Minnesota, as well as one indefinitely idled mine in Michigan. Following the AM USA Transaction, we now have an aggregate annual production capacity of approximately 28 million long tons of iron ore pellets, including our 85.3% share of the Hibbing mine production. Historically, our share of production capacity was approximately 21 million long tons of iron ore pellets annually. Our iron ore mines produce from deposits located within the Biwabik and Negaunee Iron Formation, which are classified as Lake Superior type iron formations that formed under similar sedimentary conditions in shallow marine basins approximately two billion years ago. Magnetite and hematite are the predominant iron oxide ore minerals present, with lesser amounts of goethite and limonite. Quartz is the predominant waste mineral present, with lesser amounts of other chiefly iron bearing silicate and carbonate minerals. The ore minerals liberate from the waste minerals upon fine grinding.
The following represents iron ore production for the last three fiscal years:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Iron Ore Production |
| (In Millions of Long Tons) |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
Hibbing1 | 7 | | | 2 | | | 2 | |
Minorca1 | 3 | | | — | | | — | |
Northshore2 | 5 | | | 4 | | | 5 | |
| Tilden | 7 | | | 6 | | | 8 | |
| United Taconite | 5 | | | 5 | | | 5 | |
| Total | 27 | | | 17 | | | 20 | |
1Tonnage shown is reflective of ownership percentage during respective periods. |
2As announced in February 2022, it is anticipated that the Northshore mine will be temporarily idled for approximately four months during 2022. |
The following provides an overview of our iron ore properties:
All the infrastructure necessary to mine and process significant commercial quantities of iron ore is currently in place at all of our mine locations. Infrastructure items include high voltage electrical supplies, natural gas pipelines that connect to the North American distribution system, water sources, paved roads and highways, railroads for transporting crude ore and finished products, port facilities that connect to the Great Lakes, and accommodations for employees. Local and state infrastructure also includes hospitals, schools, airports, equipment suppliers, fuel suppliers, commercial laboratories, and communication systems. Labor is readily available with major population centers within 25 miles of all of our properties.
All of our iron ore mining operations grant leases, licenses, and easements for various purposes, including miscellaneous community land uses, utility infrastructure, and other third-party uses, that encumber our properties but do not materially inhibit operations. Certain assets also serve as collateral securing obligations under our ABL Facility and our senior secured notes. We maintain the requisite state and federal permits and are in material compliance with all material permits.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property (Cliffs Ownership) | Location | Surface Rights & Mineral Leases | Facilities & Condition | History | Book Value of Long- Lived Assets (In Millions) |
Hibbing
(85.3%) | The property is located immediately north of the city of Hibbing, MN in the center of Minnesota’s Mesabi Iron Range. The mining and processing operation is located between latitude 47°25’48” N and 47°31’48” N and longitude 93°04’54” W and 92°54’36” W. | Hibbing holds 30,670 acres of surface rights, of which 1,150 acres are associated with mineral leases.The majority of the mineral rights are leased. The property is comprised of 6,640 acres of mineral leases expiring between 2022 and 2056. Leases are maintained by making minimum prepaid royalty payments. Mining leases routinely are renegotiated and renewed as they approach their respective expiration dates. | Open pit truck and shovel mine, a concentrator that utilizes single stage crushing, AG mills and magnetic separation to produce a magnetite concentrate, which is then delivered to an on-site pellet plant. From the site, pellets are transported by BNSF rail to a ship loading port at Superior, Wisconsin, operated by BNSF. | Mining began in 1976 as a joint venture between Bethlehem Steel Corporation and Steel Company of Canada. Cliffs first became involved in the joint venture when it purchased Pickands Mather's 15% share in 1986. Prior to the AM USA Transaction, we owned 23% of Hibbing, ArcelorMittal USA had a 62.3% interest and U.S. Steel had a 14.7% interest. On December 9, 2020, as a result of the AM USA Transaction, we acquired an additional 62.3% ownership stake in the Hibbing mine and became the majority owner and mine manager. | $199 |
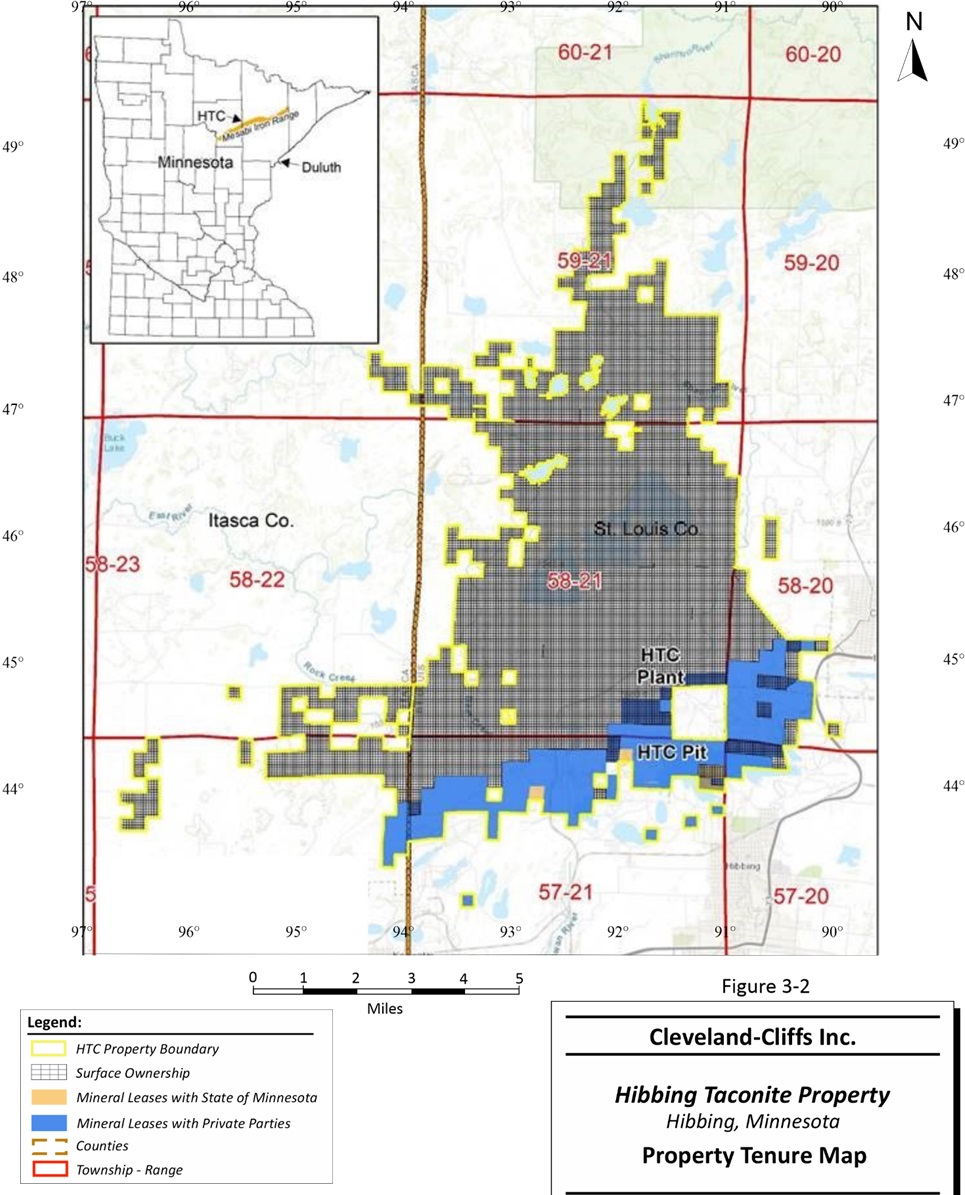
For more information, see Exhibit 96.1, the Technical Report Summary on the Hibbing Taconite Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by the QP, SLR with an effective date of December 31, 2021.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property (Cliffs Ownership) | Location | Surface Rights & Mineral Leases | Facilities & Condition | History | Book Value of Long- Lived Assets (In Millions) |
Minorca
(100.0%) | The property is located in the center of Minnesota’s Mesabi Iron Range. The Laurentian Pit is located near the City of Gilbert, MN at latitude 47°30'0"N and longitude 92°26’30"W, East 1 Pit is located at latitude 47°31'30"N and longitude 92°23’30"W, and East 2 Pit is located just west of the City of Biwabik at latitude 47°32'0"N and longitude 92°22’30"W. The Minorca plant is located approximately seven miles to the northeast, near the town of Virginia, MN at latitude 47°33'30"N and longitude 92°31.5'30"W. | Minorca holds 13,690 acres of surface rights, of which 282 acres are associated with mineral leases.100% of the mineral rights are leased. The property is comprised of 3,135 acres of mineral leases expiring between 2035 and 2056. Leases are maintained by making minimum prepaid royalty payments. Mining leases routinely are renegotiated and renewed as they approach their respective expiration dates. | This operation includes a concentrating and pelletizing facility, along with two open pit iron ore mines located approximately seven miles from the processing facilities. The processing operations consist of a crushing facility, a three-line concentration facility and a single-line straight grate pelletizing plant. Pellets are transported by CN rail to ports on Lake Superior. | Commenced operations in 1976 as an asset of Inland Steel Company. In 1998, Ispat International purchased Inland Steel and, in 2004, merged with LNM Holdings and International Steel Group to form Mittal Steel, which in 2007 merged with Arcelor to form ArcelorMittal. Minorca has been wholly owned by Cliffs since 2020 with the AM USA Transaction. | $231 |
| | | | | |
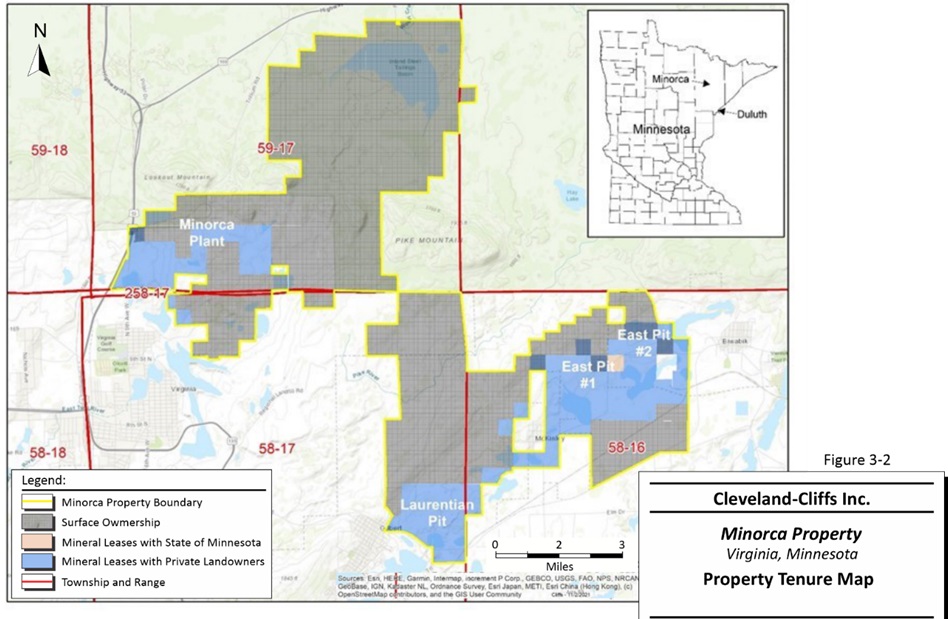
For more information, see Exhibit 96.2, Technical Report Summary on the Minorca Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by the QP, SLR with an effective date of December 31, 2021.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property (Cliffs Ownership) | Location | Surface Rights & Mineral Leases | Facilities & Condition | History | Book Value of Long- Lived Assets (In Millions) |
Northshore
(100.0%) | The mine is located on the northeastern edge of the Mesabi Iron Range in northeastern Minnesota, approximately four miles southeast of Babbitt, MN at latitude 47°40'12.15"N and longitude 91°53'1.28"W. The processing facility is approximately forty one miles to the southeast and immediately adjacent to the city of Silver Bay in Lake County, MN at latitude 47°17'38.95"N and longitude 91°15'23.38"W. | Northshore holds 28,041 acres of surface rights, of which 8,966 acres are associated with mineral leases. 100% of the mineral rights are leased. The property is comprised of 10,356 acres of mineral leases. Some leases do not expire until the mineral reserves are exhausted while others expire between 2034 and 2075. Leases are maintained by making minimum prepaid royalty payments. Mining leases routinely are renegotiated and renewed as they approach their respective expiration dates. | Open pit truck and shovel mine where two stages of crushing occur before the ore is transported along a wholly owned 47-mile rail line to the plant site in Silver Bay. At the plant site, two additional stages of crushing occur before the ore is sent to the concentrator. The concentrator utilizes rod mills and magnetic separation to produce a magnetite concentrate, which is delivered to the pellet plant located on-site. The plant can produce both standard and DR-grade pellets. The plant site has its own ship loading port located on Lake Superior. | Operations commenced in 1952 as an asset of the Reserve Mining Company and continued production until 1986 when Reserve Mining declared bankruptcy. Cyprus Minerals Company purchased the facilities in 1989. Cyprus subsequently sold the facilities to Cliffs in 1994. | $246 |
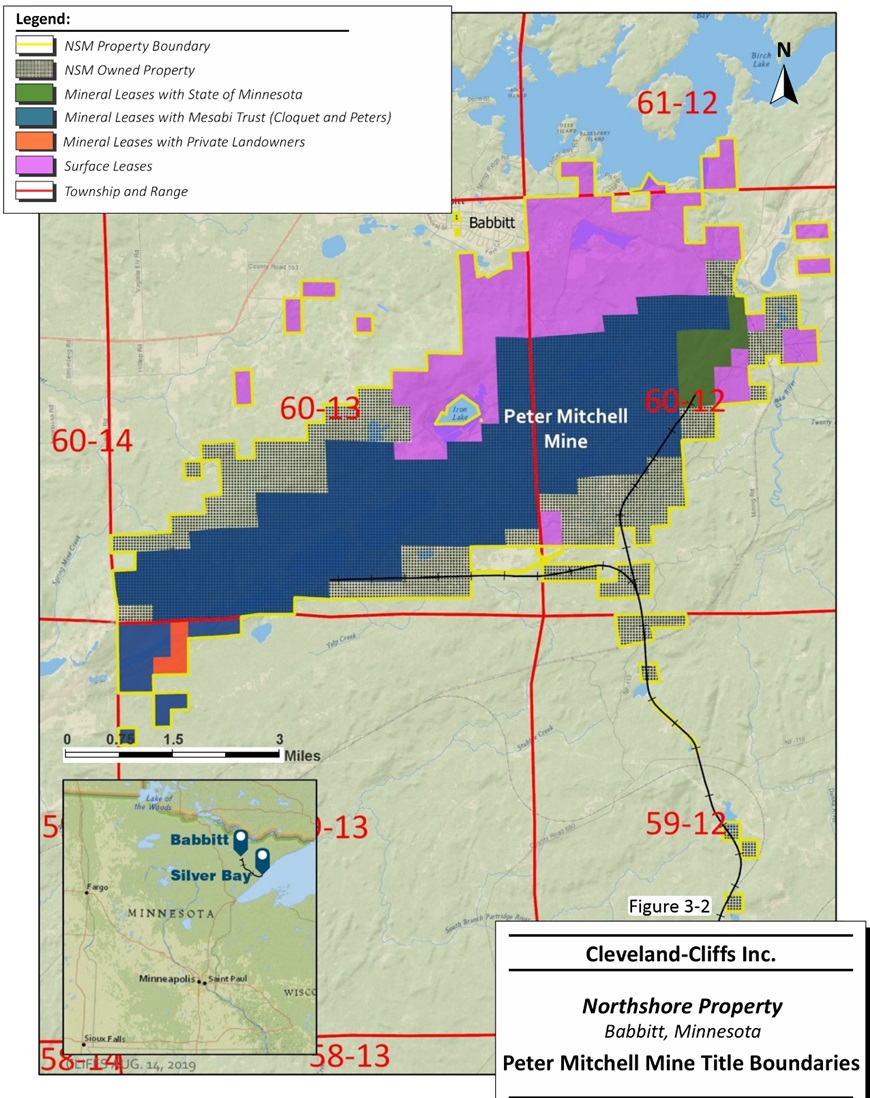
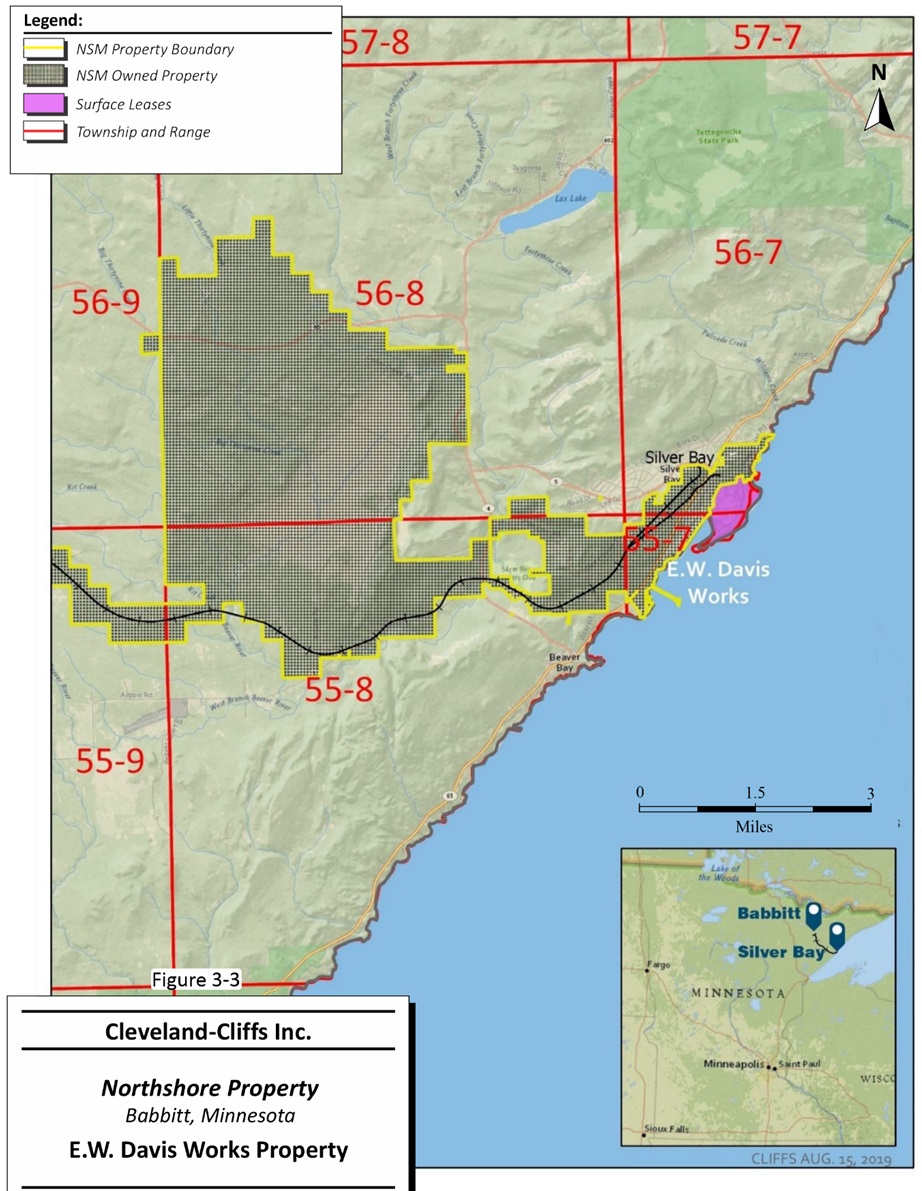
For more information, see Exhibit 96.3, Technical Report Summary on the Northshore Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by the QP, SLR with an effective date of December 31, 2021.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property (Cliffs Ownership) | Location | Surface Rights & Mineral Leases | Facilities & Condition | History | Book Value of Long- Lived Assets (In Millions) |
Tilden
(100.0%) | The property is located in Marquette County in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, on the Marquette Iron Range, approximately five miles south of the city of Ishpeming, MI at latitude 46° 29' N and longitude 87° 40' W. | Tilden holds 21,100 acres of surface rights and leases 2,470 acres of mineral rights expiring between 2061 and 2070. Leases are maintained by making minimum prepaid royalty payments. Mining leases routinely are renegotiated and renewed as they approach their respective expiration dates. | Open pit truck and shovel mine, a concentrator that utilizes single stage crushing, AG mills, and floatation to produce hematite concentrates that are then supplied to the on-site pellet plant. From the site, pellets are transported by our LS&I rail to a ship loading port at Marquette, Michigan, operated by LS&I. | The property commenced operations in 1974 under a partnership of Algoma Steel, Stelco, J&L Steel, Wheeling-Pittsburgh Steel, Sharon Steel, and Cleveland-Cliffs Iron Company. The property has since been at least partially in the possession of a subsidiary of Cliffs. In 2001, Cliffs acquired Algoma Steel's 45% interest in Tilden. In 2017, Cliffs became the sole owner of Tilden. | $219 |
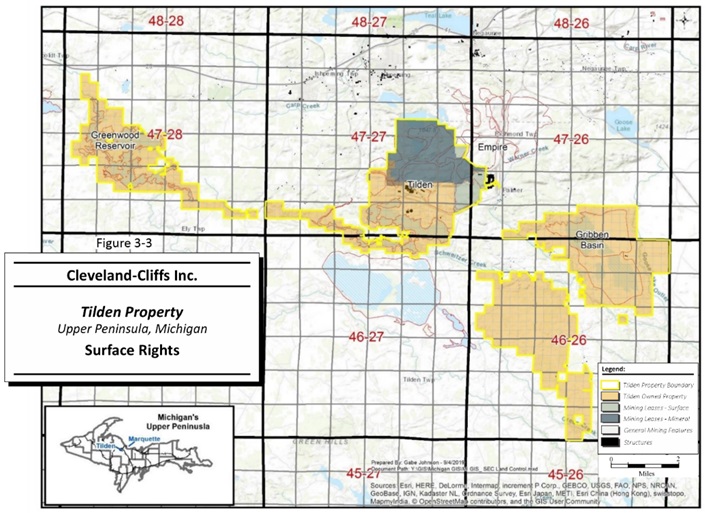
For more information, see Exhibit 96.5, Technical Report Summary on the Tilden Property, Michigan, USA, prepared for the Company by the QP, SLR with an effective date of December 31, 2021.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property (Cliffs Ownership) | Location | Surface Rights & Mineral Leases | Facilities & Condition | History | Book Value of Long- Lived Assets (In Millions) |
United Taconite
(100%) | The mine and offices are located on Minnesota's Mesabi Iron Range just north of Eveleth, MN at latitude 47°29'1.62" N, longitude 92°32'23.69" W. The processing facilities are located approximately eight miles to the southeast. | United Taconite owns 14,199 acres of surface rights, of which 703 acres are associated with mineral leases. An additional 145 acres of surface rights are leased from the State of Minnesota., We lease 100% of the mineral rights comprising of 4,908 acres expiring between 2037 and 2066, with the exception of the State of Minnesota mineral lease, which expires in 2027. Leases are maintained by making minimum prepaid royalty payments. Mining leases routinely are renegotiated and renewed as they approach their respective expiration dates. | Open pit truck and shovel mine where two stages of crushing occur before the ore is transported by rail, operated by CN, to the plant site. At the plant site an additional stage of crushing occurs before the ore is sent to the concentrator. The concentrator utilizes rod mills and magnetic separation to produce a magnetite concentrate, which is delivered to the on-site pellet plant. From the plant site, pellets are transported by CN rail to a ship loading port at Duluth, MN, operated by CN. | The property commenced operations as an asset of Eveleth Taconite Company in 1965 before it was purchased by United Taconite (70% Cliffs and 30% Laiwu Steel) in December 2003. The Property has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Cliffs since 2008. | $567 |
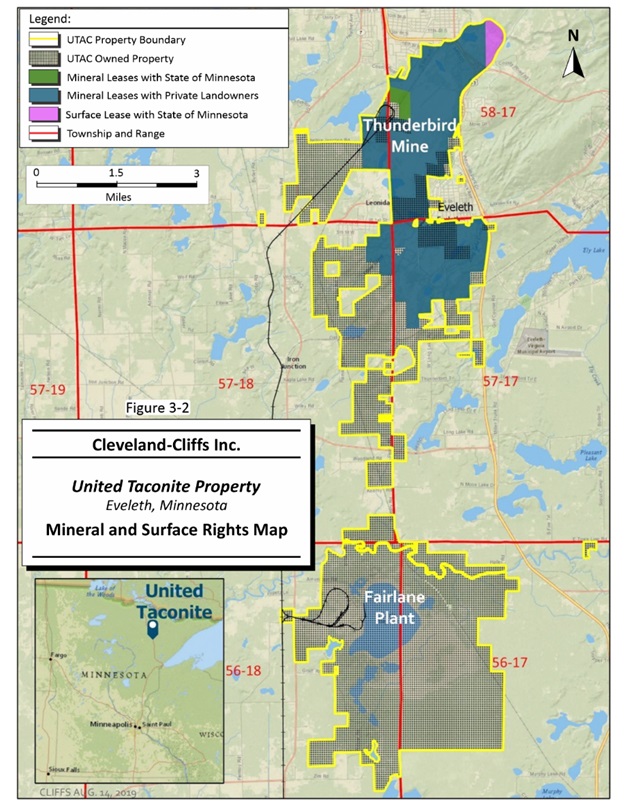
For more information, see Exhibit 96.4, Technical Report Summary on the United Taconite Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by the QP, SLR with an effective date of December 31, 2021.
Mineral Resources
Mineral resources are defined under Item 1300 of Regulation S-K as a concentration or occurrence of material of economic interest in or on the Earth’s crust in such form, grade or quality, and quantity that there are reasonable prospects for economic extraction. A mineral resource is a reasonable estimate of mineralization, taking into account relevant factors such as cut-off grade, likely mining dimensions, location or continuity, that, with the assumed justifiable technical and economic conditions, is likely to, in whole or part, become economically extractable.
A detailed breakdown of the mineral resources exclusive of mineral reserves is presented in the table below. Mineral resources were defined and constrained within open-pit shells, prepared by Cliffs, and based on a US$90.00/WLT pellet price, while meeting defined cut-off grade criteria and existing pellet specifications. All mineral resource estimates were reviewed and validated by the QP, SLR.
The following represents iron ore mineral resources, exclusive of mineral reserves, as of December 31, 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Iron Ore Mineral Resources |
| as of December 31, 2021 |
| (In Millions of Long Tons) |
| Measured | Indicated | Measured + Indicated | Process | Inferred |
| Tonnage | % Grade | Tonnage | % Grade | Tonnage | % Grade | Recovery | Tonnage | % Grade |
| Total Iron Ore | 1,351 | | 22.5 | | 1,483 | | 23.6 | | 2,834 | | 23.1 | | 31% | 420 | | 32.4 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Michigan | — | | — | | 135 | | 35.5 | | 135 | | 35.5 | | 36% | 350 | | 34.7 | |
| Minnesota | 1,351 | | 22.5 | | 1,348 | | 22.4 | | 2,699 | | 22.4 | | 31% | 70 | | 21.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Hibbing1 | 8 | | 19.2 | | 1 | | 18.7 | | 9 | | 19.2 | | 25% | — | | — | |
| Minorca | 484 | | 22.9 | | 317 | | 22.9 | | 801 | | 22.9 | | 33% | 30 | | 21.1 | |
| Northshore | 767 | | 22.1 | | 391 | | 22.4 | | 1,158 | | 22.2 | | 26% | 14 | | 19.8 | |
| Tilden | — | | — | | 135 | | 35.5 | | 135 | | 35.5 | | 36% | 350 | | 34.7 | |
| United Taconite | 92 | | 23.6 | | 639 | | 22.2 | | 731 | | 22.4 | | 32% | 26 | | 21.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
1Hibbing is reported at 85.3% based on our ownership level. | |
Reference point selected is the saleable tons based on the process recovery. |
Process recovery may change based on the required saleable product mix and is reported as wet product percentage. |
Mineral resources are estimated using the following cut-off grades: 25% FeT for Tilden hematite; 15% magnetic Fe for Northshore; 16% magnetic Fe for Minorca; 17% magnetic Fe for United Taconite; and 13% magnetic Fe for Hibbing. |
| Tonnage is reported in long tons equivalent to 2,240 pounds and has been rounded to the nearest 100,000. |
| Mineral resources are reported at a $90.00/LT wet standard pellet price freight-on-board (FOB) Lake Superior, which is based on the mine planning model's three-year trailing average of the realized product revenue rate. |
Our mineral resource estimates have not been previously disclosed. The material assumptions and criteria used for the mineral resource estimates, including but not limited to leases, permits and geotechnical pit design, are covered in more detail in Sections 11 through 13 of the respective Technical Report Summaries filed as Exhibits 96.1 through 96.5 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Mineral Reserves
Mineral reserves are defined under Item 1300 of Regulation S-K as an estimate of tonnage and grade or quality of indicated and measured mineral resources that, in the opinion of the QP, can be the basis of an economically viable project. More specifically, it is the economically mineable part of a measured or indicated mineral resource, which includes diluting materials and allowances for losses that may occur when the material is mined or extracted.
Proven mineral reserves are defined under Item 1300 of Regulation S-K as the economically mineable part of a measured mineral resource and can only result from conversion of a measured mineral resource. Probable mineral reserves are defined under Item 1300 of Regulation S-K as the economically mineable part of an indicated and, in some cases, a measured mineral resource. All mineral reserves are classified as proven or probable and are supported by LoM plans.
Mineral reserves are based on pricing that does not exceed the three-year trailing average index price of iron pellets adjusted to realized price. We evaluate and analyze, and engage QPs to review and verify mineral reserves in accordance with our mineral policy and SEC requirements and then complete updated LoM plans. The table below identifies the year in which the latest updated LoM plan was completed.
Mineral reserves estimates for our iron mines are constrained by fully designed open pits developed using three-dimensional modeling techniques. These open pits incorporate design slopes, practical mining shapes and access ramps to assure the accuracy of our mineral reserve estimates. All operations' mineral reserves have been adjusted net of production through year-end 2021. All mineral reserve estimates as of December 31, 2021 were reviewed and validated by the QP, SLR.
The following represents iron ore mineral reserves as of December 31, 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Iron Ore Mineral Reserves |
| as of December 31, 2021 |
| (In Millions of Long Tons) |
| Last LoM Plan | Proven | Probable | Proven & Probable | Process |
| Reserve Analysis | Tonnage | % Grade | Tonnage | % Grade | Tonnage | % Grade | Recovery |
| Total Iron Ore | | 638 | | 23.6 | | 1,682 | | 26.6 | | 2,320 | | 25.8 | | 33% |
| | | | | | | | |
| Michigan | | 4 | | 35.3 | | 516 | | 34.7 | | 520 | | 34.7 | | 37% |
| Minnesota | | 634 | | 23.5 | | 1,166 | | 23.0 | | 1,800 | | 23.2 | | 31% |
| | | | | | | | |
Hibbing1 | 2021 | 85 | | 18.7 | | 8 | | 18.7 | | 93 | | 18.7 | | 25% |
| Minorca | 2021 | 103 | | 23.6 | | 7 | | 25.3 | | 110 | | 23.7 | | 34% |
| Northshore | 2020 | 303 | | 25.3 | | 519 | | 24.1 | | 822 | | 24.6 | | 29% |
| Tilden | 2021 | 4 | | 35.3 | | 516 | | 34.7 | | 520 | | 34.7 | | 37% |
| United Taconite | 2019 | 143 | | 23.1 | | 632 | | 22.1 | | 775 | | 22.3 | | 33% |
| | | | | | | | |
1Hibbing is reported at 85.3% based on our ownership level. |
Reference point selected by the QP is the saleable tons based on the process recovery. |
Process recovery may change based on the required saleable product mix and is reported as wet product percentage. |
Mineral reserves are estimated using the following cut-off grades: 25% FeT for Tilden hematite; 19% magnetic Fe for Northshore; 16% magnetic Fe for Minorca; 17% magnetic Fe for United Taconite; and 13% magnetic Fe for Hibbing. |
| Tonnage is reported in long tons equivalent to 2,240 pounds and has been rounded to the nearest 100,000. |
| Mineral reserves are classified as probable if not scheduled within the first 20 years. |
| Mineral reserves are reported at a $90.00/LT wet standard pellet price freight-on-board (FOB) Lake Superior, which is based on the mine planning model's three-year trailing average of the realized product revenue rate. |
The material assumptions and criteria used for the mineral reserves estimates, including but not limited to leases, permits and geotechnical pit design, are covered in more detail in Sections 11 through 13 of the respective Technical Report Summaries filed as Exhibits 96.1 through 96.5 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
For comparison purposes, the following represents iron ore mineral reserves as of December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Iron Ore Mineral Reserves |
| as of December 31, 2020 |
| (In Millions of Long Tons) |
| Proven | Probable | Proven & Probable | Process |
| Tonnage | % Grade | Tonnage | % Grade | Tonnage | % Grade | Recovery |
| Total Iron Ore | 822 | | 26.2 | | 1,596 | | 26.0 | | 2,418 | | 26.0 | | 31% |
| | | | | | | |
| Michigan | 168 | | 35.2 | | 418 | | 34.8 | | 586 | | 34.8 | | 34% |
| Minnesota | 654 | | 23.9 | | 1,178 | | 23.0 | | 1,832 | | 23.3 | | 30% |
| | | | | | | |
Hibbing1 | 65 | | 19.7 | | 21 | | 19.6 | | 86 | | 19.7 | | 27% |
| Minorca | 113 | | 23.6 | | 7 | | 25.3 | | 120 | | 23.7 | | 31% |
| Northshore | 318 | | 25.3 | | 519 | | 24.1 | | 837 | | 24.6 | | 29% |
| Tilden | 168 | | 35.2 | | 418 | | 34.8 | | 586 | | 34.8 | | 34% |
| United Taconite | 158 | | 23.1 | | 631 | | 22.1 | | 789 | | 22.3 | | 31% |
| | | | | | | |
1Hibbing is reported at 85.3% based on our ownership level. |
Reference point selected was the saleable tons based on the process recovery. |
Process recovery may change based on the required saleable product mix and is reported as wet product percentage. |
Mineral reserves are estimated using the following cut-off grades: 25% FeT for Tilden hematite; 19% magnetic Fe for Northshore; 16% magnetic Fe for Minorca; 17% magnetic Fe for United Taconite; and 15% magnetic Fe for Hibbing. |
| Tonnage is reported in long tons equivalent to 2,240 pounds and has been rounded to the nearest 100,000. |
| Mineral Reserves are classified as probable if not scheduled within the first 20 years. |
| Mineral Reserves are reported at a $90.00/LT wet standard pellet price freight-on-board (FOB) Lake Superior, which is based on the mine planning model's three-year trailing average of the realized product revenue rate. |
Overall, as compared to the mineral reserve estimates as of December 31, 2020, mineral reserves estimates as of December 31, 2021 decreased by 4%, which was driven by mining depletion. The mineral reserves of Minorca, Northshore and United Taconite as of December 31, 2021 have decreased mainly due to depletion through mining, the mineral reserves for Tilden as of December 31, 2021 have decreased primarily due to the mine plan changes, and the mineral reserves for Hibbing as of December 31, 2021 have increased primarily due to the mine plan changes.
Internal Controls Disclosure
We demonstrated repeated attainment of annual production and quality targets for at least 40 years at each material iron ore mine operated by the Company. Internal controls the Company uses in its industry-standard approach to exploration and mineral resource and reserve estimation efforts are governed by its Mineral Reserve and Mineral Resource Estimation Policy and are detailed in Cliffs’ minimum operating standards for Resource Estimation and Strategic Mine Planning. The controls include: confirmation of drill collar locations and drill hole traces, drill logging and sample collection and security, database verification and security, QA/QC programs, internal and third-party QP statistical analysis, third-party QP model validation, and reconciliation. Modeling and analysis of the Company’s resources has been developed by Company personnel or third-party consultant SLR and reviewed by internal management and the external independent QP, SLR. Reserve estimations have been completed by Company personnel and reviewed by internal management and the QP, SLR.
Drill hole collar surveying methods have evolved with advancements in technology, moving from optical methods to global positioning system, which is currently in use. For the deposit type, all survey methods used for the collar locations are expected to provide adequate accuracy for the drill hole locations. Due to the relatively shallow depth and vertical nature of drill holes at Cliffs’ Minnesota mining operations, downhole deviation surveys are typically not conducted. Drill holes pierce the generally shallow-dipping, tabular iron formation at near perpendicular angles. At the more geologically and structurally complex Tilden mine in Michigan, where drilling deeper than 500 feet is required, downhole surveys have moved from a clay-impression procedure to the gyroscopic method currently in use.
Drill core is transported directly from the drill rig to each site’s core logging facility by either the drilling contractor or Cliffs’ personnel. Temporary core storage is located at each site’s secure logging facility. Depending on the mining operation, unused sample reserves, parts, concentrates, and splits are securely stored in labeled boxes or barrels at a Cliffs laboratory facility or logging facility, or via a contracted external laboratory.
Cliffs QA/QC programs are site-specific and range from in-development to well-developed, long standing protocols that involve formal procedures for the use of crude material standards developed from on-site material, as well as regularly inserted coarse and concentrate duplicate samples, control chart analysis, and reporting. Cliffs typically uses internal and external labs for geometallurgical analyses that are accredited with ASQ/ANSI ISO-9001:2015 for their system of quality management. Quality sample results are monitored and enacted on where warranted. Also, Cliffs has implemented a drill campaign reporting practice to ensure results are documented, with defined and illustrated failure metrics, outcomes of investigations, comparisons with previous year’s results, and recommendations. The QP, SLR reviewed Cliffs QA/QC practices and provided recommendations for further work. Where QA/QC programs are still in development and prior to resource estimation, Cliffs conducted data verification studies utilizing a suite of blind crude ore standards, and blind duplicates from historical sample reserves within the LoM plan. Where unaccredited labs provided data used in resource estimation, check lab studies were initiated to verify analytical results. Cliffs is currently working towards aligning QA/QC protocols at each mine to the Company’s current best practice.
Cliffs maintains exploration drill hole data in an externally-managed, access-controlled acQuire database that is backed up online at regularly scheduled intervals to provide data redundancy and security. Certification of database integrity is accomplished by both visual and statistical inspections comparing geology, assay values, and survey locations cross-referenced back to laboratory data and geologic logs. Any discrepancies identified are corrected by referring to hard-copy assay and core log information archived in Cliffs' Mine Engineering department file cabinets. Prior to modeling, a secondary validation check is completed using built-in data validation routines in the modeling software.
Cliffs performs routine drill hole database verification with every new drilling program and new block model build, including: check of unique drill hole IDs and collar coordinates; check of assay or lithology points extending past the specified maximum depth of drill hole; check of abnormal dips and azimuths of downhole drill hole surveys; check of negative, overlapping, and missing intervals; and check of incorrect lithologic codes and assay values.
In 2020 and 2021, Cliffs geologists completed data verification exercises within the LoM plan area for each mining operation. This was audited by the QP, SLR to assess accuracy and completeness. Database values were checked against source documents including collar surveys, geologic logs, and assay certificates. Data verification included collar coordinates, depth intervals of geologic units and assay samples, and results of geometallurgical analyses applied to mineral resource estimation and mine planning.
Cliffs’ mineral resource estimates were validated by the QP, SLR using standard industry techniques including statistical comparisons with composite samples and parallel nearest neighbor estimates, swath plots, as well as visual reviews in cross-section and plan. A visual review comparing blocks to drill holes for key economic variables, completed after the block modeling work, was performed to ensure general lithologic and analytical conformance. Cliffs’ mining operations have demonstrated good agreement between planned and actual product produced over more than 40 years for each operation.
Cliffs classifies the mineral resources based primarily on drill hole spacing and influenced by geologic continuity, ranges of economic criteria, and reconciliation. Some post-processing is undertaken to ensure spatial consistency and remove isolated and fringe blocks. The resource area for each operation is limited by a polygon and subsequent pit shell based on practical mining limits. To ensure that all mineral resource statements satisfy the “reasonable prospects for economic extraction” requirement, in the definition of the mineral resources under Item 1300 of Regulation S-K, factors significant to technical feasibility and potential economic viability are considered (e.g., ability to obtain permits, and legal and land tenure considerations). Mineral resources are defined and constrained within optimized, open-pit shells, prepared by Cliffs and reviewed by the QP, SLR and based on a US$90.00/WLT pellet value and target pellet iron content.
Grade and tonnage reconciliations are run on current production versus modeled production, which provides insight on the accuracy of the modeled assay data versus actual production for each mining operation.
For a discussion of comprehensive risk inherent in the estimation of mineral reserves, see Part I - Item 1A, Risk Factors - V. Sustainability and Development Risks - We rely on estimates of our recoverable mineral reserves, which is complex due to the geological characteristics of the properties and the number of assumptions made.
Coal Mining and Cokemaking
Princeton is a coal mining complex located in West Virginia that specializes in surface and underground mining of metallurgical coal to produce coke and pulverized coal injection coal. We have annual rated metallurgical coal production capacity of 2.3 million net tons from our Princeton mine. In 2021, the mine produced 1.4 million net tons of coal. We own 100% of the Princeton mine, which has been operating since 1995. We own 52% of the mineral rights and lease 48% via multiple mineral leases having varying expiration dates. Mining leases routinely are renegotiated and renewed as they approach their respective expiration dates. Princeton's operations consist of two open-pit surface mines, two underground mines, a preparation plant and two rail loadouts.
In 2021, our cokemaking facilities produced 2.9 million net tons of coke. Mountain State Carbon produces furnace coke and related by-products from its plant in Follansbee, West Virginia, which consists of four batteries. Monessen produces furnace coke and related by-products in Monessen, Pennsylvania, which was temporarily idled due to the COVID-19 pandemic and restarted production during the third quarter of 2021. Warren produces furnace coke and related by-products from its plant in Warren, Ohio, and supplies its coke to the Cleveland facility. We also operate cokemaking facilities located within Burns Harbor and Middletown Works.
As a result of our internal usage of HBI, coupled with our ongoing evaluation of coke use strategies, we idled our coke facility at Middletown Works during the third quarter of 2021, and we intend to permanently idle our Mountain State Carbon coke plant in the second quarter of 2022.
Other Businesses
Our Tubular operating segment consists of our subsidiary Tubular Components, which has plants in Walbridge, Ohio and Columbus, Indiana. The Walbridge plant operates six electric resistance welded tube mills. The Columbus plant operates five electric resistance welded tube mills and four high-speed cold saws on leased property. Tubular Components shut down and ceased tube production at the Queretaro, Mexico plant in April 2021. The high-speed cold saw that was operating at the Queretaro plant was relocated to the Columbus plant and the tube mill returned to the U.S. is replacing an existing, older tube mill currently in operation.
Our Tooling and Stamping operating segment consists of our subsidiary Tooling and Stamping, which provides advanced-engineered solutions, tool design and build, hot- and cold-stamped steel components and complex assemblies for the automotive market across ten plants, of which certain of these are under long-term lease agreements, in Ontario, Alabama and Kentucky. Its facilities feature seven large-bed, hot-stamping presses, providing 13 lines of production; 81 cold-stamping presses ranging from 150 net tons to 3,000 net tons of pressing capacity; 17 large-bed, high-tonnage tryout presses with prove-out capabilities for new tool builds; and 149 multi-axis welding assembly cells. Construction of our new facility in Tennessee is substantially complete and the facility began producing prototype components in the third quarter of 2021. Commercial start of production at the Tennessee location is expected to begin in the second quarter of 2022.
Legal Proceedings Relating to our Business
JSW Steel Litigation. On June 8, 2021, JSW Steel filed a complaint against Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., AK Steel Holding Corporation (now known as Cleveland-Cliffs Steel Holding Corporation), Nucor Corporation and U.S. Steel in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas. JSW Steel alleges that the defendants engaged in a group boycott against JSW Steel in violation of federal and Texas antitrust laws by refusing to sell semi-finished steel slabs to JSW Steel, beginning in 2018 and continuing through the present; civil conspiracy among the defendants; and tortious interference with JSW Steel’s contractual rights and business relations involving its vendors and customers. JSW Steel’s allegations involve the tariffs and quotas imposed on steel imports by the U.S. government under Section 232 beginning in March 2018, which JSW Steel alleges raised the price of imported slabs, and statements made to the U.S. government related to exemption requests submitted by JSW Steel in 2018 and 2021. JSW Steel further claims that this alleged anticompetitive conduct negatively impacted JSW Steel’s costs, production and revenues and prevented it from pursuing expansion plans at its Ohio and Texas facilities that would compete with the defendants. JSW Steel is seeking to hold the defendants jointly and severally liable for treble damages in an amount in excess of $500 million and other relief. We filed a Motion to Dismiss in the case during 2021, and discovery remains stayed until the court decides our motion. We believe the claims asserted against us are without merit, and we are vigorously defending against them.
Mesabi Metallics Adversary Proceeding. On September 7, 2017, Mesabi Metallics Company LLC (f/k/a Essar Steel Minnesota LLC) ("Mesabi Metallics") filed a complaint against Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. in the Essar Steel Minnesota
LLC and ESML Holdings Inc. bankruptcy proceeding that is pending in the United States Bankruptcy Court, District of Delaware. Mesabi Metallics alleges tortious interference with its contractual rights and business relations involving certain vendors, suppliers and contractors, violations of federal and Minnesota antitrust laws through monopolization, attempted monopolization and restraint of trade, violation of the automatic stay, and civil conspiracy with unnamed Doe defendants. Mesabi Metallics amended its complaint to add additional defendants, including, among others, our subsidiary, Cleveland-Cliffs Minnesota Land Development Company LLC ("Cliffs Minnesota Land"), and to add additional claims, including avoidance and recovery of unauthorized post-petition transfers of real estate interests, claims disallowance, civil contempt and declaratory relief. Mesabi Metallics seeks, among other things, unspecified damages and injunctive relief. Cliffs and Cliffs Minnesota Land filed counterclaims against Mesabi Metallics, Chippewa Capital Partners ("Chippewa"), and Thomas M. Clarke ("Clarke") for tortious interference and civil conspiracy, as well as additional claims against Chippewa and Clarke for aiding and abetting tortious interference, for which we seek, among other things, damages and injunctive relief. Our counterclaim against Clarke for libel was dismissed on jurisdictional grounds. The parties filed various dispositive motions on certain of the claims, including a motion for partial summary judgment to settle a dispute over real estate transactions between Cliffs Minnesota Land and Glacier Park Iron Ore Properties LLC ("GPIOP"). A ruling in favor of Cliffs, Cliffs Minnesota Land and GPIOP was issued on July 23, 2018, finding that Mesabi Metallics' leases had terminated and upholding Cliffs' and Cliffs Minnesota Land's purchase and lease of the contested real estate interests. Mesabi Metallics filed a Motion for Leave to File an Interlocutory Appeal, which was denied on September 10, 2019. Discovery is ongoing. We believe the claims asserted against us are without merit, and we intend to continue to vigorously defend against any remaining claims in the lawsuit.
Certain Legacy Legal Proceedings Relating to our Steel Operations. Certain of our acquired subsidiaries have been named as defendants, among many other named defendants, in numerous lawsuits filed since 1990 claiming injury allegedly resulting from exposure to asbestos. Similar lawsuits seeking monetary relief continue to be filed in various jurisdictions in the U.S., which cases are vigorously defended. Although predictions about the outcome of pending litigation is subject to uncertainties, based upon present knowledge, we believe it is unlikely that the resolution in the aggregate of these claims will have a materially adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
Legal Proceedings Relating to Environmental Matters
SEC regulations require us to disclose certain information about administrative or judicial proceedings involving the environment and to which a governmental authority is a party if we reasonably believe that such proceedings may result in monetary sanctions above a stated threshold. Pursuant to SEC regulations, we use a threshold of $1 million for purposes of determining whether disclosure of any such proceedings is required. We believe that this threshold is reasonably designed to result in disclosure of any such proceedings that are material to our business or financial condition.
Information for this item relating to certain other environmental proceedings may be found under the heading Burns Harbor Water Issues in NOTE 20 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES to the consolidated financial statements in Part II – Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
| | | | | |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
We are committed to protecting the occupational health and well-being of each of our employees. Safety is one of our core values, and we strive to ensure that safe production is the first priority for all employees. Our internal objective is to achieve zero injuries and incidents across the Company by focusing on proactively identifying needed prevention activities, establishing standards and evaluating performance to mitigate any potential loss to people, equipment, production and the environment. We have implemented intensive employee training that is geared toward maintaining a high level of awareness and knowledge of safety and health issues in the work environment through the development and coordination of requisite information, skills and attitudes. We believe that through these policies, we have developed an effective safety management system.
Under the Dodd-Frank Act, each operator of a coal or other mine is required to include certain mine safety results within its periodic reports filed with the SEC. As required by the reporting requirements included in §1503(a) of the Dodd-Frank Act and Item 104 of Regulation S-K, the required mine safety results regarding certain mining safety and health matters for each of our mine locations that are covered under the scope of the Dodd-Frank Act are included in Exhibit 95 of Part IV – Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
PART II
| | | | | |
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Stock Exchange Information
Our common shares (ticker symbol CLF) are listed on the NYSE.
Holders
At February 10, 2022, we had 2,532 shareholders of record.
Shareholder Return Performance
The following graph shows changes over the past five-year period in the value of $100 invested in: (1) Cliffs' common shares; (2) S&P 500 Index; (3) S&P SmallCap 600 Index; (4) S&P MidCap 400 Index; and (5) S&P Metals and Mining Select Industry Index. Due to the increased market capitalization of the Company, we were included within the S&P MidCap 400 Index and removed from the S&P SmallCap 600 Index during the year ended December 31, 2021. The values of each investment are based on price change plus reinvestment of all dividends reported to shareholders, based on monthly granularity.
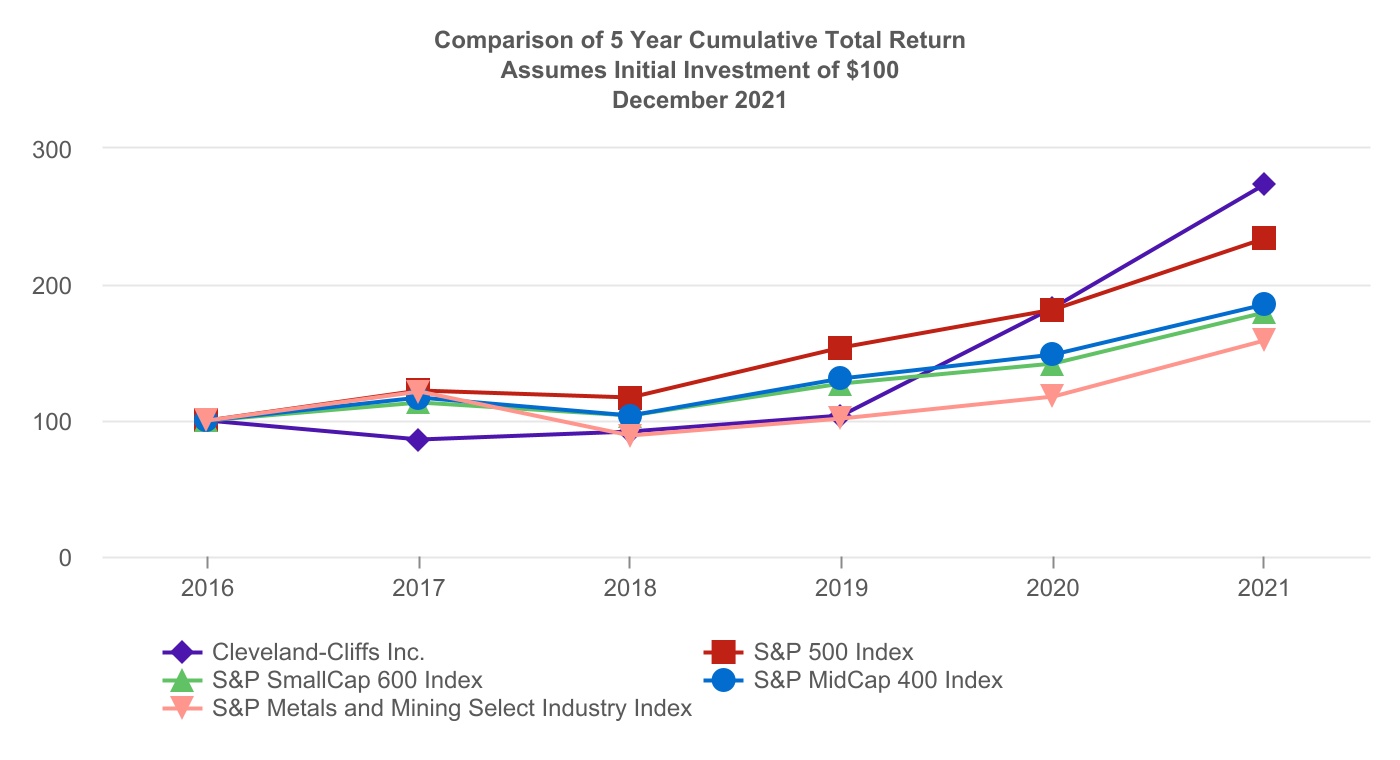
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2016 | | 2017 | | 2018 | | 2019 | | 2020 | | 2021 |
| Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. | Return % | | — | | | (14.27) | | 6.66 | | 12.60 | | 77.46 | | 49.52 |
| Cum $ | | 100.00 | | 85.73 | | 91.44 | | 102.96 | | 182.71 | | 273.19 |
| S&P 500 Index | Return % | | — | | | 21.80 | | (4.39) | | 31.48 | | 18.39 | | 28.68 |
| Cum $ | | 100.00 | | 121.80 | | 116.45 | | 153.11 | | 181.27 | | 233.25 |
| S&P SmallCap 600 Index | Return % | | — | | | 13.15 | | (8.52) | | 22.74 | | 11.24 | | 26.74 |
| Cum $ | | 100.00 | | 113.15 | | 103.51 | | 127.05 | | 141.33 | | 179.12 |
| S&P MidCap 400 Index | Return % | | — | | | 16.23 | | (11.10) | | 26.17 | | 13.65 | | 24.73 |
| Cum $ | | 100.00 | | | 116.23 | | 103.33 | | 130.37 | | 148.16 | | 184.80 |
| S&P Metals and Mining Select Industry Index | Return % | | — | | | 20.61 | | (26.76) | | 14.70 | | 15.97 | | 34.94 |
| Cum $ | | 100.00 | | 120.61 | | 88.33 | | 101.32 | | 117.50 | | 158.56 |
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table presents information with respect to repurchases by the Company of our common shares during the periods indicated:
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | | Total Number of Shares (or Units) Purchased1 | | Average Price Paid per Share
(or Unit) | | Total Number of Shares (or Units) Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | | Maximum Number (or Approximate Dollar Value) of Shares (or Units) that May Yet be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs2 |
| October 1 - 31, 2021 | | 534 | | | $ | 19.66 | | | — | | | $ | — | |
| November 1 - 30, 2021 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| December 1 - 31, 2021 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | 534 | | | $ | 19.66 | | | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
1 All shares were delivered to us to satisfy tax withholding obligations due upon the vesting or payment of stock awards. |
2 On February 10, 2022, our Board of Directors authorized a program to repurchase our outstanding common shares in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions, which may include purchases pursuant to Rule 10b5-1 plans or accelerated share repurchases, up to a maximum of $1 billion. We are not obligated to make any purchases, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at any time. The share repurchase program does not have a specific expiration date. |
| | | | | |
| Item 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations is designed to provide a reader of our financial statements with a narrative from the perspective of management on our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and other factors that may affect our future results. The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and related notes that appear in Part II – Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Overview
The year 2021 represented a period of record financial performance in our Company's 174-year history. The advantages of our unique, vertically integrated business model as well as the immediate benefits of the transformational acquisitions we completed in 2020 were on full display during the year as we achieved these phenomenal results. Our commercial actions, along with a healthy demand environment for steel, drove substantially higher selling prices for the majority of products we sell, and we adjusted production to meet the needs of our order book. Combined with this, we believe we were able to manage costs better than our peers due to our vertically integrated footprint, which reduces the impact of material price inflation on our major cost inputs. As a result, we produced record revenues, record net income, record Adjusted EBITDA and record operating cash flow in 2021.
The HRC index averaged $1,573 per net ton for 2021, a record year that was also 174% higher than 2020. The record prices for steel products in 2021 resulted from both supply and demand factors, each driven by a rapid recovery from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Stay-at-home mandates and fiscal stimulus drove strong demand for consumer goods, such as HVAC products and appliances. Demand from machinery and equipment producers has also been robust. The demand for light vehicles was also strong; however, automotive supply chain difficulties have limited the demand for steel from automotive manufacturers. On the supply side, spot steel availability was limited throughout the year.
We expect healthy demand to continue into 2022 as we start to see the impacts of the Infrastructure and Jobs Act of 2021, growing environmentally-focused capital projects, healthy economic conditions and pent-up automotive demand, as supply chain issues begin to show signs of waning. With strong demand and steel prices in the U.S. reaching all-time highs in 2021, we were well positioned to negotiate our fixed price contracts, which represent approximately 45% of our volumes, at favorable levels, which should enable us to deliver strong financial results and free cash flow in 2022, even if HRC pricing falls considerably.
As a result of our healthy free cash flow in 2021, we were able to complete several strategic and financial transactions, including the FPT Acquisition. FPT is one of the largest processors of prime scrap in the country, representing approximately 15% of the entire U.S. merchant market. We believe this acquisition is a complementary addition to our footprint, as prime scrap demand is expected to grow with new flat-rolled EAF capacity set to come online over the next five years and as the worldwide focus on decarbonization continues. We expect to be able to leverage our long-standing flat-rolled automotive and other customer relationships into recycling partnerships to further grow our prime scrap presence. Additionally, FPT allows us to optimize productivity at our existing EAFs and BOFs and furthers our commitment to environmentally-friendly, low-carbon intensity steelmaking with a cleaner materials mix.
Another use of our robust cash flow was the complete redemption of our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock for $1,343 million during the third quarter of 2021. This transaction reduced our diluted share count by approximately 10%, providing a meaningful return to our shareholders. During February 2021, we executed a series of favorable debt and equity capital market transactions in an effort to extend our average debt maturity profile and increase our ratio of unsecured debt to secured debt. We also completed additional financing transactions, including the redemption of all $396 million aggregate principal amount of our 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes in June 2021, and provided notice of our election to redeem all remaining $294 million aggregate principal amount of our 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes in December 2021, which was completed in January 2022.
In 2021, we reached full run-rate nameplate annual capacity at our state-of-the-art direct reduction plant in Toledo, Ohio. This facility produces high-quality HBI and is the first of its kind in the Great Lakes region. While we originally expected to be a merchant seller of HBI, following the 2020 Acquisitions, we have instead maximized the value of our HBI by utilizing it primarily in our blast furnaces, which allows us to improve costs and productivity while reducing our coke rates and reducing our carbon emissions. As a result of our internal usage of HBI, coupled with our ongoing evaluation of coke use strategies, we idled our coke facility at Middletown Works in 2021 and we intend to permanently idle our Mountain State Carbon coke plant in 2022.
Along with these notable accomplishments, we have been able to continue successfully navigating through the COVID-19 pandemic while preserving the health and safety of both our workforce and our Company for the long term. The health and safety of our employees has always been our top priority. In an effort to best protect our workforce and our Company, we launched a vaccine incentive program in July 2021 that was developed in partnership with our labor unions. Throughout the 45 days the program was in place, the vaccination rate more than doubled, and we achieved a total vaccination rate of over 75% throughout our workforce. The initiative resulted in a payout of $45 million in total cash incentives to our vaccinated workforce. The successful vaccination program allowed us to operate efficiently and safely throughout the remainder of 2021 and into 2022.
We also continued our best practices from both a safety and environmental standpoint. During 2021, our safety TRIR (including contractors) was 1.37 per 200,000 hours worked. Throughout 2021, we made continued progress towards our goal of reducing GHG emissions with our increased usage of HBI and scrap in our facilities, as well as more efficient recycling of gases at certain facilities. We are also partnering with the U.S. Department of Energy as part of the Better Climate Challenge initiative, as we aim to build on our GHG emission reduction progress.
Recent Developments
Acquisition of FPT
On November 18, 2021, we completed the acquisition of FPT, a leading prime ferrous scrap processor in the U.S. These operations consist of 22 scrap processing facilities, primarily in the Midwest region of the U.S. Refer to NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS for additional information.
Financing Transactions
On December 1, 2021, we issued a notice of redemption for all $294 million in aggregate principal amount outstanding of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes. The 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes were redeemed on January 18, 2022, through a combination settlement, with the aggregate principal amount of $294 million paid in cash, and 24 million common shares delivered to noteholders, with a fair value of $499 million in settlement of the premium due per the terms of the indenture, plus cash in respect of the accrued and unpaid interest of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes to, but not including, the redemption date per the terms of the indenture.
On December 17, 2021, we entered into the Third ABL Amendment. The Third ABL Amendment modified our ABL Facility to, among other things, increase the amount of tranche A revolver commitments available thereunder by an additional $1 billion and exchange $150 million of tranche B revolver commitments available thereunder for tranche
A revolver commitments. After giving effect to the Third ABL Amendment, the aggregate principal amount of tranche A revolver commitments under our ABL Facility is $4.5 billion and there are no longer any tranche B revolver commitments. This action increased our liquidity by $1.0 billion. The increase is a result of a larger projected borrowing base driven by more favorable market conditions.
Share Repurchase Program
On February 10, 2022, our Board of Directors authorized a program to repurchase our outstanding common shares in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions, which may include purchases pursuant to Rule 10B5-1 plans or accelerated share repurchases, up to a maximum of $1 billion. We are not obligated to make any purchases and the program may be suspended or discontinued at any time. The share repurchase program does not have a specific expiration date.
Results of Operations
Overview
Our total revenues, net income (loss), diluted EPS and Adjusted EBITDA were as follows:
See "— Results of Operations — Adjusted EBITDA" below for a reconciliation of our Net Income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA.
The results for 2021 include the FPT operations subsequent to November 18, 2021 and full-year results for all other operations. The results for 2020 include AK Steel operations subsequent to March 13, 2020, ArcelorMittal USA operations subsequent to December 9, 2020, and our results from operations previously reported as part of our historical Mining and Pelletizing segment.
Revenues
During the year ended December 31, 2021, our consolidated Revenues increased by $15,090 million, compared to 2020. The increase was primarily due to the addition of 12.1 million net tons of steel shipments from our Steelmaking segment resulting from the 2020 Acquisitions, along with an increase in the average steel product selling price of $240 per net ton.
Revenues by Product Line
The following represents our consolidated Revenues by product line for the years ended:
The change in product mix for 2021, compared to 2020, is due primarily to the inclusion of full-period results for the 2020 Acquisitions. The results for 2020 include AK Steel operations subsequent to March 13, 2020, ArcelorMittal USA operations subsequent to December 9, 2020, and our results from operations previously reported as part of our historical Mining and Pelletizing segment.
Revenues by Market
The following table represents our consolidated Revenues and percentage of revenues attributable to each of the markets we supply:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Revenue | | % | | Revenue | | % |
| Automotive | $ | 5,152 | | | 25 | % | | $ | 2,391 | | | 45 | % |
| Infrastructure and Manufacturing | 5,427 | | | 27 | % | | 818 | | | 15 | % |
| Distributors and Converters | 7,741 | | | 38 | % | | 722 | | | 13 | % |
| Steel producers | 2,124 | | | 10 | % | | 1,423 | | | 27 | % |
| Total revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | | | $ | 5,354 | | | |
The change in percentages of net revenues to each market in 2021 compared to 2020 was driven primarily by the AM USA Transaction, which increased overall sales to automotive customers, but reduced the total percentage exposure, increased exposure to infrastructure and manufacturing and distributors and converters customers, and drove more in-house iron ore sales, which reduced the percentage of sales to steel producers.
Automotive Market
The largest end user for our steel products is the automotive industry in North America, which makes light vehicle production a key driver of demand. During 2021, North American light vehicle production was approximately 13.0 million units, the same as the prior year. Production the past two years has been down approximately 3.0 million units compared to the prior ten-year average, primarily due to the global semiconductor shortage, as well as other material shortages and supply chain disruptions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic. This has caused several outages amongst light vehicle manufacturers despite strong consumer demand. In light of these production outages, we have been able to redirect certain volumes originally intended for this end market to the spot market, where demand has been strong and pricing has reached all-time highs. The percentage of sales to the automotive market should increase in 2022 as fixed price contract prices increase and volumes expand as the material shortage issues ease.
During 2021, light vehicle sales in the U.S. were 15.1 million units, representing a 3% increase over the prior year. These improved sales, combined with continued production difficulties, brought light vehicle inventories to an all-time low of 22 days' supply during the third quarter of 2021.
Infrastructure and Manufacturing
We sell a variety of our steel products, including plate, carbon, stainless, electrical, tinplate and rail, to the infrastructure and manufacturing market. This market includes sales to manufacturers of HVAC, appliances, power transmission and distribution transformers, storage tanks, ships and railcars, wind towers, machinery parts, heavy equipment, military armor, food preservation, and railway lines. Domestic construction activity and the replacement of aging infrastructure directly affects sales of steel to this market. Residential construction spending surged in 2021 due to overwhelming demand for new houses. Nonresidential construction spending was slightly down in 2021; however, the sector saw a surge in spending in the second half of the year that will likely continue into 2022 with the passing of the Infrastructure and Jobs Act of 2021. The Infrastructure and Jobs Act of 2021 is also expected to increase demand for steel products related to renewable energy as well as the modernization of the U.S. electrical grid. Our plate products can be used in windmills, which we estimate contain 130 metric tons of steel per megawatt of electrical generating capacity. Additionally, we estimate solar panels consume 40 metric tons of steel per megawatt of electrical generating capacity. We also expect to see an increase in charging stations for EVs, which we will benefit from as we are the sole producer of electrical steel in the U.S.
Distributors and Converters
Virtually all of the grades of steel we produce are sold to the steel distributors and converters market. This market generally represents downstream steel service centers, which source various types of steel from us and fabricate it according to their customers' needs, which also includes automotive customers. Our steel is typically sold to this market on a spot basis or under short-term contracts linked to steel pricing indices. Demand and pricing for this market can be highly dependent on a variety of factors outside our control, including global and domestic commodity steel production capacity, the relative health of countries’ economies and whether they are consuming or exporting excess steel production, the provisions of international trade agreements and fluctuations in international currencies and, therefore, are subject to market changes in steel prices.
The price for domestic HRC, which is an important attribute in the profitability of this end market, averaged $1,573 per net ton for the year ended December 31, 2021, 174% higher than the prior year. The record prices for steel products in 2021 resulted from both supply and demand factors, each driven by a rapid recovery since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
Steel Producers Market
The steel producers market represents third-party sales to other steel producers, including those who operate blast furnaces and EAFs. It includes sales of raw materials and semi-finished and finished goods, including iron ore pellets, coal, coke, HBI, scrap and steel products.
The increase in revenues from the steel producers market for 2021, as compared to 2020, is primarily due to the inclusion of full-period results for the AK Steel and ArcelorMittal USA operations. This was partially offset by a decrease in iron ore product revenues during 2021, as compared to 2020, primarily as a result of the 2020 Acquisitions, as our iron ore pellet production is now predominately consumed internally and the respective intercompany revenue is eliminated in consolidation.
The largest component of sales to this market during the year ended December 31, 2021 was third-party slab sales, which are primarily made under a long-term supply agreement that was initiated in connection with the closing of the AM USA Transaction. Additionally, while it has fallen from peak 2021 levels in recent months, the price of iron ore has also risen dramatically over the past year, which, along with strong demand, has been an important factor in rising steel prices globally. The Platts 62% Price averaged $159 per metric ton during 2021, a 46% increase compared to the prior year. While higher iron ore prices play a role in increased steel prices, we also directly benefit from higher iron ore prices for the portion of iron ore pellets we sell to third parties.
Operating Costs
Cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold increased by $10,808 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, as compared to 2020, primarily due to the addition of 12.1 million net tons of steel shipments resulting from the 2020 Acquisitions.
Selling, general and administrative expenses
As a result of the 2020 Acquisitions, our Selling, general and administrative expenses increased by $178 million during the year ended December 31, 2021, as compared to 2020.
Acquisition-related costs
The following table represents the components of Acquisition-related costs:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Severance | $ | (15) | | | $ | (38) | | | $ | (2) | |
| Third-party expenses | (5) | | | (52) | | | (7) | |
| Total | $ | (20) | | | $ | (90) | | | $ | (9) | |
Refer to NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS for further information on the acquisitions.
Miscellaneous – net
Miscellaneous – net increased by $20 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, as compared to 2020. The increase in miscellaneous expense was primarily due to the acquisition-related loss on equity method investment during 2021.
Other Income (Expense)
Interest expense, net
Interest expense, net increased by $99 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, as compared to the prior year. The increase during 2021 was primarily due to borrowings on our ABL Facility, a decrease in capitalized interest during 2021 due to the completion of our Toledo direct reduction plant in December 2020 and the full-year interest on the incremental debt that we incurred in connection with the AK Steel Merger.
Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt
The loss on extinguishment of debt of $88 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 primarily resulted from the redemption of $396 million aggregate principal amount of 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes, $395 million aggregate principal amount of 4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes and $347 million aggregate principal amount of 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes.
This compares to a gain on extinguishment of debt of $130 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 primarily related to the repurchase of $748 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding senior notes of various series using the net proceeds from the issuance of an additional $555 million aggregate principal amount of our 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes on April 24, 2020 and other sources of cash. Refer to NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES for further details.
Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component
The increase of $156 million in Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component primarily relates to the expected return on assets component. The higher return is primarily attributable to the full-year effect of additional pension and OPEB plan assets acquired in the 2020 Acquisitions. Refer to NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS for further details.
Income Taxes
Our effective tax rate is affected by permanent items, primarily depletion. It also is affected by discrete items that may occur in any given period but are not consistent from period to period. The following represents a summary of our tax provision and corresponding effective rates:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | $ | (773) | | | $ | 111 | |
| Effective tax rate | 20 | % | | 57 | % |
A reconciliation of our income tax attributable to continuing operations compared to the U.S. federal statutory rate is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | | |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | |
| Tax at U.S. statutory rate | | $ | 799 | | | 21 | % | | $ | (41) | | | 21 | % | | | | |
| Increase (decrease) due to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percentage depletion in excess of cost depletion | | (99) | | | (3) | | | (42) | | | 22 | | | | | |
| Non-taxable income related to noncontrolling interests | | (9) | | | — | | | (9) | | | 4 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| State taxes, net | | 86 | | | 2 | | | (11) | | | 6 | | | | | |
| Other items, net | | (4) | | | — | | | (8) | | | 4 | | | | | |
| Provision for income tax expense (benefit) and effective income tax rate including discrete items | | $ | 773 | | | 20 | % | | $ | (111) | | | 57 | % | | | | |
The increase in income tax expense in 2021, as compared to the prior year, is directly related to the increase in the pre-tax book income year-over-year.
See NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES for further information.
Adjusted EBITDA
We evaluate performance on an operating segment basis, as well as a consolidated basis, based on Adjusted EBITDA, which is a non-GAAP measure. This measure is used by management, investors, lenders and other external users of our financial statements to assess our operating performance and to compare operating performance to other companies in the steel industry. In addition, management believes Adjusted EBITDA is a useful measure to assess the earnings power of the business without the impact of capital structure and can be used to assess our ability to service debt and fund future capital expenditures in the business.
The following table provides a reconciliation of our Net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 3,033 | | | $ | (81) | |
| Less: | | | |
| Interest expense, net | (337) | | | (238) | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | (773) | | | 111 | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | (897) | | | (308) | |
| Total EBITDA | $ | 5,040 | | | $ | 354 | |
| Less: | | | |
EBITDA from noncontrolling interests1 | $ | 75 | | | $ | 56 | |
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt | (88) | | | 130 | |
| Severance costs | (15) | | | (38) | |
| Acquisition-related costs excluding severance costs | (5) | | | (52) | |
| Acquisition-related loss on equity method investment | (31) | | | — | |
| Amortization of inventory step-up | (161) | | | (96) | |
| Impact of discontinued operations | 3 | | | 1 | |
| Total Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 5,262 | | | $ | 353 | |
| | | |
1 EBITDA of noncontrolling interests includes the following: | | | |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | $ | 45 | | | $ | 41 | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | 30 | | | 15 | |
| EBITDA of noncontrolling interests | $ | 75 | | | $ | 56 | |
The following table provides a summary of our Adjusted EBITDA by segment:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Adjusted EBITDA: | | | |
| Steelmaking | $ | 5,422 | | | $ | 433 | |
| Other Businesses | 9 | | | 47 | |
| Corporate and eliminations | (169) | | | (127) | |
| Total Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 5,262 | | | $ | 353 | |
Adjusted EBITDA from our Steelmaking segment for the year ended December 31, 2021, increased by $4,989 million, as compared to 2020. The results were favorably impacted by the operating results of the acquired steelmaking operations. Our Steelmaking Adjusted EBITDA included $232 million of Selling, general and administrative expenses for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Adjusted EBITDA from Corporate and eliminations primarily relates to Selling, general and administrative expenses at our Corporate headquarters.
Steelmaking
The following is a summary of our Steelmaking segment results included in our consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020. The results for 2021 include the FPT operations
subsequent to November 18, 2021 and full-year results for all other Steelmaking operations. The results for 2020 include the AK Steel operations subsequent to March 13, 2020, the ArcelorMittal USA operations subsequent to December 9, 2020, and our results from operations previously reported as part of our Mining and Pelletizing segment.
The following is a summary of the Steelmaking segment operating results:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Operating Results - In Millions | | | |
| Revenues | $ | 19,901 | | | $ | 4,965 | |
| Cost of goods sold | $ | (15,379) | | | $ | (4,749) | |
| Selling Price - Per Ton | | | |
| Average net selling price per net ton of steel products | $ | 1,187 | | | $ | 947 | |
The following table represents our segment Revenues by product line:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars In Millions,
Sales Volumes In Thousands) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Revenue | | Volume1 | | Revenue | | Volume1 |
| Hot-rolled steel | $ | 5,615 | | | 4,886 | | | $ | 386 | | | 633 | |
| Cold-rolled steel | 3,186 | | | 2,790 | | | 490 | | | 682 | |
| Coated steel | 5,864 | | | 5,056 | | | 1,747 | | | 1,911 | |
| Stainless and electrical steel | 1,622 | | | 674 | | | 868 | | | 416 | |
| Plate | 1,316 | | | 1,020 | | | 46 | | | 62 | |
| Other steel products | 1,247 | | | 1,460 | | | 46 | | | 79 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Other | 1,051 | | | N/A | | 1,382 | | | N/A |
| Total | $ | 19,901 | | | | | $ | 4,965 | | | |
| | | | | | | |
1 All steel product volumes are stated in net tons. |
Operating Results
Steelmaking revenues for 2021 increased by $14,936 million as compared to 2020, primarily due to the addition of sales following the 2020 Acquisitions. Results for the year ended December 31, 2021 were also impacted positively by the increase in the price for domestic HRC, which is the most significant index driving our revenues and profitability. The HRC index averaged $1,573 per net ton for 2021, 174% higher than 2020. The price of HRC reached an all-time high in 2021, as a direct result of favorable supply-demand dynamics driven by a rapid recovery since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. We have also benefited from higher steel shipments due to stronger demand.
Cost of goods sold for 2021 increased by $10,630 million as compared to 2020, predominantly due to additional sales as discussed above.
As a result, Adjusted EBITDA was $5,422 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to $433 million for the prior year. Adjusted EBITDA for 2021 was positively impacted by the addition of sales following the 2020 Acquisitions, the increase in the price for HRC and the higher demand for steel products, as discussed above.
Production
Our steelmaking facilities produced a total of 18 million net tons of raw steel during the year ended December 31, 2021. Due to the timing of the 2020 Acquisitions and the idling of facilities in response to impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, our steelmaking facilities produced a total of 4 million net tons of raw steel during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Liquidity, Cash Flows and Capital Resources
Our primary sources of liquidity are Cash and cash equivalents and cash generated from our operations, availability under the ABL Facility and other financing activities. Our capital allocation decision-making process is focused on preserving healthy liquidity levels, while maintaining the strength of our balance sheet and creating financial flexibility to manage through the inherent cyclical demand for our products and volatility in commodity prices. We are focused on maximizing the cash generation of our operations, reducing debt, and aligning capital investments with our strategic priorities and the requirements of our business plan, including regulatory and permission-to-operate related projects.
Following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. in 2020, our primary focus was to maintain adequate levels of liquidity to manage through a potentially prolonged economic downturn. Now that business conditions have improved, allowing us to generate a healthy free cash flow during 2021, we have had the ability to make investments to both improve and grow our business, particularly as it pertains to scrap metal. We entered into the scrap business on November 18, 2021 with the FPT Acquisition. We were also able to reduce our diluted share count and effectively return capital to shareholders via the cash redemption of all of the outstanding shares of our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock during the third quarter of 2021. In December 2021, we also increased our liquidity by amending our ABL Facility to increase the aggregate revolver commitments from $3.5 billion to $4.5 billion. Additionally, we expect to be able to return capital to shareholders in 2022 through our share repurchase program, which was authorized by our Board on February 10, 2022.
In addition, we anticipate that the current strong market environment will provide us ample opportunities to reduce our debt with our own free cash flow generation. We also continue to look at the composition of our debt, as we are interested in both extending our average maturity length and increasing our ratio of unsecured debt to secured debt, which can be accomplished with cash provided by operating activities. On January 18, 2022, we took action to reduce our debt by redeeming all of our then-outstanding 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes. The notes were redeemed through a combination settlement, with the aggregate principal amount of $294 million paid in cash, and 24 million common shares delivered to noteholders per the terms of the indenture.
In furtherance of these goals, we also consummated the following financing transactions during 2021:
On February 11, 2021, we sold 20 million common shares at a price per share of $16.12, in an underwritten public offering. We used the net proceeds from the offering, plus cash on hand, to redeem $322 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes. Prior to such use, the net proceeds were used to temporarily reduce the outstanding borrowings under our ABL Facility.
On February 17, 2021, we issued $500 million aggregate principal amount of 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and $500 million aggregate principal amount of 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes in an offering that was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act. We used the net proceeds from the notes offering to redeem all of the outstanding 4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes and 6.375% 2025 Senior Notes issued by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and all of the outstanding 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes, 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes and 6.375% 2025 AK Senior Notes issued by AK Steel Corporation (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Steel Corporation), and pay fees and expenses in connection with such redemptions, and reduce borrowings under our ABL Facility.
Additionally, on June 28, 2021, we redeemed the entirety of our outstanding 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes using available liquidity. Pursuant to the terms of the indenture governing the 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes, we paid $415 million, including $396 million aggregate principal amount, plus make-whole premiums and accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date.
These actions give us additional financial flexibility and will better prepare us to navigate more easily through potentially volatile industry conditions in the future.
Based on our outlook for the next 12 months, which is subject to continued changing demand from customers and volatility in domestic steel prices, we expect to have ample liquidity through cash generated from operations and availability under our ABL Facility sufficient to meet the needs of our operations, service and repay our debt obligations and return capital to shareholders.
The following discussion summarizes the significant items impacting our cash flows during 2021 and comparative years as well as expected impacts to our future cash flows over the next 12 months. Refer to the Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows for additional information.
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $2,785 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to net cash used by operating activities of $258 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. The year-over-year improvement was driven by improved operating results, partially offset by changes in working capital. Changes in working capital included increases in inventory primarily related to the global semiconductor shortage and increased raw material and production costs, as well as increases in receivables primarily related to rising prices. Additionally, we had incremental pension and OPEB payments and contributions of $268 million, which included $118 million of deferred 2020 pension contributions in connection with the CARES Act.
Investing Activities
Net cash used by investing activities was $1,379 million and $2,042 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2021, we had net cash outflows of $761 million related to the FPT Acquisition, net of cash acquired. We had total capital expenditures of $705 million and $525 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Included in the total capital expenditures, we had cash outflows for expansion capital expenditures relating to the development of our Toledo direct reduction plant of $64 million and $348 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Additionally, included in the total capital expenditures, we spent $641 million and $177 million primarily on sustaining capital expenditures during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Sustaining capital spend includes infrastructure, mobile equipment, fixed equipment, product quality, environment, health and safety.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we had net cash outflows of $658 million related to the AM USA Transaction, net of cash acquired. Additionally, during the year ended December 31, 2020, we had net cash outflows of $869 million related to the AK Steel Merger, net of cash acquired, which included $590 million used to repay the former AK Steel Corporation revolving credit facility and $324 million used to purchase outstanding 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes.
We anticipate total cash used for capital expenditures during the next 12 months to be between $800 and $900 million.
Financing Activities
Net cash used by financing activities was $1,470 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $2,059 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. Cash outflows from financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2021 included the redemption of all 583,273 shares outstanding of our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock at a redemption price of $1,343 million during the third quarter of 2021, along with $1.4 billion for repayments of debt. We used available liquidity to redeem all $396 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of our 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes. We used the net proceeds from the issuance of the 20 million common shares, and cash on hand, to redeem $322 million in aggregate principal amount of 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes. We used the net proceeds from the issuances of the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes to redeem all of the outstanding 4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes, 6.375% 2025 Senior Notes, 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes, 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes and 6.375% 2025 AK Senior Notes, and pay fees and expenses in connection with such redemptions, and reduce borrowings under our ABL Facility.
Cash inflows from financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2021 included the issuances of $500 million aggregate principal amount of 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes, $500 million aggregate principal amount of 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes and 20 million common shares for proceeds of $322 million, along with net borrowings of $73 million under credit facilities.
Net cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2020 primarily related to the issuances of $845 million aggregate principal amount of 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes, $955 million aggregate principal amount of 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes and net borrowings of $1,510 million under our ABL Facility. The net proceeds from the initial issuance of $725 million aggregate principal amount of the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes, along with cash on hand, were used to purchase $373 million aggregate principal amount of 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes and $367 million aggregate principal amount of 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes and to pay for the $44 million of debt issuance costs in the first quarter of 2020. The net proceeds from the additional issuance of $555 million aggregate principal amount of the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes were used to repurchase $736 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding senior notes.
The following represents our future cash commitments and contractual obligations as of December 31, 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments Due by Period (In Millions) |
| Total | | Less than
1 Year | | 1 - 3
Years | | 3 - 5
Years | | More than 5 Years |
Long-term debt1 | $ | 5,369 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 36 | | | $ | 3,355 | | | $ | 1,978 | |
Interest on debt1 | 1,497 | | | 262 | | | 453 | | | 361 | | | 421 | |
| Operating lease obligations | 378 | | | 68 | | | 103 | | | 74 | | | 133 | |
| Finance lease obligations | 345 | | | 105 | | | 127 | | | 47 | | | 66 | |
| Purchase obligations: | | | | | | | | | |
| Open purchase orders | 374 | | | 328 | | | 1 | | | — | | | 45 | |
Minimum "take or pay" purchase commitments2 | 8,590 | | | 2,785 | | | 2,947 | | | 1,493 | | | 1,365 | |
| Total purchase obligations | 8,964 | | | 3,113 | | | 2,948 | | | 1,493 | | | 1,410 | |
| Other long-term liabilities: | | | | | | | | | |
Pension funding minimums3 | 132 | | | 4 | | | 61 | | | 67 | | | — | |
OPEB claim payments3 | 613 | | | 138 | | | 242 | | | 233 | | | — | |
| Environmental and asset retirement obligations | 655 | | | 54 | | | 76 | | | 30 | | | 495 | |
| Other | 91 | | | 4 | | | 24 | | | 18 | | | 45 | |
| Total other long-term liabilities | 1,491 | | | 200 | | | 403 | | | 348 | | | 540 | |
| Total | $ | 18,044 | | | $ | 3,748 | | | $ | 4,070 | | | $ | 5,678 | | | $ | 4,548 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
1 Refer to NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES for additional information regarding our debt and related interest rates. |
2 Includes minimum railroad and vessel transportation obligations, minimum electric power demand charges, minimum diesel and natural gas obligations and minimum port facility obligations. Additionally, includes our coke purchase commitments related to our coke supply agreement with SunCoke Middletown. |
3 Estimates beyond five years for pension and OPEB contributions and payments are not included due to the uncertainty of future investment performance, funding legislation, discount rates, healthcare costs, plan design and other factors. Refer to NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS for additional information regarding our pension and OPEB obligations. |
Refer to NOTE 20 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES for additional information regarding our future commitments and obligations.
Capital Resources
We expect to fund our business obligations from available cash, current and future operations and existing and future borrowing arrangements. We also may pursue other funding strategies in the capital markets to strengthen our liquidity, extend debt maturities and/or fund strategic initiatives. The following represents a summary of key liquidity measures:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31,
2021 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 48 | |
| |
Available borrowing base on ABL Facility1 | $ | 4,500 | |
| Borrowings | (1,609) | |
| Letter of credit obligations | (175) | |
| Borrowing capacity available | $ | 2,716 | |
| |
| |
1 As of December 31, 2021, the ABL Facility had a maximum borrowing base of $4.5 billion, determined by applying customary advance rates to eligible accounts receivable, inventory and certain mobile equipment. |
Our primary sources of funding are cash and cash equivalents, which totaled $48 million as of December 31, 2021, cash generated by our business, availability under our ABL Facility and other financing activities. Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and on deposit. The combination of cash and availability under our ABL Facility gives us $2.8 billion in liquidity entering the first quarter of 2022, which is expected to be adequate to fund operations, letter of credit obligations, capital expenditures and other cash commitments for at least the next 12 months.
As of December 31, 2021, we were in compliance with the ABL Facility liquidity requirements and, therefore, the springing financial covenant requiring a minimum Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio of 1.0 to 1.0 was not applicable. We believe that the cash on hand and our ABL Facility provide us sufficient liquidity to support our operating, investing and financing activities. We have the capability to issue additional unsecured notes and, subject to the limitations set forth in our existing senior notes indentures, additional secured debt, if we elect to access the debt capital markets. However, our ability to issue additional notes could be limited by market conditions.
We intend from time to time to seek to retire or repurchase our outstanding senior notes with cash on hand, borrowings from existing credit sources or new debt financings and/or exchanges for debt or equity securities, in open market purchases, privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. Such repurchases, if any, will depend on prevailing market conditions, our liquidity requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors, and the amounts involved may be material.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
In the normal course of business, we are a party to certain arrangements that are not reflected on our Statements of Consolidated Financial Position. These arrangements include minimum "take or pay" purchase commitments, such as minimum electric power demand charges, minimum coal, diesel and natural gas purchase commitments, minimum railroad transportation commitments and minimum port facility usage commitments; and financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk, such as bank letters of credit and bank guarantees.
Information about our Guarantors and the Issuer of our Guaranteed Securities
The accompanying summarized financial information has been prepared and presented pursuant to SEC Regulation S-X, Rule 3-10, “Financial Statements of Guarantors and Issuers of Guaranteed Securities Registered or Being Registered,” and Rule 13-01 "Financial Disclosures about Guarantors and Issuers of Guaranteed Securities and Affiliates Whose Securities Collateralized a Registrant's Securities." Certain of our subsidiaries (the "Guarantor subsidiaries") have fully and unconditionally, and jointly and severally, guaranteed the obligations under (a) the 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes, the 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes, the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and the 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes issued by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. on a senior unsecured basis and (b) the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured
Notes and the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes on a senior secured basis. See NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES for further information.
The following presents the summarized financial information on a combined basis for Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. (parent company and issuer of the guaranteed obligations) and the Guarantor subsidiaries, collectively referred to as the obligated group. Transactions between the obligated group have been eliminated. Information for the non-Guarantor subsidiaries was excluded from the combined summarized financial information of the obligated group.
Each Guarantor subsidiary is consolidated by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. as of December 31, 2021. Refer to Exhibit 22, incorporated herein by reference, for the detailed list of entities included within the obligated group as of December 31, 2021. The guarantee of a Guarantor subsidiary with respect to Cliffs' 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes, the 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes, the 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes, the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes, the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and the 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes will be automatically and unconditionally released and discharged, and such Guarantor subsidiary’s obligations under the guarantee and the related indentures (the “Indentures”) will be automatically and unconditionally released and discharged, upon the occurrence of any of the following, along with the delivery to the trustee of an officer’s certificate and an opinion of counsel, each stating that all conditions precedent provided for in the applicable Indenture relating to the release and discharge of such Guarantor subsidiary’s guarantee have been complied with:
(a) any sale, exchange, transfer or disposition of such Guarantor subsidiary (by merger, consolidation, or the sale of) or the capital stock of such Guarantor subsidiary after which the applicable Guarantor subsidiary is no longer a subsidiary of the Company or the sale of all or substantially all of such Guarantor subsidiary’s assets (other than by lease), whether or not such Guarantor subsidiary is the surviving entity in such transaction, to a person which is not the Company or a subsidiary of the Company; provided that (i) such sale, exchange, transfer or disposition is made in compliance with the applicable Indenture, including the covenants regarding consolidation, merger and sale of assets and, as applicable, dispositions of assets that constitute notes collateral, and (ii) all the obligations of such Guarantor subsidiary under all debt of the Company or its subsidiaries terminate upon consummation of such transaction;
(b) designation of any Guarantor subsidiary as an “excluded subsidiary” (as defined in the Indentures); or
(c) defeasance or satisfaction and discharge of the Indentures.
Each entity in the summarized combined financial information follows the same accounting policies as described in the consolidated financial statements. The accompanying summarized combined financial information does not reflect investments of the obligated group in non-Guarantor subsidiaries. The financial information of the obligated group is presented on a combined basis; intercompany balances and transactions within the obligated group have been eliminated. The obligated group's amounts due from, amounts due to, and transactions with, non-Guarantor subsidiaries and related parties have been presented in separate line items.
Summarized Combined Financial Information of the Issuer and Guarantor Subsidiaries:
The following table is summarized combined financial information from the Statements of Condensed Consolidated Financial Position of the obligated group:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| Current assets | $ | 6,539 | | | $ | 4,903 | |
| Non-current assets | 12,753 | | | 10,535 | |
| Current liabilities | (3,222) | | | (2,767) | |
| Non-current liabilities | (9,081) | | | (10,563) | |
| | | |
The following table is summarized combined financial information from the Statements of Condensed Consolidated Operations of the obligated group:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended |
| December 31, 2021 |
| Revenues | $ | 19,973 | |
| Cost of goods sold | (15,582) | |
| Income from continuing operations | 2,923 | |
| Net income | 2,929 | |
| Net income attributable to Cliffs shareholders | 2,929 | |
As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the obligated group had the following balances with non-Guarantor subsidiaries and other related parties:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| Balances with non-Guarantor subsidiaries: | | | |
| Accounts receivable, net | $ | 199 | | | $ | 69 | |
| Accounts payable | (186) | | | (17) | |
| | | |
| Balances with other related parties: | | | |
| Accounts receivable, net | $ | 3 | | | $ | 2 | |
| | | |
| Accounts payable | (7) | | | (6) | |
| | | |
Additionally, for the year ended December 31, 2021, the obligated group had Revenues of $139 million and Cost of goods sold of $117 million, in each case with other related parties.
Market Risks
We are subject to a variety of risks, including those caused by changes in commodity prices and interest rates. We have established policies and procedures to manage such risks; however, certain risks are beyond our control.
Pricing Risks
In the ordinary course of business, we are exposed to market risk and price fluctuations related to the sale of our products, which are impacted primarily by market prices for HRC, and the purchase of energy and raw materials used in our operations, which are impacted by market prices for electricity, natural gas, ferrous and stainless steel scrap, chrome, metallurgical coal, coke, nickel and zinc. Our strategy to address market risk has generally been to obtain competitive prices for our products and services and allow operating results to reflect market price movements dictated by supply and demand; however, we make forward physical purchases and enter into hedge contracts to manage exposure to price risk related to the purchases of certain raw materials and energy used in the production process.
Our financial results can vary for our operations as a result of fluctuations in market prices. We attempt to mitigate these risks by aligning fixed and variable components in our customer pricing contracts, supplier purchasing agreements and derivative financial instruments.
Some customer contracts have fixed-pricing terms, which increase our exposure to fluctuations in raw material and energy costs. To reduce our exposure, we enter into annual, fixed-price agreements for certain raw materials. Some of our existing multi-year raw material supply agreements have required minimum purchase quantities. Under adverse economic conditions, those minimums may exceed our needs. Absent exceptions for force majeure and other circumstances affecting the legal enforceability of the agreements, these minimum purchase requirements may compel us to purchase quantities of raw materials that could significantly exceed our anticipated needs or pay damages to the supplier for shortfalls. In these circumstances, we would attempt to negotiate agreements for new purchase quantities. There is a risk, however, that we would not be successful in reducing
purchase quantities, either through negotiation or litigation. If that occurred, we would likely be required to purchase more of a particular raw material in a particular year than we need, negatively affecting our results of operations and cash flows.
Certain of our customer contracts include variable-pricing mechanisms that adjust selling prices in response to changes in the costs of certain raw materials and energy, while other of our customer contracts exclude such mechanisms. We may enter into multi-year purchase agreements for certain raw materials with similar variable-price mechanisms, allowing us to achieve natural hedges between the customer contracts and supplier purchase agreements. Therefore, in some cases, price fluctuations for energy (particularly natural gas and electricity), raw materials (such as scrap, chrome, zinc and nickel) or other commodities may be, in part, passed on to customers rather than absorbed solely by us. There is a risk, however, that the variable-price mechanisms in the sales contracts may not necessarily change in tandem with the variable-price mechanisms in our purchase agreements, negatively affecting our results of operations and cash flows.
Our strategy to address volatile natural gas rates and electricity rates includes improving efficiency in energy usage, identifying alternative providers and utilizing the lowest cost alternative fuels. If we are unable to align fixed and variable components between customer contracts and supplier purchase agreements, we use cash-settled commodity price swaps and options to hedge the market risk associated with the purchase of certain of our raw materials and energy requirements. Additionally, we routinely use these derivative instruments to hedge a portion of our natural gas and zinc requirements. Our hedging strategy is designed to protect us from excessive pricing volatility. However, since we do not typically hedge 100% of our exposure, abnormal price increases in any of these commodity markets might still negatively affect operating costs.
The following table summarizes the negative effect of a hypothetical change in the fair value of our derivative instruments outstanding as of December 31, 2021, due to a 10% and 25% change in the market price of each of the indicated commodities:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Positive or Negative Effect on
Pre-tax Income |
| Commodity Derivative | 10% Increase or Decrease | | 25% Increase or Decrease |
| Natural gas | $ | 32 | | | $ | 81 | |
| | | |
| Zinc | 6 | | | 15 | |
Valuation of Goodwill and Other Long-Lived Assets
We assign goodwill arising from acquired companies to the reporting units that are expected to benefit from the synergies of the acquisition. Goodwill is tested on a qualitative basis for impairment at the reporting unit level on an annual basis (October 1) and between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying value. These events or circumstances could include a significant change in the business climate, legal factors, operating performance indicators, competition, or sale or disposition of a significant portion of a reporting unit. As necessary, should our qualitative test indicate that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carry amount, we perform a quantitative test to determine the amount of impairment, if any, to the carrying value of the reporting unit and its associated goodwill.
Application of the goodwill impairment test requires judgment, including the identification of reporting units, assignment of assets and liabilities to reporting units, assignment of goodwill to reporting units and if a quantitative assessment is deemed necessary in determination of the fair value of each reporting unit. The fair value of each reporting unit is estimated using a discounted cash flow methodology, which considers forecasted cash flows discounted at an estimated weighted average cost of capital. Assessing the recoverability of our goodwill requires significant assumptions regarding the estimated future cash flows and other factors to determine the fair value of a reporting unit, including, among other things, estimates related to forecasts of future revenues, expected Adjusted EBITDA, expected capital expenditures and working capital requirements, which are based upon our long-range plan estimates. The assumptions used to calculate the fair value of a reporting unit may change from year to year based on operating results, market conditions and other factors. Changes in these assumptions could materially affect the determination of fair value for each reporting unit.
Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment upon the occurrence of events or changes in circumstances that would indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. Such indicators may include: a significant decline in expected future cash flows; a sustained, significant decline in market pricing; a significant
adverse change in legal or environmental factors or in the business climate; changes in estimates of our recoverable reserves; and unanticipated competition. Any adverse change in these factors could have a significant impact on the recoverability of our long-lived assets and could have a material impact on our consolidated statements of operations and statements of financial position.
A comparison of each asset group's carrying value to the estimated undiscounted net future cash flows expected to result from the use of the assets, including cost of disposition, is used to determine if an asset is recoverable. Projected future cash flows reflect management's best estimate of economic and market conditions over the projected period, including growth rates in revenues and costs, and estimates of future expected changes in operating margins and capital expenditures. If the carrying value of the asset group is higher than its undiscounted net future cash flows, the asset group is measured at fair value and the difference is recorded as a reduction to the long-lived assets. We estimate fair value using a market approach, an income approach or a cost approach. For the year ended December 31, 2021, we concluded that an event triggering the need for an impairment assessment did not occur.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest payable on our senior notes is at fixed rates. Interest payable under our ABL Facility is at a variable rate based upon the applicable base rate plus the applicable base rate margin depending on the excess availability. As of December 31, 2021, we had $1,609 million outstanding under our ABL Facility. An increase in prevailing interest rates would increase interest expense and interest paid for any outstanding borrowings under our ABL Facility. For example, a 100 basis point change to interest rates under our ABL Facility at the December 31, 2021 borrowing level would result in a change of $16 million to interest expense on an annual basis.
Additionally, a portion of our borrowing capacity and outstanding indebtedness under the ABL Facility bears interest at a variable rate based on LIBOR. For a discussion of the attendant risk, see Part I - Item 1A, Risk Factors - III. Financial Risks - Our existing and future indebtedness may limit cash flow available to invest in the ongoing needs of our businesses, which could prevent us from fulfilling our obligations under our senior notes, ABL Facility and other debt, and we may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our debt, which may not be successful.
Supply Concentration Risks
Many of our operations and mines rely on one source for each of electric power and natural gas. A significant interruption or change in service or rates from our energy suppliers could materially impact our production costs, margins and profitability.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Refer to NOTE 1 - BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES of the consolidated financial statements for a description of recent accounting pronouncements, including the respective dates of adoption and effects on results of operations and financial condition.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Management's discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations is based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. Preparation of financial statements requires management to make assumptions, estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, costs and expenses, and the related disclosures of contingencies. Management bases its estimates on various assumptions and historical experience, which are believed to be reasonable; however, due to the inherent nature of estimates, actual results may differ significantly due to changed conditions or assumptions. On a regular basis, management reviews the accounting policies, assumptions, estimates and judgments to ensure that our financial statements are fairly presented in accordance with GAAP. However, because future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty, actual results could differ from our assumptions and estimates, and such differences could be material. Management believes that the following critical accounting estimates and judgments have a significant impact on our financial statements.
Business Combinations
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination are recognized and measured based on their estimated fair values at the acquisition date, while the acquisition-related costs are expensed as incurred. Any excess of the purchase consideration when compared to the fair value of the net tangible and intangible assets acquired, if any, is recorded as goodwill. We engaged independent valuation specialists to assist with the
determination of the fair value of assets acquired, liabilities assumed, noncontrolling interest, and goodwill, for the acquisitions. If the initial accounting for the business combination is incomplete by the end of the reporting period in which the acquisition occurs, an estimate will be recorded. Subsequent to the acquisition date, and not later than one year from the acquisition date, we will record any material adjustments to the initial estimate based on new information obtained that would have existed as of the date of the acquisition. Any adjustment that arises from information obtained that did not exist as of the date of the acquisition will be recorded in the period the adjustment arises.
Valuation of Goodwill and Other Long-Lived Assets
The valuation of goodwill and other long-lived assets includes various assumptions and are considered critical accounting estimates. Refer to "–Market Risks" above for additional information.
Mineral Reserves
We regularly evaluate, and engage QPs to review and validate, our mineral reserves and update them as required in accordance with Subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K. We perform an in-depth evaluation of our mineral reserve estimates by mine on a periodic basis, in addition to routine annual assessments. The determination of mineral reserves requires us and third-party QPs to make significant estimates and assumptions related to key inputs, including, but not limited to, (1) the determination of the size and scope of the iron ore body through technical modeling, (2) the estimates of future iron ore prices, production costs and capital expenditures, and (3) management’s mine plan for the proven and probable mineral reserves. The significant estimates and assumptions could be affected by future industry conditions, geological conditions and ongoing mine planning. Additional capital and development expenditures may be required to maintain effective production capacity. Generally, as mining operations progress, haul distances increase. Alternatively, changes in economic conditions or the expected quality of mineral resources and reserves could decrease effective production capacity. Technological progress could alleviate such factors or increase capacity of mineral reserves.
We use our mineral reserve estimates, combined with our estimated annual production levels, to determine the mine closure dates utilized in recording the fair value liability for asset retirement obligations for our active operating mines. Refer to NOTE 14 - ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS, for further information. Since the liability represents the present value of the expected future obligation, a significant change in mineral reserves or mine lives could have a substantial effect on the recorded obligation. We also utilize mineral reserves for evaluating potential impairments of mine asset groups as they are indicative of future cash flows and in determining maximum useful lives utilized to calculate depreciation, depletion and amortization of long-lived mine assets and in determining the estimated fair value of mineral reserves established through the purchase price allocation in a business combination. The consolidated asset retirement obligation balance was $449 million as of December 31, 2021, of which $208 million related to active iron ore mine operations. The total asset balance associated with our Steelmaking reportable segment was $18,326 million as of December 31, 2021, of which $1,622 million related to long-lived assets associated with our combined iron ore mine asset groups, and is inclusive of $231 million related to iron ore mineral reserves acquired through the AM USA Transaction. Depreciation, depletion and amortization expense for our combined iron ore mine asset groups was $172 million for the year ended December 31, 2021. Increases or decreases in mineral reserves or mine lives could significantly affect these items.
Asset Retirement Obligations
The accrued closure obligation is predominantly related to our indefinitely idled and closed iron ore mining operations and provides for contractual and legal obligations associated with the eventual closure of those operations. We perform an in-depth evaluation of the liability every three years in addition to our routine annual assessments. In 2020, we employed third-party specialists to assist in the evaluation. Our obligations are determined based on detailed estimates adjusted for factors that a market participant would consider (e.g., inflation, overhead and profit), which are escalated at an assumed rate of inflation to the estimated closure dates and then discounted using the current credit-adjusted risk-free interest rate. The estimate also incorporates incremental increases in the closure cost estimates and changes in estimates of mine lives for our active mine sites. The closure date for each of our active mine sites is determined based on the exhaustion date of the remaining mineral reserves, which is dependent on our estimate of mineral reserves. The estimated obligations for our active mine sites are particularly sensitive to the impact of changes in mine lives given the difference between the inflation and discount rates. The closure dates for a majority of our steelmaking facilities are indefinite, and as such, the asset retirement obligations are recorded at present values using estimated ranges of the economic lives of the underlying assets. Changes in the base estimates of legal and contractual closure costs due to changes in legal or contractual requirements, available technology,
inflation, overhead or profit rates also could have a significant impact on the recorded obligations. Refer to NOTE 14 - ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS, for further information.
Environmental Remediation Costs
We have a formal policy for environmental protection and remediation. Our obligations for known environmental matters at active and closed operations have been recognized based on estimates of the cost of investigation and remediation at each facility. If the obligation can only be estimated as a range of possible amounts, with no specific amount being more likely, the minimum of the range is accrued. Management reviews its environmental remediation sites quarterly to determine if additional cost adjustments or disclosures are required. The characteristics of environmental remediation obligations, where information concerning the nature and extent of clean-up activities is not immediately available and which are subject to changes in regulatory requirements, result in a significant risk of increase to the obligations as they mature. Expected future expenditures are discounted to present value unless the amount and timing of the cash disbursements cannot be reasonably estimated.
Income Taxes
Our income tax expense, deferred tax assets and liabilities and reserves for unrecognized tax benefits reflect management's best assessment of estimated future taxes to be paid. We are subject to income taxes in the U.S. and various foreign jurisdictions. Significant judgments and estimates are required in determining the consolidated income tax expense.
Deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between tax and financial statement recognition of revenue and expense. In evaluating our ability to recover our deferred tax assets, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent financial operations. In projecting future taxable income, we begin with historical results adjusted for the results of discontinued operations and changes in accounting policies and incorporate assumptions including the amount of future state, federal and foreign pretax operating income, the reversal of temporary differences, and the implementation of feasible and prudent tax planning strategies. These assumptions require significant judgment about the forecasts of future taxable income and are consistent with the plans and estimates we are using to manage the underlying businesses.
At December 31, 2021 and 2020, we had a valuation allowance of $409 million and $836 million, respectively, against our deferred tax assets. Of these amounts, $70 million and $439 million relate to the U.S. deferred tax assets at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, and $339 million and $397 million relate to foreign deferred tax assets, respectively.
Our losses in Luxembourg in recent periods represent sufficient negative evidence to require a full valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets in that jurisdiction. We intend to maintain a valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets related to these operating losses, unless and until sufficient positive evidence exists to support the realization of such assets.
Changes in tax laws and rates also could affect recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities in the future. The calculation of our tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax laws and regulations in various jurisdictions across our global operations. The ultimate impact of U.S. income tax reform legislation may differ from our current estimates due to changes in the interpretations and assumptions made as well as additional regulatory guidance that may be issued.
Accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the financial statements requires that a tax benefit from an uncertain tax position be recognized when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on technical merits.
We recognize tax liabilities in accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes, and we adjust these liabilities when our judgment changes because of evaluation of new information not previously available. Due to the complexity of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in payment that is materially different from our current estimate of the tax liabilities. These differences will be reflected as increases or decreases to income tax expense in the period in which they are determined. Refer to NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES, for further information.
Employee Retirement Benefit Obligations
We offer defined benefit pension plans, defined contribution pension plans and OPEB plans, primarily consisting of retiree healthcare benefits, to most employees in North America as part of a total compensation and benefits program.
The following is a summary of our U.S. defined benefit pension and OPEB funding and expense:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension | | OPEB |
| | Funding | | Expense (Benefit) | | Funding | | Expense (Benefit) |
| 2019 | | $ | 16 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | (2) | |
| 2020 | | 50 | | | (31) | | | 25 | | | 8 | |
20211 | | 163 | | | (189) | | | 180 | | | 86 | |
| 2022 (Estimated) | | 4 | | | (179) | | | 138 | | | 72 | |
| | | | | | | | |
1 The 2021 pension funding includes $118 million that was deferred as a result of the CARES Act. |
Assumptions used in determining the benefit obligations and the value of plan assets for defined benefit pension plans and OPEB plans, primarily consisting of retiree healthcare benefits, that we offer are evaluated periodically by management. Critical assumptions, such as the discount rate used to measure the benefit obligations, the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets, the medical care cost trend, and the rate of compensation increase are reviewed annually.
The following represents weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations and net benefit costs:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension | | Other Benefits |
| December 31, | | December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Discount rate | 2.75 | | % | | 2.34 | | % | | 3.01 | | % | | 2.71 | | % |
| Compensation rate increase | 2.52 | | | | 2.56 | | | | 3.00 | | | | 3.00 | | |
| Expected return on plan assets | 6.84 | | | | 7.69 | | | | 5.20 | | | | 6.82 | | |
For the pension plans, the weighted-average expected return on plan assets for 2022 is 6.87%, an increase from 6.84% in 2021. For the OPEB plans, the weighted-average expected return on plan assets for 2022 is 4.86%, a decrease from 5.20% in 2021.
The following represents assumed weighted-average health care cost trend rates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year | 2.36 | | % | | 6.05 | | % |
| Ultimate health care cost trend rate | 4.50 | | | | 4.59 | | |
| Year that the ultimate rate is reached | 2031 | | | | 2031 | | |
The discount rates used to measure plan liabilities as of the December 31 measurement date are determined individually for each plan. The discount rates are determined by matching the projected cash flows used to determine the plan liabilities to a projected yield curve of high-quality corporate bonds available at the measurement date. Discount rates for expense are calculated using the granular approach for each plan.
Depending on the plan, we use either company-specific base mortality tables or tables issued by the Society of Actuaries. We use the Pri-2012 mortality tables from the Society of Actuaries with adjustments for blue collar, white collar or no collar depending on the plan. On December 31, 2021, the assumed mortality improvement projection was updated from generational scale MP-2020 to generational scale MP-2021 for the Pri-2012 mortality tables.
Following are sensitivities of potential further changes in these key assumptions on the estimated 2022 pension and OPEB expense and the pension and OPEB obligations as of December 31, 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Increase (Decrease) in Expense | | Increase in
Benefit Obligation |
| Pension | | OPEB | | Pension | | OPEB |
| Decrease discount rate 0.25% | $ | (3) | | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 147 | | | $ | 111 | |
| Decrease return on assets 1.00% | 54 | | | 8 | | | N/A | | N/A |
Changes in actuarial assumptions, including discount rates, employee retirement rates, mortality, compensation levels, plan asset investment performance and healthcare costs, are determined based on analyses of actual and expected factors. Changes in actuarial assumptions and/or investment performance of plan assets may have a significant impact on our financial condition due to the magnitude of our retirement obligations.
Refer to NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS for further information.
Forward-Looking Statements
This report contains statements that constitute "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of the federal securities laws. As a general matter, forward-looking statements relate to anticipated trends and expectations rather than historical matters. Forward-looking statements are subject to uncertainties and factors relating to our operations and business environment that are difficult to predict and may be beyond our control. Such uncertainties and factors may cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. These statements speak only as of the date of this report, and we undertake no ongoing obligation, other than that imposed by law, to update these statements. Investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. Uncertainties and risk factors that could affect our future performance and cause results to differ from the forward-looking statements in this report include, but are not limited to:
•disruptions to our operations relating to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, including the heightened risk that a significant portion of our workforce or on-site contractors may suffer illness or otherwise be unable to perform their ordinary work functions;
•continued volatility of steel, iron ore and scrap metal market prices, which directly and indirectly impact the prices of the products that we sell to our customers;
•uncertainties associated with the highly competitive and cyclical steel industry and our reliance on the demand for steel from the automotive industry, which has been experiencing a trend toward light weighting and supply chain disruptions, such as the semiconductor shortage, that could result in lower steel volumes being consumed;
•potential weaknesses and uncertainties in global economic conditions, excess global steelmaking capacity, oversupply of iron ore, prevalence of steel imports and reduced market demand, including as a result of the prolonged COVID-19 pandemic;
•severe financial hardship, bankruptcy, temporary or permanent shutdowns or operational challenges, due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic or otherwise, of one or more of our major customers, including customers in the automotive market, key suppliers or contractors, which, among other adverse effects, could lead to reduced demand for our products, increased difficulty collecting receivables, and customers and/or suppliers asserting force majeure or other reasons for not performing their contractual obligations to us;
•risks related to U.S. government actions with respect to Section 232, the USMCA and/or other trade agreements, tariffs, treaties or policies, as well as the uncertainty of obtaining and maintaining effective antidumping and countervailing duty orders to counteract the harmful effects of unfairly traded imports;
•impacts of existing and increasing governmental regulation, including potential environmental regulations relating to climate change and carbon emissions, and related costs and liabilities, including failure to receive or maintain required operating and environmental permits, approvals, modifications or other authorizations of, or from, any governmental or regulatory authority and costs related to implementing
improvements to ensure compliance with regulatory changes, including potential financial assurance requirements;
•potential impacts to the environment or exposure to hazardous substances resulting from our operations;
•our ability to maintain adequate liquidity, our level of indebtedness and the availability of capital could limit our financial flexibility and cash flow necessary to fund working capital, planned capital expenditures, acquisitions, and other general corporate purposes or ongoing needs of our business;
•our ability to reduce our indebtedness or return capital to shareholders within the currently expected timeframes or at all;
•adverse changes in credit ratings, interest rates, foreign currency rates and tax laws;
•the outcome of, and costs incurred in connection with, lawsuits, claims, arbitrations or governmental proceedings relating to commercial and business disputes, environmental matters, government investigations, occupational or personal injury claims, property damage, labor and employment matters, or suits involving legacy operations and other matters;
•supply chain disruptions or changes in the cost or quality of energy sources, including electricity, natural gas and diesel fuel, or critical raw materials and supplies, including iron ore, industrial gases, graphite electrodes, scrap metal, chrome, zinc, coke and metallurgical coal;
•problems or disruptions associated with transporting products to our customers, moving manufacturing inputs or products internally among our facilities, or suppliers transporting raw materials to us;
•uncertainties associated with natural or human-caused disasters, adverse weather conditions, unanticipated geological conditions, critical equipment failures, infectious disease outbreaks, tailings dam failures and other unexpected events;
•disruptions in, or failures of, our information technology systems, including those related to cybersecurity;
•liabilities and costs arising in connection with any business decisions to temporarily idle or permanently close an operating facility or mine, which could adversely impact the carrying value of associated assets and give rise to impairment charges or closure and reclamation obligations, as well as uncertainties associated with restarting any previously idled operating facility or mine;
•our ability to realize the anticipated synergies and benefits of our recent acquisition transactions and to successfully integrate the acquired businesses into our existing businesses, including uncertainties associated with maintaining relationships with customers, vendors and employees and known and unknown liabilities we assumed in connection with the acquisitions;
•our level of self-insurance and our ability to obtain sufficient third-party insurance to adequately cover potential adverse events and business risks;
•challenges to maintaining our social license to operate with our stakeholders, including the impacts of our operations on local communities, reputational impacts of operating in a carbon-intensive industry that produces GHG emissions, and our ability to foster a consistent operational and safety track record;
•our ability to successfully identify and consummate any strategic capital investments or development projects, cost-effectively achieve planned production rates or levels, and diversify our product mix and add new customers;
•our actual economic mineral reserves or reductions in current mineral reserve estimates, and any title defect or loss of any lease, license, easement or other possessory interest for any mining property;
•availability of workers to fill critical operational positions and potential labor shortages caused by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, as well as our ability to attract, hire, develop and retain key personnel;
•our ability to maintain satisfactory labor relations with unions and employees;
•unanticipated or higher costs associated with pension and OPEB obligations resulting from changes in the value of plan assets or contribution increases required for unfunded obligations;
•the amount and timing of any repurchases of our common shares; and
•potential significant deficiencies or material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting.
For additional factors affecting our businesses, refer to Part I – Item 1A. Risk Factors. You are urged to carefully consider these risk factors.
| | | | | |
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
Information regarding our market risk is presented under the caption "Market Risks," which is included in Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and is incorporated by reference and made a part hereof.
| | | | | |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Statements of Consolidated Financial Position
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Subsidiaries
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 48 | | | $ | 112 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 2,154 | | | 1,169 | |
| Inventories | 5,188 | | | 3,828 | |
| | | |
| Other current assets | 263 | | | 189 | |
| Total current assets | 7,653 | | | 5,298 | |
| Non-current assets: | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 9,186 | | | 8,743 | |
| Goodwill | 1,116 | | | 1,406 | |
| | | |
| Other non-current assets | 1,020 | | | 1,324 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 18,975 | | | $ | 16,771 | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 2,073 | | | $ | 1,575 | |
| Accrued employment costs | 585 | | | 460 | |
| State and local taxes | 138 | | | 147 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Other current liabilities | 765 | | | 747 | |
| Total current liabilities | 3,561 | | | 2,929 | |
| Non-current liabilities: | | | |
| Long-term debt | 5,238 | | | 5,390 | |
| Pension liability, non-current | 578 | | | 1,224 | |
| OPEB liability, non-current | 2,383 | | | 2,889 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 1,441 | | | 1,260 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 13,201 | | | 13,692 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (See Note 20) | | | |
Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock - no par value | | | |
Authorized, Issued and Outstanding - no shares (2020 - 583,273 shares) | — | | | 738 | |
| Equity: | | | |
Common Shares - par value $0.125 per share | | | |
Authorized - 1,200,000,000 shares (2020 - 600,000,000 shares); | | | |
Issued - 506,832,537 shares (2020 - 506,832,537 shares); | | | |
Outstanding - 500,158,955 shares (2020 - 477,517,372 shares) | 63 | | | 63 | |
| Capital in excess of par value of shares | 4,892 | | | 5,431 | |
| Retained deficit | (1) | | | (2,989) | |
Cost of 6,673,582 common shares in treasury (2020 - 29,315,165 shares) | (82) | | | (354) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 618 | | | (133) | |
| Total Cliffs shareholders' equity | 5,490 | | | 2,018 | |
| Noncontrolling interest | 284 | | | 323 | |
| TOTAL EQUITY | 5,774 | | | 2,341 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE PREFERRED STOCK AND EQUITY | $ | 18,975 | | | $ | 16,771 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Statements of Consolidated Operations
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Subsidiaries
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | $ | 5,354 | | | $ | 1,990 | |
| Operating costs: | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | (15,910) | | | (5,102) | | | (1,414) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | (422) | | | (244) | | | (113) | |
| Acquisition-related costs | (20) | | | (90) | | | (7) | |
| Miscellaneous – net | (80) | | | (60) | | | (27) | |
| Total operating costs | (16,432) | | | (5,496) | | | (1,561) | |
| Operating income (loss) | 4,012 | | | (142) | | | 429 | |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | |
| Interest expense, net | (337) | | | (238) | | | (101) | |
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt | (88) | | | 130 | | | (18) | |
| Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component | 210 | | | 54 | | | (1) | |
| Other non-operating income | 6 | | | 3 | | | 4 | |
| Total other expense | (209) | | | (51) | | | (116) | |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes | 3,803 | | | (193) | | | 313 | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | (773) | | | 111 | | | (18) | |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | 3,030 | | | (82) | | | 295 | |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | 3 | | | 1 | | | (2) | |
| Net income (loss) | 3,033 | | | (81) | | | 293 | |
| Income attributable to noncontrolling interest | (45) | | | (41) | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders | $ | 2,988 | | | $ | (122) | | | $ | 293 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per common share attributable to Cliffs shareholders - basic | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | $ | 5.62 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.07 | |
| Discontinued operations | 0.01 | | | — | | | (0.01) | |
| $ | 5.63 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.06 | |
| Earnings (loss) per common share attributable to Cliffs shareholders - diluted | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | $ | 5.35 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.04 | |
| Discontinued operations | 0.01 | | | — | | | (0.01) | |
| $ | 5.36 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.03 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Subsidiaries
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 3,033 | | | $ | (81) | | | $ | 293 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Changes in pension and OPEB, net of tax | 684 | | | 181 | | | (35) | |
| Changes in foreign currency translation | (2) | | | 3 | | | — | |
| Changes in derivative financial instruments, net of tax | 69 | | | 2 | | | — | |
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 751 | | | 186 | | | (35) | |
| Comprehensive income | 3,784 | | | 105 | | | 258 | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | (45) | | | (41) | | | — | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to Cliffs shareholders | $ | 3,739 | | | $ | 64 | | | $ | 258 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Subsidiaries
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 3,033 | | | $ | (81) | | | $ | 293 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided (used) by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | 897 | | | 308 | | | 85 | |
| Amortization of inventory step-up | 161 | | | 96 | | | — | |
| Deferred income taxes | 767 | | | (101) | | | 17 | |
| Pension and OPEB costs (credits) | (103) | | | (23) | | | 20 | |
| Loss (gain) on extinguishment of debt | 88 | | | (130) | | | 18 | |
| | | | | |
| Other | 139 | | | (70) | | | 93 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of business combination: | | | | | |
| Receivables and other assets | (858) | | | (42) | | | 255 | |
| Inventories | (1,370) | | | (146) | | | (136) | |
| Pension and OPEB payments and contributions | (343) | | | (75) | | | (20) | |
| Payables, accrued expenses and other liabilities | 374 | | | 6 | | | (57) | |
| Net cash provided (used) by operating activities | 2,785 | | | (258) | | | 568 | |
| INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | | |
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | (705) | | | (525) | | | (656) | |
| Acquisition of FPT, net of cash acquired | (761) | | | — | | | — | |
| Acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA, net of cash acquired | 54 | | | (658) | | | — | |
| Acquisition of AK Steel, net of cash acquired | — | | | (869) | | | — | |
| Other investing activities | 33 | | | 10 | | | 12 | |
| Net cash used by investing activities | (1,379) | | | (2,042) | | | (644) | |
| FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | | |
| Series B Redeemable Preferred Stock redemption | (1,343) | | | — | | | — | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common shares | 322 | | | — | | | — | |
| Repurchase of common shares | — | | | — | | | (253) | |
| | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of debt | 1,000 | | | 1,763 | | | 721 | |
| Debt issuance costs | (20) | | | (76) | | | (7) | |
| Repayments of debt | (1,372) | | | (1,023) | | | (729) | |
| Borrowings under credit facilities | 5,962 | | | 2,060 | | | — | |
| Repayments under credit facilities | (5,889) | | | (550) | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other financing activities | (130) | | | (115) | | | (126) | |
| Net cash provided (used) by financing activities | (1,470) | | | 2,059 | | | (394) | |
| | | | | |
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | (64) | | | (241) | | | (470) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 112 | | | 353 | | | 823 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 48 | | | $ | 112 | | | $ | 353 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Statements of Consolidated Changes in Equity
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Subsidiaries
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Cliffs Shareholders | | | | |
| Number
of
Common
Shares Outstanding | | Par Value of Common
Shares Issued | | Capital in
Excess of
Par Value
of Shares | | Retained Earnings
(Deficit) | | Common
Shares
in
Treasury | | AOCI
(Loss) | | Non-
controlling
Interest | | Total |
| December 31, 2018 | 293 | | | $ | 37 | | | $ | 3,917 | | | $ | (3,060) | | | $ | (186) | | | $ | (284) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 424 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | — | | | — | | | — | | | 293 | | | — | | | (35) | | | — | | | 258 | |
| Stock and other incentive plans | 2 | | | — | | | (44) | | | — | | | 48 | | | — | | | — | | | 4 | |
| Common share repurchases | (24) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (253) | | | — | | | — | | | (253) | |
Common share dividends ($0.27 per share) | — | | | — | | | — | | | (75) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (75) | |
| December 31, 2019 | 271 | | | $ | 37 | | | $ | 3,873 | | | $ | (2,842) | | | $ | (391) | | | $ | (319) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 358 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | — | | | — | | | — | | | (122) | | | — | | | 186 | | | 41 | | | 105 | |
| Stock and other incentive plans | 2 | | | — | | | (24) | | | — | | | 37 | | | — | | | — | | | 13 | |
| Acquisition of AK Steel | 127 | | | 16 | | | 602 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 330 | | | 948 | |
| Acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA | 78 | | | 10 | | | 980 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 13 | | | 1,003 | |
Common share dividends ($0.06 per share) | — | | | — | | | — | | | (25) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (25) | |
| Net distributions to noncontrolling interests | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (61) | | | (61) | |
| December 31, 2020 | 478 | | | $ | 63 | | | $ | 5,431 | | | $ | (2,989) | | | $ | (354) | | | $ | (133) | | | $ | 323 | | | $ | 2,341 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | — | | | — | | | — | | | 2,988 | | | — | | | 751 | | | 45 | | | 3,784 | |
| Issuance of common shares | 20 | | | — | | | 78 | | | — | | | 244 | | | — | | | — | | | 322 | |
| Stock and other incentive plans | 2 | | | — | | | (8) | | | — | | | 28 | | | — | | | — | | | 20 | |
| Series B Redeemable Preferred Stock redemption | — | | | — | | | (604) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (604) | |
| 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes redemption | — | | | — | | | (5) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (5) | |
| Acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA - Measurement period adjustments | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (22) | | | (22) | |
| Net distributions to noncontrolling interests | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (62) | | | (62) | |
| December 31, 2021 | 500 | | | $ | 63 | | | $ | 4,892 | | | $ | (1) | | | $ | (82) | | | $ | 618 | | | $ | 284 | | | $ | 5,774 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Subsidiaries
NOTE 1 - BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Business, Consolidation and Presentation
Nature of Business
Cliffs is the largest flat-rolled steel producer in North America. Founded in 1847 as a mine operator, we are also the largest manufacturer of iron ore pellets in North America. We are vertically integrated from mined raw materials, direct reduced iron and ferrous scrap to primary steelmaking and downstream finishing, stamping, tooling and tubing. We serve a diverse range of markets due to our comprehensive offering of flat-rolled steel products and are the largest supplier of steel to the automotive industry in North America. Headquartered in Cleveland, Ohio, we employ approximately 26,000 people across our operations in the United States and Canada.
Unless otherwise noted, discussion of our business and results of operations in this Annual Report on Form 10-K refers to our continuing operations.
Acquisition of FPT
On November 18, 2021, we completed the acquisition of FPT. FPT is a leading prime ferrous scrap processor in the U.S. FPT's operations consist of 22 scrap facilities located primarily in the Midwest region of the United States.
Refer to NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS for further information.
Business Operations
We are organized into four operating segments based on differentiated products, Steelmaking, Tubular, Tooling and Stamping, and European Operations. We primarily operate through one reportable segment – the Steelmaking segment.
Basis of Consolidation
The condensed consolidated financial statements consolidate our accounts and the accounts of our wholly owned subsidiaries, all subsidiaries in which we have a controlling interest and VIEs for which we are the primary beneficiary. All intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated upon consolidation.
Investments in Affiliates
We have investments in several businesses accounted for using the equity method of accounting. These investments are included within our Steelmaking segment. We review an investment for impairment when circumstances indicate that a loss in value below its carrying amount is other than temporary.
As of December 31, 2019, our 23% ownership in Hibbing was recorded as an equity method investment. As a result of the acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA, we acquired an additional 62.3% ownership interest in Hibbing. As of both December 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, our ownership in the Hibbing joint venture was 85.3% and was fully consolidated within our operating results with a noncontrolling interest.
Our investment in affiliates of $128 million and $105 million as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, was classified in Other non-current assets.
Significant Accounting Policies
We consider the following policies to be beneficial in understanding the judgments involved in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements and the uncertainties that could impact our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform with the current year presentation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the
reporting period. Our mineral reserves; future realizable cash flow; environmental, reclamation and closure obligations; valuation of business combinations, long-lived assets, inventory, tax assets and post-employment, post-retirement and other employee benefit liabilities; reserves for contingencies and litigation require the use of various management estimates and assumptions. Actual results could differ from estimates. Management reviews its estimates on an ongoing basis. Changes in facts and circumstances may alter such estimates and affect the results of operations and financial position in future periods.
Business Combinations
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination are recognized and measured based on their estimated fair values at the acquisition date, while the acquisition-related costs are expensed as incurred. Any excess of the purchase consideration when compared to the fair value of the net tangible and intangible assets acquired, if any, is recorded as goodwill. We engaged independent valuation specialists to assist with the determination of the fair value of assets acquired, liabilities assumed, noncontrolling interest, and goodwill, for the acquisitions. If the initial accounting for the business combination is incomplete by the end of the reporting period in which the acquisition occurs, an estimate will be recorded. Subsequent to the acquisition date, and not later than one year from the acquisition date, we will record any material adjustments to the initial estimate based on new information obtained that would have existed as of the date of the acquisition. Any adjustment that arises from information obtained that did not exist as of the date of the acquisition will be recorded in the period the adjustment arises.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and on deposit as well as all short-term securities held for the primary purpose of general liquidity. We routinely monitor and evaluate counterparty credit risk related to the financial institutions in which our short-term investment securities are held. Where right of offset exists, we report cash balances net.
Trade Accounts Receivable and Allowance for Credit Loss
Trade accounts receivable are recorded at the point control transfers and represent the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferred goods and do not bear interest. We establish provisions for expected lifetime losses on accounts receivable at the time a receivable is recorded based on historical experience, customer credit quality and forecasted economic conditions. We regularly review our accounts receivable balances and the allowance for credit loss and establish or adjust the allowance as necessary using the specific identification method in accordance with CECL. We evaluate the aggregation and risk characteristics of receivable pools and develop loss rates that reflect historical collections, current forecasts of future economic conditions over the time horizon we are exposed to credit risk, and payment terms or conditions that may materially affect future forecasts.
Inventories
Inventories are generally stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value using average cost, excluding depreciation and amortization. Certain iron ore inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market using the LIFO method.
Refer to NOTE 2 - SUPPLEMENTARY FINANCIAL STATEMENT INFORMATION for further information.
Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities
We are exposed to certain risks related to the ongoing operations of our business, including those caused by changes in commodity prices and energy rates. We have established policies and procedures, including the use of certain derivative instruments, to manage such risks.
Derivative financial instruments are recognized as either assets or liabilities in the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position and measured at fair value. On the date a qualifying hedging instrument is executed, we designate the hedging instrument as a hedge of the variability of cash flows to be received or paid related to a forecasted transaction (cash flow hedge). We formally document all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as our risk-management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. This process includes linking all derivatives that are designated as cash flow hedges to specific firm commitments or forecasted transactions. We also formally assess, both at the hedge's inception and on an ongoing basis, whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the related hedged items. When it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge, we discontinue hedge
accounting prospectively and record all future changes in fair value in the period of the instrument's earnings or losses.
For derivative instruments that have been designated as cash flow hedges, the changes in fair value are recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Amounts recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) are reclassified to earnings or losses in the period the underlying hedged transaction affects earnings or when the underlying hedged transaction is no longer reasonably possible of occurring.
For derivative instruments that have not been designated as cash flow hedges, changes in fair value are recorded in the period of the instrument's earnings or losses.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Our properties are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of plant and equipment is computed principally by the straight-line method based on estimated useful lives. Depreciation continues to be recognized when operations are idled temporarily. Depreciation and depletion are recorded over the following estimated useful lives:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asset Class | | Basis | | Life |
| Land, land improvements and mineral rights | | | | |
| Land and mineral rights | | Units of production | | Life of mine |
| Land improvements | | Straight line | | 20 to 45 years |
| Buildings | | Straight line | | 20 to 45 years |
| Equipment | | Straight line/Double declining balance | | 3 to 27 years |
Refer to NOTE 6 - PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT for further information.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess purchase price paid over the fair value of the net assets from an acquisition. Goodwill is not amortized for financial statement purposes, but it is assessed for impairment on an annual basis on October 1 (or more frequently if necessary).
Refer to NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS and NOTE 7 - GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES for further information.
Other Intangible Assets and Liabilities
Intangible assets and liabilities are subject to periodic amortization on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives.
Refer to NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS and NOTE 7 - GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES for further information.
Leases
We determine if an arrangement contains a lease at inception. We recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities associated with leases based on the present value of the future minimum lease payments over the lease term at the commencement date. Lease terms reflect options to extend or terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that the option will be exercised. For short-term leases (leases with an initial lease term of 12 months or less), right-of-use assets and lease liabilities are not recognized in the consolidated balance sheet. Operating lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Refer to NOTE 13 - LEASE OBLIGATIONS for further information.
Asset Impairment
We monitor conditions that may affect the carrying value of our long-lived tangible and intangible assets when events and circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the asset groups may not be recoverable. In order to determine if assets have been impaired, assets are grouped and tested at the lowest level for which identifiable, independent cash flows are available ("asset group"). The measurement of the impairment loss to be recognized is
based on the difference between the fair value and the carrying value of the asset group. Fair value can be determined using a market approach, income approach or cost approach.
For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, no impairment indicators were present that would indicate the carrying value of any of our asset groups may not be recoverable; as a result, no impairment assessments were required.
Fair Value Measurements
ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for classification of fair value measurements. The valuation hierarchy is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date. Inputs refer broadly to the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. Inputs may be observable or unobservable. Observable inputs are inputs that reflect the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on market data obtained from independent sources. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect our own views about the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on the best information available in the circumstances. The three-tier hierarchy of inputs is summarized below:
•Level 1 — Valuation is based upon quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
•Level 2 — Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, or other inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
•Level 3 — Valuation is based upon other unobservable inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement.
The classification of assets and liabilities within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety.
Refer to NOTE 9 - FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS and NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS for further information.
Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits
We offer defined benefit pension plans, defined contribution pension plans and OPEB plans, primarily consisting of retiree healthcare benefits as part of our total compensation and benefits programs.
We recognize the funded or unfunded status of our pension and OPEB obligations on the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position based on the difference between the market value of plan assets and the actuarial present value of our retirement obligations on that date, on a plan-by-plan basis. If the plan assets exceed the pension and OPEB obligations, the amount of the surplus is recorded as an asset; if the pension and OPEB obligations exceed the plan assets, the amount of the underfunded obligations is recorded as a liability. Year-end balance sheet adjustments to pension and OPEB assets and obligations are recorded as Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position.
The actuarial estimates of the PBO and APBO incorporate various assumptions including the discount rates, the rates of increases in compensation, healthcare cost trend rates, mortality, retirement timing and employee turnover. The discount rate is determined based on the prevailing year-end rates for high-grade corporate bonds with a duration matching the expected cash flow timing of the benefit payments from the various plans. The remaining assumptions are based on our estimates of future events by incorporating historical trends and future expectations. The amount of net periodic cost that is recorded in the Statements of Consolidated Operations consists of several components including service cost, interest cost, expected return on plan assets, and amortization of previously unrecognized amounts. Service cost represents the value of the benefits earned in the current year by the participants. Interest cost represents the cost associated with the passage of time. Certain items, such as plan amendments, gains and/or losses resulting from differences between actual and assumed results for demographic and economic factors affecting the obligations and assets of the plans, and changes in other assumptions are subject to deferred recognition for income and expense purposes. The expected return on plan assets is calculated on a plan-by-plan basis using each plan's strategic asset allocation and our expected long-term capital market return assumptions. Service costs are classified within Cost of goods sold, Selling, general and administrative expenses and Miscellaneous – net while the interest cost, expected return on assets, amortization of prior service costs/credits,
net actuarial gain/loss, and other costs are classified within Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component.
Refer to NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS for further information.
Labor Agreements
At December 31, 2021, we employed approximately 26,000 people, of which approximately 18,500 were represented by labor unions under various agreements. We have ten agreements that expire in 2022 and three agreements that expire in 2023. Workers at some of our North American facilities are covered by agreements with the USW, UAW and IAM, as well as several other smaller unions that have various expiration dates.
Asset Retirement Obligations
Asset retirement obligations are recognized when incurred and recorded as liabilities at fair value. The fair value of the liability is determined as the discounted value of the expected future cash flows. The asset retirement obligation is accreted over time through periodic charges to earnings. In addition, the asset retirement cost is capitalized and amortized over the life of the related asset. Reclamation costs are adjusted periodically to reflect changes in the estimated present value resulting from the passage of time and revisions to the estimates of either the timing or amount of the reclamation costs. We review, on an annual basis, unless otherwise deemed necessary, the asset retirement obligation for each applicable operation in accordance with the provisions of ASC Topic 410, Asset Retirement and Environmental Obligations. We perform an in-depth evaluation of the liability every three years in addition to our routine annual assessments.
Future reclamation costs for inactive operations are accrued based on management’s best estimate at the end of each period of the costs expected to be incurred at a site. Such cost estimates include, where applicable, ongoing maintenance and monitoring costs. Changes in estimates at inactive operations are reflected in earnings in the period an estimate is revised.
Refer to NOTE 14 - ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS for further information.
Environmental Remediation Costs
Certain of our operating activities are subject to various laws and regulations governing protection of the environment. We conduct our operations to protect the public health and environment and believe our operations are in compliance with applicable laws and regulations in all material respects. Our environmental liabilities, including obligations for known environmental remediation exposures, have been recognized based on the estimated cost of investigation and remediation at each site. If the cost can only be estimated as a range of possible amounts with no point in the range being more likely, the minimum of the range is accrued. Future expenditures are discounted unless the amount and timing of the cash disbursements cannot be reasonably estimated. It is possible that additional environmental obligations could be incurred, the extent of which cannot be assessed. Potential insurance recoveries have not been reflected in the determination of the liabilities.
Refer to NOTE 20 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES for further information.
Revenue Recognition
Sales are recognized when our performance obligations are satisfied. Generally, our performance obligations are satisfied, control of our products is transferred and revenue is recognized at a single point in time, when title transfers to our customer for product shipped according to shipping terms. Shipping and other transportation costs charged to customers are treated as fulfillment activities and are recorded in both revenue and cost of sales at the time control is transferred to the customer.
Refer to NOTE 4 - REVENUES for further information.
Repairs and Maintenance
Repairs, maintenance and replacement of components are expensed as incurred. The cost of major equipment overhauls is capitalized and depreciated over the estimated useful life, which is the period until the next scheduled overhauls. All other planned and unplanned repairs and maintenance costs are expensed when incurred.
Share-Based Compensation
The fair value of each performance share grant is estimated on the date of grant using a Monte Carlo simulation to forecast relative TSR performance. A correlation matrix of historical and projected stock prices was developed for both the Company and its predetermined peer group of mining and metals companies. The fair value assumes that the performance objective will be achieved. The expected term of the grant represents the time from the grant date to the end of the service period. We estimate the volatility of our common shares and that of the peer group of mining and metals companies using daily price intervals for all companies. The risk-free interest rate is the rate at the grant date on zero-coupon government bonds, with a term commensurate with the remaining performance period.
The fair value of the restricted stock units is determined based on the closing price of our common shares on the grant date.
Upon vesting of share-based compensation awards, we issue shares from treasury shares before issuing new shares. Forfeitures are recognized when they occur.
The fair value of stock options is estimated on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes model using the grant date price of our common shares, the option exercise price, the option’s expected term, the volatility of our common shares, the risk-free interest rate and the dividend yield over the option’s expected term.
Refer to NOTE 11 - STOCK COMPENSATION PLANS for additional information.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are based on income for financial reporting purposes, calculated using tax rates by jurisdiction, and reflect a current tax liability or asset for the estimated taxes payable or recoverable on the current year tax return and expected annual changes in deferred taxes. Any interest or penalties on income tax are recognized as a component of Income tax benefit (expense).
We account for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized within Net income (loss) in the period that includes the enactment date.
We record net deferred tax assets to the extent we believe these assets will more likely than not be realized. In making such determination, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent financial results of operations.
Accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the financial statements requires that a tax benefit from an uncertain tax position be recognized when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on technical merits.
Refer to NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES for further information.
Foreign Currency
Our financial statements are prepared with the U.S. dollar as the reporting currency, and the functional currency of all subsidiaries is the U.S. dollar, except for our European Operations for which the functional currency is the Euro.
Earnings Per Share
We present both basic and diluted EPS amounts for continuing operations and discontinued operations. Total basic EPS amounts are calculated by dividing Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders, less the earnings allocated to our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock, by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period presented.
Total diluted EPS amounts are calculated by dividing Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares, common share equivalents under stock plans using the treasury-stock method, common share equivalents of the Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock using the if-
converted method and the calculated common share equivalents in excess of the conversion rate related to our 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes using the treasury-stock method. Common share equivalents are excluded from EPS computations in the periods in which they have an anti-dilutive effect.
Refer to NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES and NOTE 19 - EARNINGS PER SHARE for further information.
Variable Interest Entities
We assess whether we have a variable interest in legal entities in which we have a financial relationship and, if so, whether or not those entities are VIEs. A VIE is an entity with insufficient equity at risk for the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support or in which equity investors lack the characteristics of a controlling financial interest. If an entity is determined to be a VIE, we evaluate whether we are the primary beneficiary. The primary beneficiary analysis is a qualitative analysis based on power and economics. We conclude that we are the primary beneficiary and consolidate the VIE if we have both (i) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly influence the VIE's economic performance and (ii) the obligation to absorb losses of, or the right to receive benefits from, the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE.
Refer to NOTE 18 - VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES for additional information.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Issued and Not Effective
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-06, Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40). This update requires certain convertible instruments to be accounted for as a single liability measured at its amortized cost. Additionally, the update requires the use of the "if-converted" method, removing the treasury stock method, when calculating diluted shares. The two methods of adoption are the full and modified retrospective approaches. We expect to utilize the modified retrospective approach. Using this approach, the guidance shall be applied to transactions outstanding as of the beginning of the fiscal year in which the amendment is adopted. Subsequent to the year ended December 31, 2021, we redeemed all of our outstanding 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes; therefore, there will be no impact as a result of our adoption of this update as of January 1, 2022. Refer to NOTE 21 - SUBSEQUENT EVENTS for further information.
NOTE 2 - SUPPLEMENTARY FINANCIAL STATEMENT INFORMATION
Allowance for Credit Losses
The following is a roll-forward of our allowance for credit losses associated with Accounts receivable, net:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Allowance for credit losses as of January 1 | $ | (5) | | | $ | — | |
| Decrease (increase) in allowance | 1 | | | (5) | |
| Allowance for credit losses as of December 31 | $ | (4) | | | $ | (5) | |
Inventories
The following table presents the detail of our Inventories in the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Product inventories | | | |
| Finished and semi-finished goods | $ | 2,814 | | | $ | 2,125 | |
| | | |
| Raw materials | 2,070 | | | 1,431 | |
| Total product inventories | 4,884 | | | 3,556 | |
| Manufacturing supplies and critical spares | 304 | | | 272 | |
| Inventories | $ | 5,188 | | | $ | 3,828 | |
The excess of current cost over LIFO cost of iron ore inventories was $124 million and $104 million at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. As of December 31, 2021, the product inventory balance for iron ore inventories increased, resulting in a LIFO increment in 2021. The effect of the inventory build was an increase in Inventories of $45 million in the Statements of Consolidated Operations for the year ended December 31, 2021. As of December 31, 2020, the product inventory balance for iron ore inventories decreased, resulting in the liquidation of a LIFO layer. The effect of the inventory reduction was an increase in Cost of goods sold of $30 million in the Statements of Consolidated Operations for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Cash Flow Information
A reconciliation of capital additions to cash paid for capital expenditures is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Capital additions | $ | 857 | | | $ | 483 | | | $ | 690 | |
| Less: | | | | | |
| Non-cash accruals | 102 | | | (86) | | | 15 | |
| Right-of-use assets - finance leases | 50 | | | 44 | | | 29 | |
| Grants | — | | | — | | | (10) | |
| Cash paid for capital expenditures including deposits | $ | 705 | | | $ | 525 | | | $ | 656 | |
Cash payments (receipts) for interest and income taxes are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Taxes paid on income | $ | 166 | | | $ | 5 | | | $ | — | |
| Income tax refunds | (16) | | | (120) | | | (118) | |
Interest paid on debt obligations net of capitalized interest1 | 299 | | | 170 | | | 98 | |
| | | | | |
1 Capitalized interest was $6 million, $53 million and $25 million for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively. |
Other Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Fair value of settlement of a pre-existing relationship as part of consideration in connection with FPT Acquisition | $ | (20) | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Fair value of common shares issued as part of consideration in connection with AM USA Transaction | — | | | 990 | | | — | |
| Fair value of Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock issued as part of consideration in connection with AM USA Transaction | — | | | 738 | | | — | |
| Fair value of settlement of a pre-existing relationship as part of consideration in connection with AM USA Transaction | — | | | 237 | | | — | |
| Fair value of common shares issued as consideration in connection with AK Steel Merger | — | | | 618 | | | — | |
| Fair value of equity awards assumed in connection with AK Steel Merger | — | | | 4 | | | — | |
NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS
In 2020, we acquired two major steelmakers, AK Steel and ArcelorMittal USA, vertically integrating our legacy iron ore business with steel production. In 2021, we also entered into the scrap business with the FPT Acquisition. We are vertically integrated from mined raw materials, direct reduced iron and ferrous scrap to primary steelmaking and downstream finishing, stamping, tooling and tubing. We now have a presence across the entire steel manufacturing process, from mining to pelletizing to the development and production of finished high value steel products. The AK Steel Merger combined Cliffs, a historic producer of iron ore pellets, with AK Steel, a producer of flat-rolled carbon, stainless and electrical steel products, to create a vertically integrated producer of value-added iron ore and steel products. The AM USA Transaction transformed us into a fully-integrated steel enterprise with the size and scale to expand product offerings and improve through-the-cycle margins. The FPT Acquisition gives us a competitive advantage in sourcing prime scrap, a key raw material for our steelmaking facilities.
FPT Acquisition
Overview
On November 18, 2021, pursuant to the FPT Acquisition Agreement, we completed the FPT Acquisition, in which we were the acquirer. Following the FPT Acquisition, the operating results of FPT are included in our consolidated financial statements. For the period subsequent to the FPT Acquisition (November 18, 2021 through December 31, 2021), FPT generated Revenues of $153 million and a loss of $18 million included within Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders, which included $22 million related to amortization of the fair value inventory step-up.
Additionally, we incurred acquisition-related costs, excluding severance costs, of $1 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 in connection with the FPT Acquisition, which was recorded in Acquisition-related costs on the Statements of Consolidated Operations.
The fair value of the total purchase consideration was determined as follows:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Cash consideration (subject to customary working capital adjustments) | $ | 775 | |
| Fair value of settlement of a pre-existing relationship | (20) | |
| Total purchase consideration | $ | 755 | |
The cash portion of the purchase price is subject to customary working capital adjustments. Additionally, if the Company decides to make any elections under Section 338(h)(10) of the IRC with respect to entities acquired in connection with the FPT Acquisition, the final cash consideration could potentially change.
Valuation Assumption and Purchase Price Allocation
We estimated fair values at November 18, 2021 for the preliminary allocation of consideration to the net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed in connection with the FPT Acquisition. During the measurement period, we will continue to obtain information to assist in finalizing the fair value of assets acquired and
liabilities assumed, which may differ materially from these preliminary estimates. If we determine any measurement period adjustments are material, we will apply those adjustments, including any related impacts to net income, in the reporting period in which the adjustments are determined. We are in the process of conducting a valuation of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed related to the FPT Acquisition, most notably, inventories, personal and real property, leases, investments, deferred taxes, environmental obligations and intangible assets, and the final allocation will be made when completed, including the result of any identified goodwill. Accordingly, the provisional measurements noted below are preliminary and subject to modification in the future.
The preliminary purchase price allocation to assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the FPT Acquisition was:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Initial Allocation of Consideration |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 9 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 233 | |
| Inventories | 137 | |
| Other current assets | 4 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 179 | |
| Other non-current assets | 74 | |
| Accounts payable | (122) | |
| Accrued employment costs | (8) | |
| State and local taxes | (1) | |
| Other current liabilities | (8) | |
| |
| |
| |
| Other non-current liabilities | (21) | |
| |
| Net identifiable assets acquired | 476 | |
| Goodwill | 279 | |
| Total net assets acquired | $ | 755 | |
The goodwill resulting from the FPT Acquisition primarily represents the incremental benefit of providing substantial access to prime scrap for our vertically integrated steelmaking business, as well as any synergistic benefits to be realized from the FPT Acquisition within our Steelmaking segment.
The preliminary purchase price allocated to identifiable intangible assets acquired was:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) | | Weighted Average Life (In Years) |
| Customer relationships | $ | 18 | | | 15 |
| Supplier relationships | 18 | | | 18 |
| Trade names and trademarks | 7 | | | 15 |
| Total identifiable intangible assets | $ | 43 | | | 16 |
Intangible assets are classified as Other non-current assets on the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position.
Acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA
Overview
On December 9, 2020, pursuant to the terms of the AM USA Transaction Agreement, we purchased ArcelorMittal USA from ArcelorMittal. In connection with the closing of the AM USA Transaction, as contemplated by the terms of the AM USA Transaction Agreement, ArcelorMittal’s former joint venture partner in Kote and Tek exercised its put right pursuant to the terms of the Kote and Tek joint venture agreements. As a result, we purchased all of such joint venture partner’s interests in Kote and Tek. Following the closing of the AM USA Transaction, we own 100% of the interests in Kote and Tek.
We incurred acquisition-related costs, excluding severance costs, of $3 million and $26 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, in connection with the AM USA Transaction, which were recorded in Acquisition-related costs on the Statements of Consolidated Operations.
The fair value of the total purchase consideration was determined as follows:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Fair value of Cliffs common shares issued | $ | 990 | |
| Fair value of Cliffs Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock issued | 738 | |
| Fair value of settlement of a pre-existing relationship | 237 | |
| Cash consideration | 639 | |
| Total purchase consideration | $ | 2,604 | |
The fair value of Cliffs common shares issued was calculated as follows:
| | | | | |
| Number of Cliffs common shares issued | 78,186,671 |
| Closing price of Cliffs common share as of December 9, 2020 | $ | 12.66 | |
| Fair value of Cliffs common shares issued (in millions) | $ | 990 | |
The fair value of Cliffs Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock issued was calculated as follows:
| | | | | |
| Number of Cliffs Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock issued | 583,273 | |
| Redemption price per share as of December 9, 2020 | $ | 1,266 | |
| Fair value of Cliffs Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock issued (in millions) | $ | 738 | |
The fair value of the cash consideration was comprised of the following:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Cash consideration pursuant to the AM USA Transaction Agreement | $ | 505 | |
| Cash consideration for purchase of the remaining JV partner's interest of Kote and Tek | 182 | |
| Total cash consideration receivable | (48) | |
| Total cash consideration | $ | 639 | |
The cash portion of the purchase price was subject to customary working capital adjustments, and the working capital adjustments were finalized during the second quarter of 2021. We made certain elections under Section 338(h)(10) of the IRC with respect to entities acquired in connection with the AM USA Transaction, which did not change the final cash consideration.
The fair value of the settlement of a pre-existing relationship was comprised of the following:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Accounts receivable | $ | 97 | |
| Freestanding derivative asset from customer supply agreement | 140 | |
| Total fair value of settlement of a pre-existing relationship | $ | 237 | |
Valuation Assumption and Purchase Price Allocation
The allocation of consideration to the net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed in connection with the AM USA Transaction was based on estimated fair values at December 9, 2020, and was finalized during the quarter ended December 31, 2021. The following is a summary of the purchase price allocation to assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the AM USA Transaction:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Initial Allocation of Consideration | | Measurement
Period Adjustments | | Final Allocation Consideration as of December 31, 2021 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 35 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 35 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 349 | | | (3) | | | 346 | |
| Inventories | 2,115 | | | 14 | | | 2,129 | |
| Other current assets | 34 | | | 2 | | | 36 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 4,017 | | | 387 | | | 4,404 | |
| Deferred income taxes | — | | | 285 | | | 285 | |
| Other non-current assets | 158 | | | 7 | | | 165 | |
| Accounts payable | (736) | | | 8 | | | (728) | |
| Accrued employment costs | (271) | | | 5 | | | (266) | |
| State and local taxes | (76) | | | — | | | (76) | |
| Other current liabilities | (453) | | | 23 | | | (430) | |
| | | | | |
| Pension liability, non-current | (730) | | | — | | | (730) | |
| OPEB liability, non-current | (2,465) | | | — | | | (2,465) | |
| Other non-current liabilities | (598) | | | (171) | | | (769) | |
| Noncontrolling interest | (13) | | | 21 | | | 8 | |
| Net identifiable assets acquired | 1,366 | | | 578 | | | 1,944 | |
| Goodwill | 1,230 | | | (570) | | | 660 | |
| Total net assets acquired | $ | 2,596 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 2,604 | |
During the period subsequent to the AM USA Transaction, we made certain measurement period adjustments to the acquired assets and liabilities assumed due to clarification of information utilized to determine fair value during the measurement period. The measurement period adjustments related to the revaluation of the Company's previously held equity method investment, which is now being consolidated post-acquisition, resulting in a loss of $31 million, within Miscellaneous – net for the year ended December 31, 2021.
The goodwill resulting from the acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA primarily represents the growth opportunities in the automotive, construction, appliances, infrastructure and machinery and equipment markets, as well as any synergistic benefits to be realized from the AM USA Transaction, and was assigned to our flat steel operations within our Steelmaking segment.
Acquisition of AK Steel
Overview
On March 13, 2020, pursuant to the AK Steel Merger Agreement, we completed the acquisition of AK Steel, in which we were the acquirer. As a result of the AK Steel Merger, each share of AK Steel common stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the AK Steel Merger (other than excluded shares) was converted into the right to receive 0.400 Cliffs common shares and, if applicable, cash in lieu of any fractional Cliffs common shares.
We incurred acquisition-related costs, excluding severance costs, of $1 million and $26 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, in connection with the AK Steel Merger, which were recorded in Acquisition-related costs on the Statements of Consolidated Operations.
The fair value of the total purchase consideration was determined as follows:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Fair value of AK Steel debt | $ | 914 | |
| Fair value of Cliffs common shares issued for AK Steel outstanding common stock | 618 | |
| Other | 3 | |
| Total purchase consideration | $ | 1,535 | |
The fair value of Cliffs common shares issued for outstanding shares of AK Steel common stock and with respect to Cliffs common shares underlying converted AK Steel equity awards that vested upon completion of the AK Steel Merger was calculated as follows:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions,
Except Per Share Amounts) |
| Number of shares of AK Steel common stock issued and outstanding | 317 | |
| Exchange ratio | 0.400 | |
| Shares of Cliffs common shares issued to AK Steel stockholders | 127 | |
| Price per share of Cliffs common shares | $ | 4.87 | |
| Fair value of Cliffs common shares issued for outstanding AK Steel common stock | $ | 618 | |
The fair value of AK Steel's debt included in the consideration was calculated as follows:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Credit Facility | $ | 590 | |
| 7.500% Senior Secured Notes due July 2023 | 324 | |
| Fair value of debt included in consideration | $ | 914 | |
Valuation Assumption and Purchase Price Allocation
The allocation of consideration to the net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed in connection with the AK Steel Merger was based on estimated fair values at March 13, 2020, and was finalized during the quarter ended March 31, 2021. The following is a summary of the purchase price allocation to assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the AK Steel Merger:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Initial Allocation of Consideration | | Measurement Period Adjustments | | Final Allocation of Consideration as of March 31, 2021 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 38 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 39 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 666 | | | (2) | | | 664 | |
| Inventories | 1,563 | | | (243) | | | 1,320 | |
| Other current assets | 68 | | | (16) | | | 52 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 2,184 | | | 90 | | | 2,274 | |
| Deferred income taxes | — | | | 69 | | | 69 | |
| Other non-current assets | 475 | | | (4) | | | 471 | |
| Accounts payable | (636) | | | (8) | | | (644) | |
| Accrued employment costs | (94) | | | 1 | | | (93) | |
| State and local taxes | (35) | | | 4 | | | (31) | |
| Other current liabilities | (276) | | | 2 | | | (274) | |
| Long-term debt | (1,179) | | | — | | | (1,179) | |
| Pension liability, non-current | (473) | | | 10 | | | (463) | |
| OPEB liability, non-current | (400) | | | (8) | | | (408) | |
| Other non-current liabilities | (507) | | | 72 | | | (435) | |
| Noncontrolling interest | — | | | (1) | | | (1) | |
| Net identifiable assets acquired | 1,394 | | | (33) | | | 1,361 | |
| Goodwill | 141 | | | 33 | | | 174 | |
| Total net assets acquired | $ | 1,535 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,535 | |
During the period subsequent to the AK Steel Merger, we made certain measurement period adjustments to the acquired assets and liabilities assumed due to clarification of information utilized to determine fair value during the measurement period.
The goodwill resulting from the acquisition of AK Steel was assigned to our downstream Tubular and Tooling and Stamping operating segments. Goodwill is calculated as the excess of the purchase price over the net identifiable assets recognized and primarily represents the growth opportunities in light weighting solutions to automotive customers, as well as any synergistic benefits to be realized. Goodwill from the AK Steel Merger is not expected to be deductible for income tax purposes.
The purchase price allocated to identifiable intangible assets and liabilities acquired was:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) | | Weighted Average Life (In Years) |
| Intangible assets: | | | |
| Customer relationships | $ | 77 | | | 18 |
| Developed technology | 60 | | | 17 |
| Trade names and trademarks | 11 | | | 10 |
| Total identifiable intangible assets | $ | 148 | | | 17 |
| Intangible liabilities: | | | |
| Above-market supply contracts | $ | (71) | | | 12 |
Intangible assets are classified as Other non-current assets on the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position. Intangible liabilities are classified as Other non-current liabilities on the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position.
The above-market supply contracts relate to the long-term coke and energy supply agreements with SunCoke Energy, which includes SunCoke Middletown, a consolidated VIE. Refer to NOTE 18 - VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES for further information.
Pro Forma Results
2020 Acquisitions
The following table provides unaudited pro forma financial information, prepared in accordance with Topic 805, as if ArcelorMittal USA and AK Steel had been acquired as of January 1, 2019:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2020 | | 2019 |
| Revenues | $ | 12,837 | | | $ | 17,163 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders | (520) | | | (11) | |
The unaudited pro forma financial information has been calculated after applying our accounting policies and adjusting the historical results with pro forma adjustments, net of tax, that assume the 2020 Acquisitions occurred on January 1, 2019. Significant pro forma adjustments include the following:
1.The elimination of intercompany revenues between Cliffs and ArcelorMittal USA and AK Steel of $844 million and $1,499 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
2.The 2020 pro forma net loss was adjusted to exclude $96 million of non-recurring inventory acquisition accounting adjustments incurred during the year ended December 31, 2020. The 2019 pro forma net loss was adjusted to include $362 million of non-recurring inventory acquisition accounting adjustments for the year ended December 31, 2019.
3.The elimination of non-recurring transaction costs incurred by Cliffs, AK Steel and ArcelorMittal USA in connection with the 2020 Acquisitions were $93 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. The 2019 pro forma net loss was adjusted to include $93 million of non-recurring transaction cost adjustments for the year ended December 31, 2019.
4.The 2020 pro forma net loss was adjusted to exclude restructuring costs of $1,820 million of non-recurring costs incurred by ArcelorMittal USA prior to the AM USA Transaction.
5.The 2020 and 2019 pro forma net losses were adjusted to exclude $140 million and $129 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, for the impact of reversal of the fees charged for management, financial and legal services under the Industrial Franchise Agreement with the former parent.
6.Total other pro forma adjustments included reduced expenses of $32 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, primarily due to decreased depreciation expense and pension and OPEB expense, offset partially by increased interest and amortization expense.
7.Total other pro forma adjustments included an expense of $76 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, primarily due to increased interest, amortization and pension and OPEB expense, offset partially by decreased depreciation expense.
8.The income tax impact of pro forma transaction adjustments that affect Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders at a statutory rate of 24.3% resulted in an increased benefit to Income tax benefit (expense) of $170 million and $117 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
FPT Acquisition
The following table provides unaudited pro forma financial information, prepared in accordance with Topic 805, as if FPT had been acquired as of January 1, 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Revenues | $ | 21,701 | | | $ | 13,549 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders | 3,074 | | | (526) | |
The unaudited pro forma financial information has been calculated after applying our accounting policies and adjusting the historical results with pro forma adjustments, net of tax, that assume the FPT Acquisition occurred on January 1, 2020. There were no significant pro forma adjustments for the FPT Acquisition.
The unaudited pro forma financial information does not reflect the potential realization of synergies or cost savings, nor does it reflect other costs relating to the integration of the acquired companies. This unaudited pro forma financial information should not be considered indicative of the results that would have actually occurred if the 2020 Acquisitions had been consummated on January 1, 2019, or if the FPT Acquisition had been consummated on January 1, 2020, nor are they indicative of future results.
NOTE 4 - REVENUES
We generate our revenue through product sales, in which shipping terms indicate when we have fulfilled our performance obligations and transferred control of products to our customer. Our revenue transactions consist of a single performance obligation to transfer promised goods. Our contracts with customers define the mechanism for determining the sales price, which is generally fixed upon transfer of control, but the contracts generally do not impose a specific quantity on either party. Quantities to be delivered to the customer are determined at a point near the date of delivery through purchase orders or other written instructions we receive from the customer. Spot market sales are made through purchase orders or other written instructions. We consider our performance obligation to be complete and recognize revenue when control transfers in accordance with shipping terms.
Revenue is measured as the amount of consideration we expect to receive in exchange for transferring product. We reduce the amount of revenue recognized for estimated returns and other customer credits, such as discounts and volume rebates, based on the expected value to be realized. Payment terms are consistent with terms standard to the markets we serve. Sales taxes collected from customers are excluded from revenues.
Prior to the AM USA Transaction, we had a supply agreement with ArcelorMittal USA, which included supplemental revenue or refunds based on the HRC price in the year the iron ore was consumed in ArcelorMittal USA's blast furnaces. As control transferred prior to consumption, the supplemental revenue was recorded in accordance with Topic 815. All sales occurring subsequent to the AM USA Transaction are intercompany and eliminated in consolidation. Included within Revenues related to Topic 815 for the supplemental revenue portion of the supply agreement is derivative revenue of $122 million and $78 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The following table represents our Revenues by market:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Steelmaking: | | | | | |
| Automotive | $ | 4,726 | | | $ | 2,062 | | | $ | — | |
| Infrastructure and manufacturing | 5,380 | | | 784 | | | — | |
| Distributors and converters | 7,671 | | | 696 | | | — | |
Steel producers | 2,124 | | 1,423 | | | 1,990 | |
| Total Steelmaking | 19,901 | | | 4,965 | | | 1,990 | |
| Other Businesses: | | | | | |
| Automotive | 426 | | | 329 | | | — | |
| Infrastructure and manufacturing | 47 | | | 34 | | | — | |
| Distributors and converters | 70 | | | 26 | | | — | |
| Total Other Businesses | 543 | | | 389 | | | — | |
| Total revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | $ | 5,354 | | | $ | 1,990 | |
The following table represents our Revenues by product line:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars In Millions, Sales Volumes in Thousands) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Revenue | | Volume1 | | Revenue | | Volume1 | | Revenue | | Volume1 |
| Steelmaking: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Hot-rolled steel | $ | 5,615 | | | 4,886 | | | $ | 386 | | | 633 | | | $ | — | | | — | |
| Cold-rolled steel | 3,186 | | | 2,790 | | | 490 | | | 682 | | | — | | | — | |
| Coated steel | 5,864 | | | 5,056 | | | 1,747 | | | 1,911 | | | — | | | — | |
| Stainless and electrical steel | 1,622 | | | 674 | | | 868 | | | 416 | | | — | | | — | |
| Plate | 1,316 | | | 1,020 | | | 46 | | | 62 | | | — | | | — | |
| Other steel products | 1,247 | | | 1,460 | | | 46 | | | 79 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other | 1,051 | | | N/A | | 1,382 | | | N/A | | 1,990 | | | N/A |
| Total steelmaking | 19,901 | | | | | 4,965 | | | | | 1,990 | | | |
| Other Businesses: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other | 543 | | | N/A | | 389 | | | N/A | | — | | | N/A |
| Total revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | | | $ | 5,354 | | | | | $ | 1,990 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
1 All product volumes are stated in net tons. |
Deferred Revenue
The table below summarizes our deferred revenue balances:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Deferred Revenue (Current) | | Deferred Revenue (Long-Term) |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Opening balance as of January 1 | $ | 7 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 26 | |
| Net increase (decrease) | 18 | | | (15) | | | — | | | (26) | |
| Closing balance as of December 31 | $ | 25 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Prior to the AK Steel Merger, our iron ore pellet sales agreement with Severstal Dearborn, LLC, subsequently assumed by AK Steel, required supplemental payments to be paid by the customer during the period from 2009 through 2013. Installment amounts received under this arrangement in excess of sales were classified as deferred revenue in the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position upon receipt of payment and the revenue was recognized over the term of the supply agreement, which had extended until 2022, in equal annual installments. As a result of the termination of that iron ore pellet sales agreement, we realized $35 million of deferred revenue, which was recognized within Revenues in the Statements of Consolidated Operations during the year ended December 31, 2020.
NOTE 5 - SEGMENT REPORTING
We are vertically integrated from mined raw materials and direct reduced iron and ferrous scrap to primary steelmaking and downstream finishing, stamping, tooling and tubing. We are organized into four operating segments based on our differentiated products - Steelmaking, Tubular, Tooling and Stamping, and European Operations. We have one reportable segment - Steelmaking. The operating segment results of our Tubular, Tooling and Stamping, and European Operations that do not constitute reportable segments are combined and disclosed in the Other Businesses category. Our Steelmaking segment operates as the largest flat-rolled steel producer supported by being the largest iron ore pellet producer as well as a leading prime scrap processor in North America, primarily serving the automotive, infrastructure and manufacturing, and distributors and converters markets. Our Other Businesses primarily include the operating segments that provide customer solutions with carbon and stainless steel tubing products, advanced-engineered solutions, tool design and build, hot- and cold-stamped steel components, and complex assemblies. All intersegment transactions were eliminated in consolidation.
We evaluate performance on an operating segment basis, as well as a consolidated basis, based on Adjusted EBITDA, which is a non-GAAP measure. This measure is used by management, investors, lenders and other external users of our financial statements to assess our operating performance and to compare operating performance to other companies in the steel industry. In addition, management believes Adjusted EBITDA is a useful measure to assess the earnings power of the business without the impact of capital structure and can be used to assess our ability to service debt and fund future capital expenditures in the business.
Our results by segment are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Steelmaking | $ | 19,901 | | | $ | 4,965 | | | $ | 1,990 | |
| Other Businesses | 543 | | | 389 | | | — | |
| Total revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | $ | 5,354 | | | $ | 1,990 | |
| | | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA: | | | | | |
| Steelmaking | $ | 5,422 | | | $ | 433 | | | $ | 636 | |
| Other Businesses | 9 | | | 47 | | | — | |
| Corporate and eliminations | (169) | | | (127) | | | (111) | |
| Total Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 5,262 | | | $ | 353 | | | $ | 525 | |
The following table provides a reconciliation of our consolidated Net income (loss) to total Adjusted EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 3,033 | | | $ | (81) | | | $ | 293 | |
| Less: | | | | | |
| Interest expense, net | (337) | | | (238) | | | (101) | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | (773) | | | 111 | | | (18) | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | (897) | | | (308) | | | (85) | |
| 5,040 | | | 354 | | | 497 | |
| Less: | | | | | |
EBITDA from noncontrolling interests1 | 75 | | | 56 | | | — | |
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt | (88) | | | 130 | | | (18) | |
| Severance costs | (15) | | | (38) | | | (2) | |
| Acquisition-related costs excluding severance costs | (5) | | | (52) | | | (7) | |
| Acquisition-related loss on equity method investment | (31) | | | — | | | — | |
| Amortization of inventory step-up | (161) | | | (96) | | | — | |
| Impact of discontinued operations | 3 | | | 1 | | | (1) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Total Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 5,262 | | | $ | 353 | | | $ | 525 | |
| | | | | |
1 EBITDA of noncontrolling interests includes the following: | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | $ | 45 | | | $ | 41 | | | $ | — | |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization | 30 | | | 15 | | | — | |
| EBITDA of noncontrolling interests | $ | 75 | | | $ | 56 | | | $ | — | |
The following table summarizes our depreciation, depletion and amortization and capital additions by segment:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Depreciation, depletion and amortization: | | | | | |
| Steelmaking | $ | 855 | | | $ | 276 | | | $ | 80 | |
| Other Businesses | 37 | | | 27 | | | — | |
| Corporate | 5 | | | 5 | | | 5 | |
| Total depreciation, depletion and amortization | $ | 897 | | | $ | 308 | | | $ | 85 | |
| | | | | |
Capital additions1: | | | | | |
| Steelmaking | $ | 787 | | | $ | 436 | | | $ | 687 | |
| Other Businesses | 52 | | | 45 | | | — | |
| Corporate | 18 | | | 2 | | | 3 | |
| Total capital additions | $ | 857 | | | $ | 483 | | | $ | 690 | |
| | | | | |
1 Refer to NOTE 2 - SUPPLEMENTARY FINANCIAL STATEMENT INFORMATION for additional information. |
The following summarizes our assets by segment:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Assets: | | | |
| Steelmaking | $ | 18,326 | | | $ | 15,849 | |
| Other Businesses | 306 | | | 239 | |
| Total segment assets | 18,632 | | | 16,088 | |
| Corporate | 343 | | | 683 | |
| Total assets | $ | 18,975 | | | $ | 16,771 | |
Included in the consolidated financial statements are the following amounts relating to geographic location based on product destination:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| United States | $ | 18,881 | | | $ | 4,580 | | | $ | 1,505 | |
| Canada | 803 | | | 602 | | | 448 | |
| Other countries | 760 | | | 172 | | | 37 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | $ | 5,354 | | | $ | 1,990 | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net: | | | | | |
| United States | $ | 9,092 | | | $ | 8,647 | | | $ | 1,929 | |
| Canada | 93 | | | 91 | | | — | |
| Other countries | 1 | | | 5 | | | — | |
| Total property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 9,186 | | | $ | 8,743 | | | $ | 1,929 | |
NOTE 6 - PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
The following table indicates the carrying value of each of the major classes of our depreciable assets:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Land, land improvements, and mineral rights | $ | 1,291 | | | $ | 1,213 | |
| Buildings | 889 | | | 703 | |
| Equipment | 8,709 | | | 6,786 | |
| Other | 229 | | | 151 | |
| Construction in progress | 408 | | | 1,364 | |
Total property, plant and equipment1 | 11,526 | | | 10,217 | |
| Allowance for depreciation and depletion | (2,340) | | | (1,474) | |
| Property, plant, and equipment, net | $ | 9,186 | | | $ | 8,743 | |
| | | |
1 Includes right-of-use assets related to finance leases of $411 million and $361 million as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. |
We recorded depreciation expense of $848 million, $298 million and $77 million for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
We recorded capitalized interest into property, plant and equipment of $6 million, $53 million and $25 million during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The net book value of the mineral and land rights are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Mineral rights: | | | |
| Cost | $ | 780 | | | $ | 773 | |
| Depletion | (187) | | | (142) | |
| Net mineral rights | $ | 593 | | | $ | 631 | |
| | | |
| Land rights | $ | 406 | | | $ | 361 | |
We recorded depletion expense of $46 million, $8 million and $8 million for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019, respectively.
NOTE 7 - GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
Goodwill
The following is a summary of Goodwill by segment:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Steelmaking | $ | 942 | | | $ | 1,232 | |
| Other Businesses | 174 | | | 174 | |
| Total goodwill | $ | 1,116 | | | $ | 1,406 | |
The decrease of $290 million in the balance of Goodwill in our Steelmaking segment as of December 31, 2021, compared to December 31, 2020, is due to the decrease in estimated identified goodwill as a result of measurement period adjustments to the purchase price allocation for the acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA, partially offset by the increase due to the preliminary assignment of Goodwill in 2021 based on the preliminary purchase price allocation for the acquisition of FPT. Refer to NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS for further details.
Intangible Assets and Liabilities
The following is a summary of our intangible assets and liabilities:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| | Gross Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Amount | | Gross Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Amount |
Intangible assets1: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Customer relationships | | $ | 95 | | | $ | (8) | | | $ | 87 | | | $ | 77 | | | $ | (3) | | | $ | 74 | |
| Developed technology | | 60 | | | (6) | | | 54 | | | 60 | | | (3) | | | 57 | |
| Trade names and trademarks | | 18 | | | (2) | | | 16 | | | 11 | | | (1) | | | 10 | |
| Mining permits | | 72 | | | (26) | | | 46 | | | 72 | | | (25) | | | 47 | |
| Supplier relationships | | 18 | | | — | | | 18 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total intangible assets | | $ | 263 | | | $ | (42) | | | $ | 221 | | | $ | 220 | | | $ | (32) | | | $ | 188 | |
Intangible liabilities2: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Above-market supply contracts | | $ | (71) | | | $ | 14 | | | $ | (57) | | | $ | (71) | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (64) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
1 Intangible assets are classified as Other non-current assets. Amortization related to mining permits is recognized in Cost of goods sold. Amortization of all other intangible assets is recognized in Selling, general and administrative expenses. |
2 Intangible liabilities are classified as Other non-current liabilities. Amortization of all intangible liabilities is recognized in Cost of goods sold. |
Amortization expense related to intangible assets was $10 million and $8 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Estimated future amortization expense related to intangible assets is $13 million annually for the years 2022 through 2026.
Income from amortization related to intangible liabilities was $7 million in both of the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020. Estimated future amortization income related to the intangible liabilities is $5 million annually for the years 2022 through 2026.
NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES
The following represents a summary of our long-term debt:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, 2021 |
| Debt Instrument | | Issuer1 | | Annual Effective Interest Rate | | Total Principal Amount | | Unamortized Debt Issuance Costs | | Unamortized Premiums (Discounts) | | Total Debt |
| Senior Secured Notes: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes | | Cliffs | | 10.57% | | $ | 607 | | | $ | (4) | | | $ | (13) | | | $ | 590 | |
6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.99% | | 845 | | | (16) | | | (7) | | | 822 | |
| Senior Unsecured Notes: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.26% | | 294 | | | (3) | | | (39) | | | 252 | |
7.000% 2027 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 9.24% | | 73 | | | — | | | (7) | | | 66 | |
7.000% 2027 AK Senior Notes | | AK Steel | | 9.24% | | 56 | | | — | | | (5) | | | 51 | |
5.875% 2027 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.49% | | 556 | | | (3) | | | (15) | | | 538 | |
4.625% 2029 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 4.63% | | 500 | | | (8) | | | — | | | 492 | |
4.875% 2031 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 4.88% | | 500 | | | (8) | | | — | | | 492 | |
6.250% 2040 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.34% | | 263 | | | (2) | | | (3) | | | 258 | |
| IRBs due 2024 to 2028 | | AK Steel | | Various | | 66 | | | — | | | 2 | | | 68 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
ABL Facility3 | | Cliffs2 | | 1.87% | | 4,500 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,609 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total long-term debt | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 5,238 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
1 Unless otherwise noted, references in this column and throughout this NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES to "Cliffs" are to Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., and references to "AK Steel" are to AK Steel Corporation (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Steel Corporation). |
2 Refers to Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. as borrower under our ABL Facility. |
3 The total principal amount for the ABL Facility is stated at the maximum borrowing capacity. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, 2020 |
| Debt Instrument | | Issuer1 | | Annual Effective Interest Rate | | Total Principal Amount | | Unamortized
Debt Issuance Costs | | Unamortized Premiums (Discounts) | | Total Debt |
| Senior Secured Notes: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes | | Cliffs | | 5.00% | | $ | 395 | | | $ | (3) | | | $ | (1) | | | $ | 391 | |
9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes | | Cliffs | | 10.57% | | 955 | | | (8) | | | (25) | | | 922 | |
6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.99% | | 845 | | | (20) | | | (9) | | | 816 | |
| Senior Unsecured Notes: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes | | AK Steel | | 7.33% | | 34 | | | — | | | — | | | 34 | |
7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes | | AK Steel | | 6.17% | | 13 | | | — | | | — | | | 13 | |
6.375% 2025 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 8.11% | | 64 | | | — | | | (4) | | | 60 | |
6.375% 2025 AK Senior Notes | | AK Steel | | 8.11% | | 29 | | | — | | | (2) | | | 27 | |
1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.26% | | 296 | | | (4) | | | (49) | | | 243 | |
5.750% 2025 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.01% | | 396 | | | (3) | | | (4) | | | 389 | |
7.000% 2027 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 9.24% | | 73 | | | — | | | (8) | | | 65 | |
7.000% 2027 AK Senior Notes | | AK Steel | | 9.24% | | 56 | | | — | | | (6) | | | 50 | |
5.875% 2027 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.49% | | 556 | | | (4) | | | (18) | | | 534 | |
6.250% 2040 Senior Notes | | Cliffs | | 6.34% | | 263 | | | (2) | | | (3) | | | 258 | |
| IRBs due 2024 to 2028 | | AK Steel | | Various | | 92 | | | — | | | 2 | | | 94 | |
EDC Revolving Facility3 | | * | | 3.25% | | 40 | | | — | | | — | | | 18 | |
ABL Facility3 | | Cliffs2 | | 2.15% | | 3,500 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,510 | |
| Total debt | | | | | | | | | | | | 5,424 | |
| Less: current | | | | | | | | | | | | 34 | |
| Total long-term debt | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 5,390 | |
*Our subsidiaries, Fleetwood Metal Industries Inc. and The Electromac Group Inc., were the borrowers under the EDC Revolving Facility. |
1 Unless otherwise noted, references in this column and throughout this NOTE 8 - DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES to "Cliffs" are to Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., and references to "AK Steel" are to "AK Steel Corporation (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Steel Corporation). |
2 Refers to Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. as borrower under our ABL Facility. |
3 The total principal amounts for the indicated credit facilities are stated at their respective maximum borrowing capacities. |
Outstanding Senior Secured Notes
The following represents a summary of our senior secured notes' maturity and interest payable due dates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt Instrument | | Maturity | | Interest Payable
(until maturity) |
| 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes | | October 17, 2025 | | April 17 and October 17 |
| 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes | | March 15, 2026 | | March 15 and September 15 |
The senior secured notes of each series are jointly and severally and fully and unconditionally guaranteed on a senior secured basis by substantially all of our material domestic subsidiaries and are secured (subject in each case to certain exceptions and permitted liens) by (i) a first-priority lien, on a pari passu basis with the senior secured notes of the other series, on substantially all of our assets and the assets of the guarantors, other than the ABL Collateral (as defined below), and (ii) a second-priority lien on the ABL Collateral, which is junior to a first-priority lien for the benefit of the lenders under our ABL Facility.
We may redeem the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes, in whole or in part, at any time at our option upon not less than 30, and not more than 60, days' prior notice sent to the holders of the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes. The 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes are redeemable prior to October 17, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus a "make-whole" premium set forth in the indenture, plus accrued
and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption. We may also redeem up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes prior to October 17, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 109.875% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including, the date of redemption with the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings. On March 11, 2021, we exercised this optional redemption feature when we purchased $322 million aggregate principal amount of the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes using the net proceeds from the underwritten public offering of 20 million common shares. The 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes are redeemable beginning on October 17, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 107.406% of the principal amount thereof, decreasing on each April 17 thereafter until April 17, 2025, on and after which the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes are redeemable at par, in each case, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption.
We may redeem the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes in whole or in part, at any time at our option upon not less than 30, and not more than 60, days' prior notice sent to the holders of the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes. The 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes are redeemable prior to March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus a "make-whole" premium set forth in the indenture, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption. We may also redeem up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes prior to March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 106.750% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including, the date of redemption with the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings. The 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes are redeemable beginning on March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 105.063% of the principal amount thereof, decreasing on each March 15 thereafter until March 15, 2025, on and after which the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes are redeemable at par, in each case, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption.
In addition, if a change in control triggering event, as defined in the indenture, occurs with respect to the senior secured notes, we will be required to offer to purchase the notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of their principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of purchase.
The terms of the senior secured notes contain certain customary covenants; however, there are no financial covenants.
Outstanding Senior Unsecured Notes
2021 Issuances
On February 17, 2021, we entered into an indenture among Cliffs, the guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee, relating to the issuances of $500 million aggregate principal amount of 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and $500 million aggregate principal amount of 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes, each issued at par. The 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes were issued in private placement transactions exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act.
The 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes are unsecured senior obligations and rank equally in right of payment with all of our existing and future unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness. The 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by our material direct and indirect wholly owned domestic subsidiaries and, therefore, are structurally senior to any of our existing and future indebtedness that is not guaranteed by such guarantors and are structurally subordinated to all existing and future indebtedness and other liabilities of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes.
In addition, if a change in control triggering event, as defined in the indenture, occurs with respect to the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes, we will be required to offer to repurchase the notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of their principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of repurchase.
The terms of the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes contain certain customary covenants; however, there are no financial covenants.
4.625% 2029 Senior Notes
The 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes bear interest at a rate of 4.625% per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, commencing on September 1, 2021. The 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes will mature on March 1, 2029.
The 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes may be redeemed, in whole or in part, on not less than 10, nor more than 60, days’ prior notice sent to the holders of the notes. The following is a summary of redemption prices for our 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Redemption Period | | Redemption Price1 | | Restricted Amount |
| Prior to March 1, 2024 - using the proceeds of equity issuance | | 104.625 | | % | | Up to 35% of original aggregate principal |
Prior to March 1, 20242 | | 100.000 | | | | |
| Beginning March 1, 2024 | | 102.313 | | | | |
| Beginning March 1, 2025 | | 101.156 | | | | |
| Beginning on March 1, 2026 and thereafter | | 100.000 | | | | |
| | | | | |
1 Plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, up to, but excluding, the redemption date. |
2 Plus a "make-whole" premium. |
4.875% 2031 Senior Notes
The 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes bear interest at a rate of 4.875% per annum, payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, commencing on September 1, 2021. The 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes will mature on March 1, 2031.
The 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes may be redeemed, in whole or in part, on not less than 10, nor more than 60, days’ prior notice sent to the holders of the notes. The following is a summary of redemption prices for our 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Redemption Period | | Redemption Price1 | | Restricted Amount |
| Prior to March 1, 2026 - using the proceeds of equity issuance | | 104.875 | | % | | Up to 35% of original aggregate principal |
Prior to March 1, 2026 2 | | 100.000 | | | | |
| Beginning March 1, 2026 | | 102.438 | | | | |
| Beginning March 1, 2027 | | 101.625 | | | | |
| Beginning March 1, 2028 | | 100.813 | | | | |
| Beginning on March 1, 2029 and thereafter | | 100.000 | | | | |
| | | | | |
1 Plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, up to, but excluding, the redemption date. |
2 Plus a "make-whole" premium. |
1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes
The 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes bear interest at a rate of 1.500% per year, payable semiannually in arrears on January 15 and July 15 of each year. The 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes mature on January 15, 2025. The 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations and rank senior in right of payment to any of our indebtedness that is expressly subordinated in right of payment to the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes; equal in right of payment to any of our unsecured indebtedness that is not so subordinated; effectively junior in right of payment to any of our secured indebtedness to the extent of the value of the assets securing such indebtedness; and structurally junior to all indebtedness and other liabilities (including trade payables) of our subsidiaries. The terms of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes contain certain customary covenants; however, there are no financial covenants.
Holders may convert their 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes at their option at any time prior to the close of business on the business day immediately preceding July 15, 2024, only under the following circumstances: (1) during any calendar quarter commencing after the calendar quarter ending on March 31, 2018, if the last reported sale price of our common shares, par value $0.125 per share, for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during a period of 30 consecutive trading days ending on the last trading day of the immediately preceding calendar quarter is greater than or equal to 130% of the conversion price on each applicable trading day; (2) during the five-business day period after any five-consecutive trading day period (the “measurement period”) in which the trading price per $1,000 principal amount of 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes for each trading day of
the measurement period was less than 98% of the product of the last reported sale price of our common shares and the conversion rate on each such trading day; (3) if we call the notes for redemption, at any time prior to the close of business on the scheduled trading day immediately preceding the redemption date; or (4) upon the occurrence of specified corporate events. On or after July 15, 2024 until the close of business on the second scheduled trading day immediately preceding the maturity date, holders may convert their 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes at any time, regardless of the foregoing circumstances. Upon conversion, we will pay or deliver, as the case may be, cash, common shares or a combination of cash and common shares, at our election.
Upon the issuance of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes the initial conversion rate was 122.4365 common shares per $1,000 principal, with a conversion price of $8.17 per common share. The conversion rate is subject to adjustment in some circumstances, including the payment of dividends on common shares, but will not be adjusted for any accrued and unpaid interest. In addition, following certain corporate events that occur prior to the maturity date, or if we deliver a notice of redemption, we will, in certain circumstances, increase the conversion rate for a holder who elects to convert its 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes in connection with such a corporate event or notice of redemption, as the case may be. As of December 31, 2021, the conversion rate was 129.2985 common shares per $1,000 principal amount of 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes.
We may not redeem the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes prior to January 15, 2022. We may redeem all or any portion of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes, for cash at our option on or after January 15, 2022 if the last reported sale price of our common shares has been at least 130% of the conversion price then in effect for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during any 30-consecutive trading day period (including the last trading day of such period) ending on, and including, the trading day immediately preceding the date on which we provide notice of redemption at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes to be redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the redemption date.
If we undergo a fundamental change as defined in the indenture, holders may require us to repurchase for cash all or any portion of their 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes at a fundamental change repurchase price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes to be repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the fundamental change repurchase date.
In accounting for the issuance of the notes, we separated the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes into liability and equity components. The carrying amount of the liability component was calculated by measuring the fair value of similar liabilities that did not have associated convertible features. The carrying amount of the equity component of $86 million representing the conversion option was determined by deducting the fair value of the liability component from the par value of the notes. The difference represents the debt discount that is amortized to interest expense over the term of the notes. The equity component is not remeasured as long as it continues to qualify for equity classification.
On December 1, 2021, we issued a notice of redemption for all $294 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes. Refer to NOTE 21 - SUBSEQUENT EVENTS for further information on the redemption of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes.
Other Outstanding Unsecured Senior Notes
The following represents a summary of our other unsecured senior notes' maturity and interest payable due dates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt Instrument | | Maturity | | Interest Payable
(until maturity) |
| 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes | | March 15, 2027 | | March 15 and September 15 |
| 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes | | June 1, 2027 | | June 1 and December 1 |
| 6.250% 2040 Senior Notes | | October 1, 2040 | | April 1 and October 1 |
The senior notes are unsecured obligations and rank equally in right of payment with all our other existing and future unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness. The 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes and 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by our material direct and indirect wholly owned domestic subsidiaries and, therefore, are structurally senior to any of our existing and future indebtedness that is not guaranteed by such guarantors and are structurally subordinated to all existing and future indebtedness and other liabilities of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the notes. There are no subsidiary guarantees of the interest and principal amounts for the 6.250% 2040 Senior Notes.
The 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes may be redeemed, in whole or in part, at any time at our option upon not less than 30, and not more than 60 days' prior notice sent to the holders. The 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable prior to March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus a "make-whole" premium set forth in the indenture, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption. The 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable beginning on March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 103.500% of the principal amount thereof, decreasing on each March 15 thereafter until March 15, 2025, on and after which the 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable at par, in each case, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption.
The 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable prior to June 1, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus a “make-whole” premium set forth in the indenture, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption. We may also redeem up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of the 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes prior to June 1, 2022 at a redemption price equal to 105.875% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption with the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings. The 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable beginning on June 1, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 102.938% of the principal amount thereof, decreasing on each June 1 thereafter until June 1, 2025, on and after which the 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable at par, in each case, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption.
The 6.250% 2040 Senior Notes may be redeemed any time at our option upon not less than 30, nor more than 60, days' prior notice is sent to the holders. The 6.250% 2040 Senior Notes are redeemable at a redemption price equal to the greater of (1) 100% of the principal amount of the notes to be redeemed or (2) the sum of the present values of the remaining scheduled payments of principal and interest on the notes to be redeemed, discounted to the redemption date on a semi-annual basis at the treasury rate plus 40 basis points, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption.
In addition, if a change of control triggering event, as defined in the applicable indenture, occurs with respect to the unsecured notes, we will be required to offer to purchase the notes of the applicable series at a purchase price equal to 101% of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of purchase.
The terms of the unsecured notes contain certain customary covenants; however, there are no financial covenants.
AK Steel Corporation Unsecured Senior Notes
As of December 31, 2021, AK Steel had outstanding a total of $56 million aggregate principal amount of 7.000% 2027 AK Senior Notes. These senior notes are unsecured obligations and rank equally in right of payment with AK Steel's guarantees of Cliffs' unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness. These notes contain no financial covenants.
The 7.000% 2027 AK Senior Notes may be redeemed, in whole or in part, at any time at our option upon not less than 30, and not more than 60, days' prior notice sent to the holders. The 7.000% 2027 AK Senior Notes are redeemable prior to March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus a “make-whole” premium set forth in the indenture, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption. The 7.000% 2027 AK Senior Notes are redeemable beginning on March 15, 2022, at a redemption price equal to 103.500% of the principal amount thereof, decreasing on each March 15 thereafter until March 15, 2025, on and after which the 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes are redeemable at par, in each case, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption.
ABL Facility
On March 13, 2020, in connection with the AK Steel Merger, we entered into a new ABL Facility with various financial institutions to replace and refinance Cliffs’ Former ABL Facility and AK Steel Corporation’s former revolving credit facility. The ABL Facility will mature upon the earlier of March 13, 2025 or 91 days prior to the maturity of certain other material debt and provided for up to $2 billion in borrowings, including a $555 million sublimit for the issuance of letters of credit and a $125 million sublimit for swingline loans. Availability under the ABL Facility is limited to an eligible borrowing base, as applicable, determined by applying customary advance rates to eligible accounts receivable, inventory and certain mobile equipment.
On March 27, 2020, we amended our ABL Facility to, among other things, provide for a new FILO tranche B of commitments in the aggregate amount of $150 million by exchanging existing commitments under the ABL Facility.
The total commitments under the ABL Facility after giving effect to this first amendment remained at $2 billion. The terms and conditions (other than the pricing) that apply to the FILO tranche were substantially the same as the terms and conditions that apply to the tranche A facility of the ABL Facility immediately prior to the amendment.
On December 9, 2020, we entered into the Second ABL Amendment. The Second ABL Amendment modified the ABL Facility to, among other things, increase the amount of tranche A revolver commitments available thereunder by an additional $1.5 billion and increase certain dollar baskets related to certain negative covenants that apply to the ABL Facility. After giving effect to the ABL Amendment, the aggregate principal amount of tranche A revolver commitments under the ABL Facility was $3.35 billion and the aggregate principal amount of FILO tranche B revolver commitments under the ABL Facility remained at $150 million.
On December 17, 2021, we entered into the Third ABL Amendment. The Third ABL Amendment modified the ABL Facility to, among other things, increase the amount of tranche A revolver commitments available thereunder by an additional $1 billion and exchange $150 million of tranche B revolver commitments available thereunder for tranche A revolver commitments. After giving effect to the Third ABL Amendment, the aggregate principal amount of tranche A revolver commitments under the ABL Facility is $4.5 billion and there are no remaining tranche B revolver commitments under the ABL Facility. The increase is a result of a larger projected borrowing base driven by more favorable market conditions.
The ABL Facility and certain bank products and hedge obligations are guaranteed by certain of our existing wholly owned U.S. subsidiaries and are required to be guaranteed by certain of our future U.S. subsidiaries. Amounts outstanding under the ABL Facility are secured by (i) a first-priority security interest in the accounts receivable and other rights to payment, inventory, as-extracted collateral, certain investment property, deposit accounts, securities accounts, certain general intangibles and commercial tort claims, certain mobile equipment, commodities accounts and other related assets of ours, the other borrowers and the guarantors, and proceeds and products of each of the foregoing (collectively, the “ABL Collateral”) and (ii) a second-priority security interest in substantially all of our assets and the assets of the other borrowers and the guarantors other than the ABL Collateral.
Borrowings under the ABL Facility bear interest, at our option, at a base rate or, if certain conditions are met, a LIBOR rate, in each case, plus an applicable margin. We may amend our ABL Facility to replace the LIBOR rate with one or more secured overnight financing based rates or an alternative benchmark rate, giving consideration to any evolving or then-existing convention for similar dollar denominated syndicated credit facilities for such alternative benchmarks.
The ABL Facility contains customary representations and warranties and affirmative and negative covenants including, among others, covenants regarding the maintenance of certain financial ratios if certain conditions are triggered, covenants relating to financial reporting, covenants relating to the payment of dividends on, or purchase or redemption of, our capital stock, covenants relating to the incurrence or prepayment of certain debt, covenants relating to the incurrence of liens or encumbrances, covenants relating to compliance with laws, covenants relating to transactions with affiliates, covenants relating to mergers and sales of all or substantially all of our assets and limitations on changes in the nature of our business.
The ABL Facility provides for customary events of default, including, among other things, the event of nonpayment of principal, interest, fees or other amounts, a representation or warranty proving to have been materially incorrect when made, failure to perform or observe certain covenants within a specified period of time, a cross-default to certain material indebtedness, the bankruptcy or insolvency of the Company and certain of its subsidiaries, monetary judgment defaults of a specified amount, invalidity of any loan documentation, a change of control of the Company, and ERISA defaults resulting in liability of a specified amount. If an event of default exists (beyond any applicable grace or cure period), the administrative agent may, and at the direction of the requisite number of lenders shall, declare all amounts owing under the ABL Facility immediately due and payable, terminate such lenders’ commitments to make loans under the ABL Facility and/or exercise any and all remedies and other rights under the ABL Facility. For certain events of default related to insolvency and receivership, the commitments of the lenders will be automatically terminated and all outstanding loans and other amounts will become immediately due and payable.
As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, we were in compliance with the ABL Facility liquidity requirements and, therefore, the springing financial covenant requiring a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of 1.0 to 1.0 was not applicable.
The following represents a summary of our borrowing capacity under the ABL Facility:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31,
2021 |
Available borrowing base on ABL Facility1 | $ | 4,500 | |
| Borrowings | (1,609) | |
Letter of credit obligations2 | (175) | |
| Borrowing capacity available | $ | 2,716 | |
| |
1 As of December 31, 2021, the ABL Facility has a maximum available borrowing base of $4.5 billion. The borrowing base is determined by applying customary advance rates to eligible accounts receivable, inventory and certain mobile equipment. |
2 We issued standby letters of credit with certain financial institutions in order to support business obligations including, but not limited to, workers' compensation, employee severance, insurance, operating agreements and environmental obligations. |
Other Financing Arrangements
Industrial Revenue Bonds
AK Steel had outstanding $66 million aggregate principal amount of fixed-rate, tax-exempt IRBs as of December 31, 2021. The weighted-average fixed rate of these IRBs is 6.86%. These IRBs are unsecured senior debt obligations that are equal in ranking with AK Steel's senior notes and AK Steel's guarantees of Cliffs' unsubordinated indebtedness. These IRBs are effectively subordinated to AK Steel’s guarantees of Cliffs’ secured indebtedness to the extent of the value of AK Steel’s assets securing such guarantees. These IRBs contain certain customary covenants; however, there are no financial covenants.
Debt Extinguishment - 2021
During the fourth quarter of 2021, we paid in full the outstanding balance of our EDC revolving facilities for $55 million in aggregate principal amount and terminated the agreements. Prior to such terminations, the EDC revolving facilities provided for up to $80 million in borrowings.
On October 15, 2021, we redeemed $26 million in aggregate principal amount of the IRBs due 2024. During the third quarter of 2021, we repurchased $2 million in aggregate principal amount of 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes. On June 28, 2021, we redeemed all $396 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of the 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes using available liquidity. During the second quarter of 2021, we also repurchased $25 million aggregate principal amount of 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes.
On March 11, 2021, we purchased $322 million aggregate principal amount of the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes using the net proceeds from the February 11, 2021 issuance of 20 million common shares and cash on hand. On March 12, 2021, we fully redeemed the 4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes, 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes, 7.50% 2023 AK Senior Notes, 6.375% 2025 Senior Notes and 6.375% 2025 AK Senior Notes, which totaled an aggregate principal amount of $535 million.
The following is a summary of the debt extinguished and the respective impact on extinguishment:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended
December 31, 2021 |
| Debt Extinguished | | (Loss) on Extinguishment |
| 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes | $ | 347 | | | $ | (47) | |
| 4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes | 395 | | | (14) | |
| 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes | 34 | | | — | |
| 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes | 13 | | | — | |
| 6.375% 2025 Senior Notes | 64 | | | (7) | |
| 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes | 2 | | | — | |
| 6.375% 2025 AK Senior Notes | 29 | | | (3) | |
| 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes | 396 | | | (17) | |
| IRBs due 2024 | 26 | | | — | |
| Total | $ | 1,306 | | | $ | (88) | |
Debt Extinguishment - 2020
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we used the net proceeds from the offering of the additional 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes to repurchase $736 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding senior notes of various series, which resulted in a net debt reduction of $181 million. We also repurchased an additional $35 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding senior notes of various series and we redeemed $7 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 2020 IRBs, with cash on hand.
Additionally, in connection with the AK Steel Merger, we purchased $364 million aggregate principal amount of 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes and $311 million aggregate principal amount of 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes upon early settlement of tender offers made by Cliffs. The net proceeds from the offering of 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes, along with a portion of the ABL Facility borrowings, were used to fund such purchases. As the 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes and 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes were recorded at fair value just prior to being purchased, there was no gain or loss on extinguishment. Additionally, in connection with the final settlement of the tender offers, we purchased $9 million aggregate principal amount of the 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes and $56 million aggregate principal amount of the 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes with cash on hand.
The following is a summary of the debt extinguished and the respective impact on extinguishment:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended
December 31, 2020 |
| Debt Extinguished | | Gain (Loss) on Extinguishment |
| 7.625% 2021 AK Senior Notes | $ | 373 | | | $ | — | |
| 7.500% 2023 AK Senior Notes | 367 | | | 3 | |
| 4.875% 2024 Senior Secured Notes | 6 | | | 1 | |
| 6.375% 2025 Senior Notes | 168 | | | 21 | |
| 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes | 20 | | | 1 | |
| 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes | 77 | | | 16 | |
| 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes | 262 | | | 27 | |
| 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes | 195 | | | 49 | |
| 6.250% 2040 Senior Notes | 36 | | | 13 | |
| 6.375% 2025 AK Senior Notes | 9 | | | (1) | |
| Total | $ | 1,513 | | | $ | 130 | |
Debt Extinguishment - 2019
During the year ended December 31, 2019, we used the net proceeds from the issuance of $750 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes, along with cash on hand, to redeem in full all of our outstanding 4.875% 2021 Senior Notes and to fund the repurchase of $600 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes in a tender offer.
The following is a summary of the debt extinguished and the respective impact on extinguishment:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended
December 31, 2019 |
| Debt Extinguished | | (Loss) on Extinguishment |
| 4.875% 2021 Senior Notes | $ | 124 | | | $ | (5) | |
| 5.750% 2025 Senior Notes | 600 | | | (13) | |
| Total | $ | 724 | | | $ | (18) | |
Debt Maturities
The following represents a summary of our debt instrument maturities based on the principal amounts outstanding at December 31, 2021:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Maturities of Debt |
| 2022 | $ | — | |
| 2023 | — | |
| 2024 | 36 | |
| 2025 | 2,510 | |
| 2026 | 845 | |
| Thereafter | 1,978 | |
| Total maturities of debt | $ | 5,369 | |
NOTE 9 - FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
There were no significant assets or liabilities measured at fair value as of December 31, 2021 or December 31, 2020.
The valuation of financial assets classified in Level 2 was determined using a market approach based upon quoted prices for similar assets in active markets or other inputs that were observable.
Our supply agreement with ArcelorMittal USA contained provisions for supplemental revenue or refunds based on the HRC price in the year the iron ore product was consumed in ArcelorMittal USA’s blast furnaces. We accounted for these provisions as derivative instruments at the time of sale and adjusted the derivative instruments to fair value through Revenues each reporting period until the product was consumed and the amounts were settled. These instruments were classified as Level 3 assets. Upon the completion of the AM USA Transaction, the outstanding derivatives were settled as part of acquisition accounting.
The following tables represent a reconciliation of the changes in fair value of financial instruments measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Level 3 Assets |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Beginning balance - January 1 | $ | — | | | $ | 45 | |
| Total gains included in earnings | — | | | 122 | |
| Settlements | — | | | (27) | |
| Settlement of pre-existing relationship | — | | | (140) | |
| Ending balance - December 31 | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Total gains for the period included in earnings attributable to the change in unrealized gains on assets still held at the reporting date | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
The carrying values of certain financial instruments (e.g. Accounts receivable, net, Accounts payable and Other current liabilities) approximate fair value and, therefore, have been excluded from the table below. A summary of the carrying value and fair value of other financial instruments were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | (In Millions) |
| | | December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| Classification | | Carrying
Value | | Fair Value | | Carrying
Value | | Fair Value |
| Senior notes | Level 1 | | $ | 3,561 | | | $ | 3,911 | | | $ | 3,802 | | | $ | 4,446 | |
| IRBs due 2024 to 2028 | Level 1 | | 68 | | | 66 | | | 94 | | | 91 | |
| EDC Revolving Facility - outstanding balance | Level 2 | | — | | | — | | | 18 | | | 18 | |
| ABL Facility - outstanding balance | Level 2 | | 1,609 | | | 1,609 | | | 1,510 | | | 1,510 | |
| Total | | | $ | 5,238 | | | $ | 5,586 | | | $ | 5,424 | | | $ | 6,065 | |
The fair value of both current and long-term debt was determined using quoted market prices.
NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS
We offer defined benefit pension plans, defined contribution pension plans and OPEB plans to a significant portion of our employees and retirees. Benefits are also provided through multiemployer plans for certain union members.
As a result of the acquisitions of AK Steel and ArcelorMittal USA, we assumed the obligations under their defined benefit pension plans, OPEB plans, defined contribution plans and commitments to multiemployer pension plans according to collective bargaining agreements that cover certain union-represented employees. The AK Steel defined benefit pension plans and OPEB plans acquired amounted to a benefit obligation, net of assets of $949 million based on a March 13, 2020 measurement. The ArcelorMittal USA defined benefit pension plans and OPEB plans acquired amounted to a benefit obligation, net of assets of $3,294 million based on a December 9, 2020 measurement.
Defined Benefit Pension Plans
The defined benefit pension plans are largely noncontributory and limited in participation. Most plans are closed to new participants with only the legacy iron ore hourly and salaried plans still open. The pension benefit calculations vary by plan but are generally based on employees' years of service and compensation or a fixed rate and years of service. Certain salaried plans calculate benefits using a cash balance formula, which earns interest credits and allocations based on a percent of pay.
OPEB Plans
We offer postretirement health care and life insurance benefits to retirees through various plans. The vast majority of our plans are closed to new participants. In lieu of retiree medical coverage, many union-represented employees receive a 401(k) contribution per hour worked to a restricted Retiree Health Care Account. Cost sharing features between the employer and retiree vary by plan and several plans include employer caps. Retiree healthcare coverage is provided through programs administered by insurance companies whose charges are based on benefits paid. Certain labor agreements require the funding of VEBAs, which, depending on funding levels, may be used to reimburse the employer for paid benefits.
Obligations and Funded Status
The following tables and information provide additional disclosures:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Pension Benefits | | OPEB |
| Change in benefit obligations: | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Benefit obligations — beginning of year | $ | 6,565 | | | $ | 1,021 | | | $ | 3,757 | | | $ | 255 | |
| Service cost | 56 | | | 23 | | | 51 | | | 8 | |
| Interest cost | 103 | | | 64 | | | 74 | | | 19 | |
| Plan amendments | — | | | — | | | 8 | | | — | |
| Actuarial loss (gain) | (131) | | | 162 | | | (456) | | | 14 | |
| Benefits paid | (456) | | | (146) | | | (227) | | | (89) | |
| Participant contributions | — | | | — | | | 47 | | | 22 | |
| Acquired through business combinations | — | | | 5,535 | | | — | | | 3,528 | |
| Effect of settlement | (101) | | | (94) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligations — end of year | $ | 6,036 | | | $ | 6,565 | | | $ | 3,254 | | | $ | 3,757 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Change in plan assets: | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets — beginning of year | $ | 5,332 | | | $ | 749 | | | $ | 783 | | | $ | 260 | |
| Actual return on plan assets | 668 | | | 472 | | | 29 | | | 45 | |
| Participant contributions | — | | | — | | | 26 | | | 17 | |
| Employer contributions | 155 | | | 50 | | | 139 | | | 30 | |
| Benefits paid | (454) | | | (146) | | | (165) | | | (88) | |
| Acquired through business combinations | — | | | 4,301 | | | — | | | 519 | |
| Effect of settlement | (95) | | | (94) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets — end of year | $ | 5,606 | | | $ | 5,332 | | | $ | 812 | | | $ | 783 | |
| Funded status | $ | (430) | | | $ | (1,233) | | | $ | (2,442) | | | $ | (2,974) | |
| | | | | | | |
| Amounts recognized in Statements of Financial Position: | | | | | | | |
| Non-current assets | $ | 153 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 71 | | | $ | 54 | |
| Current liabilities | (5) | | | (12) | | | (130) | | | (139) | |
| Non-current liabilities | (578) | | | (1,224) | | | (2,383) | | | (2,889) | |
| Total amount recognized | $ | (430) | | | $ | (1,233) | | | $ | (2,442) | | | $ | (2,974) | |
| | | | | | | |
| Amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive loss (income): | | | | | | | |
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | (286) | | | $ | 164 | | | $ | (392) | | | $ | 56 | |
| Prior service cost (credit) | 5 | | | 6 | | | 4 | | | (6) | |
| Net amount recognized | $ | (281) | | | $ | 170 | | | $ | (388) | | | $ | 50 | |
| | | | | | | |
The accumulated benefit obligation for all defined benefit pension plans was $6,013 million and $6,537 million at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Components of Net Periodic Benefit Cost (Credit)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Pension Benefits | | OPEB |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Service cost | $ | 56 | | | $ | 23 | | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 51 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 2 | |
| Interest cost | 103 | | | 64 | | | 35 | | | 74 | | | 19 | | | 10 | |
| Expected return on plan assets | (359) | | | (140) | | | (55) | | | (40) | | | (20) | | | (17) | |
| Amortization: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net actuarial loss | 32 | | | 27 | | | 24 | | | 3 | | | 3 | | | 5 | |
| Prior service costs (credits) | 1 | | | 1 | | | 1 | | | (2) | | | (2) | | | (2) | |
| Settlements | (22) | | | (6) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Net periodic benefit cost (credit) | $ | (189) | | | $ | (31) | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | 86 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | (2) | |
For 2022, we estimate net periodic benefit cost (credit) as follows:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Defined benefit pension plans | $ | (179) | |
| OPEB plans | 72 | |
| Total | $ | (107) | |
Components of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss (Income)
The following includes details on the significant actuarial losses (gains) impacting the benefit obligation:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Pension Benefits | | OPEB |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Discount rates | $ | (224) | | | $ | 181 | | | $ | (117) | | | $ | 44 | |
| Demographic updates | 76 | | | (3) | | | 3 | | | (11) | |
| Mortality | 19 | | | (16) | | | 13 | | | (4) | |
| Per capita health care costs | — | | | — | | | (350) | | | (10) | |
| Other | (2) | | | — | | | (5) | | | (5) | |
| Actuarial loss (gain) on benefit obligation | (131) | | | 162 | | | (456) | | | 14 | |
| Actual returns on assets under (over) expected | (309) | | | (332) | | | 11 | | | (26) | |
| Amortization of net actuarial gain (loss) | (32) | | | (27) | | | 2 | | | (3) | |
| Amortization of prior service credits (costs) | (1) | | | (1) | | | (3) | | | 2 | |
| Settlements | 22 | | | 6 | | | — | | | — | |
| Other | — | | | (27) | | | 8 | | | (2) | |
| Total recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income | $ | (451) | | | $ | (219) | | | $ | (438) | | | $ | (15) | |
Contributions
Annual contributions to the pension plans are made within income tax deductibility restrictions in accordance with statutory regulations. OPEB plans are not subject to minimum regulatory funding requirements, but rather amounts are contributed pursuant to bargaining agreements.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | Pension Benefits1 | | Other Benefits2 |
| Company Contributions & Payments | | VEBA | | Direct
Payments | | Total |
| 2020 | | $ | 50 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 25 | |
| 2021 | | 163 | | | 67 | | | 113 | | | 180 | |
| 2022 (Expected) | | 4 | | | 28 | | | 110 | | | 138 | |
| | | | | | | | |
1 The 2021 pension contributions include $118 million in deferred 2020 pension contributions in connection with the CARES Act that were paid on January 4, 2021. |
2 Pursuant to the applicable bargaining agreements, benefits can be paid from certain VEBAs that are at least 70% funded (all VEBAs were over 70% funded at December 31, 2021). Certain agreements with plans holding VEBA assets have capped healthcare costs. For the Cleveland-Cliffs Steel LLC VEBA, we are required to make contributions based on earnings, and we may withdraw money from the VEBA plan to the extent funds are available for costs in excess of the cap. VEBA withdrawals are represented net of direct payments. The amount expected for 2022 in the VEBA column reflects the contribution to be made in February 2022 for earnings in the quarter ended December 31, 2021. We do not include an estimate for contributions beyond that due to the variability of the calculation. |
Estimated Future Benefit Payments
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Pension
Benefits | | OPEB |
| 2022 | $ | 475 | | | $ | 180 | |
| 2023 | 477 | | | 171 | |
| 2024 | 451 | | | 167 | |
| 2025 | 428 | | | 163 | |
| 2026 | 424 | | | 163 | |
| 2027-2031 | 1,879 | | | 823 | |
Assumptions
The discount rates used to measure plan liabilities as of the December 31 measurement date are determined individually for each plan. The discount rates are determined by matching the projected cash flows used to determine the plan liabilities to a projected yield curve of high-quality corporate bonds available at the measurement date. Discount rates for expense are calculated using the granular approach for each plan.
Depending on the plan, we use either company-specific base mortality tables or tables issued by the Society of Actuaries. We use the Pri-2012 mortality tables from the Society of Actuaries with adjustments for blue collar, white collar or no collar depending on the plan. On December 31, 2021, the assumed mortality improvement projection was updated from generational scale MP-2020 to generational scale MP-2021 for the Pri-2012 mortality tables.
The following represents weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension Benefits | | OPEB |
| December 31, | | December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Discount rate | 2.75 | % | | 2.34 | % | | 3.01 | % | | 2.71 | % |
| Interest crediting rate | 5.35 | | | 5.25 | | | N/A | | | N/A | |
| Compensation rate increase | 2.52 | | | 2.56 | | | 3.00 | | | 3.00 | |
The following represents weighted-average assumptions used to determine net benefit cost:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension Benefits | | OPEB |
| December 31, | | December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Obligation discount rate | 2.32 | | % | | 3.02 | | % | | 4.27 | | % | | 2.46 | | % | | 3.28 | | % | | 4.29 | | % |
| Service cost discount rate | 2.78 | | | | 3.34 | | | | 4.35 | | | | 3.28 | | | | 3.35 | | | | 4.49 | | |
| Interest cost discount rate | 1.64 | | | | 2.53 | | | | 3.92 | | | | 2.04 | | | | 2.51 | | | | 3.94 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest crediting rate | 5.35 | | | | 5.50 | | | | 6.00 | | | | N/A | | | N/A | | | N/A | |
| Expected return on plan assets | 6.84 | | | | 7.69 | | | | 8.25 | | | | 5.20 | | | | 6.82 | | | | 7.00 | | |
| Compensation rate increase | 2.54 | | | | 2.56 | | | | 2.53 | | | | 3.00 | | | | 3.00 | | | | 3.00 | | |
The following represents assumed weighted-average health care cost trend rates:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year | 2.36 | | % | | 6.05 | | % |
| Ultimate health care cost trend rate | 4.50 | | | | 4.59 | | |
| Year that the ultimate rate is reached | 2031 | | | 2031 | |
Plan Assets
Our financial objectives with respect to our pension and VEBA assets are to fully fund the actuarial accrued liability for each of the plans, to maximize investment returns within reasonable and prudent levels of risk, and to maintain sufficient liquidity to meet benefit obligations on a timely basis.
Our investment objective is to outperform the expected return on assets assumption used in the plans’ actuarial reports over the life of the plans. The expected return on assets takes into account historical returns and estimated future long-term returns based on capital market assumptions applied to the asset allocation strategy. The expected return is net of investment expenses paid by the plans. In addition, investment performance is monitored quarterly by benchmarking to various indices and metrics for the one-, three- and five-year periods.
The asset allocation strategy is determined through a detailed analysis of assets and liabilities by plan, which defines the overall risk that is acceptable with regard to the expected level and variability of portfolio returns, surplus (assets compared to liabilities), contributions and pension expense.
The asset allocation review process involves simulating capital market behaviors including global asset class performance, inflation and interest rates in order to evaluate various asset allocation scenarios and determine the asset mix with the highest likelihood of meeting financial objectives. The process includes factoring in the current funded status and likely future funded status levels of the plans by taking into account expected growth or decline in the contributions over time.
The asset allocation strategy varies by plan. The following table reflects the actual asset allocations for pension and VEBA assets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, as well as the 2022 weighted average target asset allocations. Equity investments include securities in large-cap, mid-cap and small-cap companies located in the U.S. and worldwide. Fixed income investments primarily include corporate bonds and government debt securities.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Assets | | VEBA Assets |
| Asset Category | | 2022
Target
Allocation | | Percentage of
Plan Assets at
December 31, | | 2022
Target
Allocation | | Percentage of
Plan Assets at
December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Equity securities | | 46.3 | % | | 47.6 | % | | 51.8 | % | | 21.2 | % | | 22.5 | % | | 22.2 | % |
| Fixed income | | 34.6 | | | 34.6 | | | 33.8 | | | 68.5 | | | 66.4 | | | 66.4 | |
| Hedge funds | | 2.2 | | | 2.2 | | | 2.2 | | | 1.4 | | | 1.8 | | | 1.8 | |
| Private equity | | 5.0 | | | 2.7 | | | 2.1 | | | 1.1 | | | — | | | 0.4 | |
| Structured credit | | 5.2 | | | 5.6 | | | 5.0 | | | 1.0 | | | 1.2 | | | 0.9 | |
| Real estate | | 5.2 | | | 5.6 | | | 3.3 | | | 1.0 | | | 2.1 | | | 1.8 | |
| Absolute return fixed income | | 1.5 | | | 1.7 | | | 1.8 | | | 5.8 | | | 6.0 | | | 6.5 | |
| Total | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % |
As a practical expedient, in accordance with ASC 820-10, certain investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy below. NAV is based on the value of the underlying assets owned by the fund, minus its liabilities, and then divided by its number of shares outstanding.
The fair value of our pension assets by asset category is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Quoted Prices in Active
Markets for Identical
Assets
(Level 1) | | Significant Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) | | Investments Measured at Net Asset Value | | Total |
| Asset Category | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 |
| Equity securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. equities | $ | 1,157 | | $ | 1,163 | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | 775 | | $ | 787 | | | $ | 1,932 | | $ | 1,950 | |
| Global equities | 617 | | 615 | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 117 | | 195 | | | 734 | | 810 | |
| Fixed income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government securities1 | 140 | | 141 | | | 310 | | 295 | | | — | | — | | | 50 | | 40 | | | 500 | | 476 | |
| U.S. corporate bonds | 502 | | 512 | | | 371 | | 466 | | | — | | — | | | 503 | | 303 | | | 1,376 | | 1,281 | |
| Non U.S. and other bonds | — | | — | | | 66 | | 46 | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 66 | | 46 | |
| Hedge funds | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 125 | | 118 | | | — | | — | | | 125 | | 118 | |
| Private equity | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 151 | | 114 | | | — | | — | | | 151 | | 114 | |
| Structured credit | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 315 | | 264 | | | — | | — | | | 315 | | 264 | |
| Real estate | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 313 | | 174 | | | — | | — | | | 313 | | 174 | |
| Absolute return fixed income | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 94 | | 99 | | | 94 | | 99 | |
| Total | $ | 2,416 | | $ | 2,431 | | | $ | 747 | | $ | 807 | | | $ | 904 | | $ | 670 | | | $ | 1,539 | | $ | 1,424 | | | $ | 5,606 | | $ | 5,332 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
1 Includes cash equivalents. |
Assets for OPEB plans include VEBA trusts pursuant to bargaining agreements that are available to fund retired employees’ life insurance obligations and medical benefits. The fair value of our other benefit plan assets by asset category is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Quoted Prices in Active
Markets for Identical
Assets
(Level 1) | | Significant Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) | | Investments Measured at Net Asset Value | | Total |
| Asset Category | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 |
| Equity securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. equities | $ | 26 | | $ | 26 | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | 103 | | $ | 93 | | | $ | 129 | | $ | 119 | |
| Global equities | 6 | | 6 | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 48 | | 49 | | | 54 | | 55 | |
| Fixed income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government securities1 | 111 | | 62 | | | 80 | | 94 | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 191 | | 156 | |
| U.S. corporate bonds | 219 | | 237 | | | 129 | | 127 | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 348 | | 364 | |
| Hedge funds | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 15 | | 14 | | | — | | — | | | 15 | | 14 | |
| Private equity | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | 3 | | | — | | — | | | — | | 3 | |
| Structured credit | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 10 | | 7 | | | — | | — | | | 10 | | 7 | |
| Real estate | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 17 | | 14 | | | — | | — | | | 17 | | 14 | |
| Absolute return fixed income | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 48 | | 51 | | | 48 | | 51 | |
| Total | $ | 362 | | $ | 331 | | | $ | 209 | | $ | 221 | | | $ | 42 | | $ | 38 | | | $ | 199 | | $ | 193 | | | $ | 812 | | $ | 783 | |
1 Includes cash equivalents. |
The following represents the fair value measurements of changes in plan assets using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Pension Assets | | VEBA Assets |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Beginning balance — January 1 | $ | 670 | | | $ | 212 | | | $ | 38 | | | $ | 34 | |
| Actual return on plan assets: | | | | | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | 124 | | | 8 | | | 6 | | | 2 | |
| Relating to assets sold during the period | 8 | | | 6 | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Purchases | 142 | | | 195 | | | — | | | — | |
| Sales | (40) | | | (13) | | | (2) | | | (1) | |
| Acquired through business combinations | — | | | 262 | | | — | | | 2 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Ending balance — December 31 | $ | 904 | | | $ | 670 | | | $ | 42 | | | $ | 38 | |
Following is a description of the inputs and valuation methodologies used to measure the fair value of our plan assets.
Equity Securities
Equity securities classified as Level 1 investments include U.S. large-, small- and mid-cap investments and international equities. These investments are comprised of securities listed on an exchange, market or automated quotation system for which quotations are readily available. The valuation of these securities is determined using a market approach and is based upon unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets in active markets.
Fixed Income
Fixed income securities classified as Level 1 investments include bonds, government debt securities and cash equivalents. These investments are comprised of securities listed on an exchange, market or automated quotation system for which quotations are readily available. The valuation of these securities is determined using a
market approach and is based upon unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets in active markets. Also included in fixed income is a portfolio of U.S. Treasury STRIPS, which are zero-coupon bearing fixed income securities backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. The securities sell at a discount to par because there are no incremental coupon payments. STRIPS are not issued directly by the Treasury, but rather are created by a financial institution, government securities broker or government securities dealer. Liquidity on the issue varies depending on various market conditions; however, in general, the STRIPS market is slightly less liquid than that of the U.S. Treasury Bond market. The STRIPS are priced daily through a bond pricing vendor and are classified as Level 2.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are alternative investments comprised of direct or indirect investment in offshore hedge funds with an investment objective to achieve equity-like returns with one half the volatility of equities and moderate correlation. The valuation techniques used to measure fair value attempt to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Considerable judgment is required to interpret the factors used to develop estimates of fair value. Valuations of the underlying investment funds are obtained and reviewed. The securities that are valued by the funds are interests in the investment funds and not the underlying holdings of such investment funds. Thus, the inputs used to value the investments in each of the underlying funds may differ from the inputs used to value the underlying holdings of such funds. Hedge funds are valued monthly and recorded on a one-month lag.
Private Equity Funds
Private equity funds are alternative investments that represent direct or indirect investments in partnerships, venture funds or a diversified pool of private investment vehicles (fund of funds).
Investment commitments are made in private equity funds based on an asset allocation strategy, and capital calls are made over the life of the funds to fund the commitments. As of December 31, 2021, remaining commitments total $151 million for our pension and OPEB plans. Committed amounts are funded from plan assets when capital calls are made. Investment commitments are not pre-funded in reserve accounts.
Private equity investments are valued quarterly and recorded on a one-quarter lag. For private equity investment values reported on a lag, current market information is reviewed for any material changes in values at the reporting date. Capital distributions for the funds do not occur on a regular frequency. Liquidation of these investments would require sale of the partnership interest.
Structured Credit
Structured credit funds provide flexibility and access to both complex and illiquid premiums by investing across global, public and private residential, commercial, corporate and specialty credit markets that are priced based on valuations provided by independent, third-party pricing agents, if available. Such values generally reflect the last reported sales price if the security is actively traded. The third-party pricing agents may also value structured credit investments at an evaluated bid price by employing methodologies that utilize actual market transactions, broker-supplied valuations or other methodologies designed to identify the market value of such securities.
Structured credit investments are valued monthly and certain funds have an initial lock-up period and withdrawal restrictions on a semi-annual and quarterly basis. For structured credit investment values reported on a lag, current market information is reviewed for any material changes in values at the reporting date.
Real Estate
The real estate portfolio for the pension plans is an alternative investment comprised of funds with strategic categories of real estate investments. All real estate holdings are appraised externally at least annually, and appraisals are conducted by reputable, independent appraisal firms that are members of the Appraisal Institute. All external appraisals are performed in accordance with the Uniform Standards of Professional Appraisal Practices. The property valuations and assumptions about each property are reviewed quarterly by the investment manager and values are adjusted if there has been a significant change in circumstances relating to the property since the last external appraisal. The fair values of the funds are updated on either a monthly or quarterly basis. Redemption requests are considered on a quarterly basis, subject to notice requirements.
The real estate fund of funds investment for the VEBA trusts invests in pooled investment vehicles that, in turn, invest in commercial real estate properties. Valuations are performed quarterly and financial statements are prepared on a semi-annual basis, with annual audited statements. Asset values for this fund are reported with a one-
quarter lag, and current market information is reviewed for any material changes in values at the reporting date. Withdrawals are permitted on the last business day of each quarter subject to a 95-day prior written notice.
Absolute Return Fixed Income
Absolute return fixed income investments consist of a global fixed income fund with the investment objective of generating positive absolute returns over a full market cycle. The fund's investments in securities, forward exchange contracts and futures contracts are reported at fair value on a recurring monthly basis. The fund's trustee values securities based upon independent pricing sources and futures contracts are valued at closing settled prices. Redemptions of the fund at NAV are permitted monthly under most circumstances.
Defined Contribution Plans
Most employees are eligible to participate in various defined contribution plans. Certain of these plans have features with matching contributions or other Company contributions based on our financial results. Company contributions to these plans are expensed as incurred. Total expense from these plans was $55 million, $22 million and $3 million in 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Multiemployer Plans
We contribute to multiemployer pension plans according to collective bargaining agreements that cover certain union-represented employees. The risks of participating in these multiemployer plans are different from the risks of participating in single-employer pension plans in the following respects:
•Assets contributed to a multiemployer plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers.
•If a participating employer stops contributing to a multiemployer plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan may be borne by the remaining participating employers.
•If the multiemployer plan becomes significantly underfunded or is unable to pay its benefits, we may be required to contribute additional amounts in excess of the rate required by the collective bargaining agreements.
•If we choose to stop participating in a multiemployer plan, we may be required to pay that plan an amount based on the underfunded status of the plan, referred to as a withdrawal liability.
Information with respect to multiemployer plans in which we participate follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension Fund | EIN/Pension Plan Number | Pension Protection Act Zone Status (a) | FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented (b) | Contributions | Surcharge Imposed (c) | Expiration Date of Collective Bargaining Agreement (d) |
| | 2021 | 2020 | | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | | |
| Steelworkers Pension Trust | 23-6648508/499 | Green | Green | No | $ | 88 | | $ | 14 | | $ | 4 | | No | 9/1/2022 to 09/1/2025 |
| IAM National Pension Fund’s National Pension Plan | 51-6031295/002 | Red | Red | Yes | 16 | | 16 | | — | | Yes | 5/31/2022 to 5/15/2023 |
Other Plans(e) | | | | | — | | — | | — | | | |
| Total | | | | | $ | 104 | | $ | 30 | | $ | 4 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| (a) The most recent Pension Protection Act zone status available in 2021 and 2020 is for each plan's year-end at December 31, 2020 and 2019. The plan's actuary certifies the zone status. Generally, plans in the red zone are less than 65% funded, plans in the yellow zone are between 65% and 80% funded, and plans in the green zone are at least 80% funded. The IAM National Pension Fund's National Pension Plan voluntarily elected to place itself in the "Red Zone" in April 2019 and has implemented a rehabilitation plan to address its underfunded status. Additional contributions will be required as part of the rehabilitation plan until the plan exits the "Red Zone". |
| (b) The "FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented" column indicates plans for which a financial improvement plan or a rehabilitation plan is either pending or has been implemented, as defined by ERISA. |
| (c) The surcharge represents an additional required contribution due as a result of the critical funding status of the plan. |
(d) We are a party to five collective bargaining agreements that require contributions to the Steelworkers Pension Trust and three collective bargaining agreements that require contributions to the IAM National Pension Fund's National Pension Plan. |
| (e) Plans that are not individually significant to our Company are presented in aggregate. |
With the 2020 Acquisitions, we are one of the largest contributors to the Steelworkers Pension Trust. Our contributions exceeded 5% of total combined contributions in 2021 and 2020. As of January 1, 2021 (the last date for which we have information), the Steelworkers Pension Trust had a total actuarial liability of $5,960 million and assets with a market value of $5,998 million, for a funded ratio of about 101%.
NOTE 11 - STOCK COMPENSATION PLANS
At December 31, 2021, we had outstanding awards under three share-based compensation plans: the 2021 Equity Plan, the A&R 2015 Equity Plan and the 2012 Amended Equity Plan. On April 28, 2021, the Company's shareholders approved the 2021 Equity Plan, which succeeded the A&R 2015 Equity Plan and made available 26.0 million new common shares plus 2.5 million shares remaining available under the A&R 2015 Equity Plan. As of December 31, 2021, there were 28.0 million remaining shares available for grant under the 2021 Equity Plan. No additional grants were issued from the 2012 Amended Equity Plan or the A&R 2015 Equity Plan after the date of approval of the 2021 Equity Plan; however, all awards previously granted under the predecessor plans will continue in accordance with the terms of the outstanding awards.
On March 13, 2020, the maximum number of shares that may be issued under the A&R 2015 Equity Plan increased by 5.7 million common shares in relation to the outstanding AK Steel stock-based incentive awards that we converted at a 0.400 rate of exchange. The converted stock-based incentive awards include 2.0 million stock options, 1.0 million long-term performance plan awards, 0.5 million performance shares, 0.2 million restricted stock awards and 0.3 million restricted stock units.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
The following table summarizes the total compensation expense recognized for stock-based compensation awards:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions, except per
share amounts) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Cost of goods sold | $ | (2) | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | (2) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | (16) | | | (13) | | | (16) | |
| Acquisition-related costs | — | | | (2) | | | — | |
| Stock based compensation expense | (18) | | | (17) | | | (18) | |
| Income tax benefit | 4 | | | 4 | | | 4 | |
| Stock based compensation expense, net of tax | $ | (14) | | | $ | (13) | | | $ | (14) | |
| | | | | |
| Decrease in basic earnings per common share | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | (0.05) | |
| Decrease in diluted earnings per common share | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | (0.05) | |
The total compensation cost related to outstanding awards not yet recognized is $24 million at December 31, 2021. This expense is expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted-average period of 1.4 years.
Performance Shares
The following table summarizes the performance award activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| Outstanding at beginning of year | 2,452,226 | | | $ | 10.34 | | | 1,935,878 | | | $ | 15.58 | | | 1,424,723 | | | $ | 14.46 | |
| Granted | 652,888 | | | 25.12 | | | 960,637 | | | 6.93 | | | 572,104 | | | 18.31 | |
| Granted - replacement awards | — | | | — | | | 1,550,216 | | | 4.59 | | | — | | | — | |
| Distributed | (1,279,509) | | | 11.74 | | | (1,938,786) | | | 12.23 | | | — | | | — | |
| Performance adjustment | 625,355 | | | 11.93 | | | 549,154 | | | 15.63 | | | — | | | — | |
| Forfeited/canceled | (80,490) | | | 11.27 | | | (604,873) | | | 5.70 | | | (60,949) | | | 15.12 | |
| Outstanding at end of year | 2,370,470 | | | $ | 14.04 | | | 2,452,226 | | | $ | 10.34 | | | 1,935,878 | | | $ | 15.58 | |
On March 13, 2020, we granted 1.0 million long-term performance plan awards and 0.5 million performance shares as AK Steel replacement awards. As of December 31, 2021, 0.2 million long-term performance plan awards and 0.1 million performance shares were outstanding as a result of qualifying termination events that triggered accelerated performance share payouts and prorated long-term performance plan awards payouts at target. The long-term performance plan awards are based on a three-year Adjusted EBITDA metric.
The outstanding performance shares vest over a period of three years and are intended to be paid out in common shares. Performance is measured on the basis of relative TSR for the period and measured against the constituents of the S&P Metals and Mining ETF Index. The number of shares actually earned at the end of the three-year period will vary, based on performance, from 0% to 200% of the number of performance shares granted.
Restricted Stock Units
The following table summarizes the restricted stock units activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| Outstanding at beginning of year | 2,143,583 | | | $ | 7.12 | | | 2,147,183 | | | $ | 9.10 | | | 4,694,360 | | | $ | 4.18 | |
| Granted | 678,420 | | | 17.45 | | | 960,637 | | | 4.87 | | | 572,104 | | | 11.24 | |
| Granted - replacement awards | — | | | — | | | 200,291 | | | 4.87 | | | — | | | — | |
| Distributed | (642,992) | | | 7.31 | | | (1,101,115) | | | 8.58 | | | (3,058,307) | | | 1.95 | |
| Forfeited/canceled | (56,185) | | | 9.50 | | | (63,413) | | | 7.31 | | | (60,974) | | | 9.31 | |
| Outstanding at end of year | 2,122,826 | | | $ | 10.31 | | | 2,143,583 | | | $ | 7.12 | | | 2,147,183 | | | $ | 9.10 | |
On March 13, 2020, we granted 0.2 million restricted stock awards as AK Steel replacement awards. The restricted stock awards relating to AK Steel vest ratably on the first, second and third anniversaries of the grant. We valued the AK Steel replacement rewards at $4.87 per share using the closing price of our common shares on March 13, 2020, the grant date.
We value our restricted stock units using the closing price of our common shares on the grant date. All of the outstanding restricted stock units are subject to continued employment, are retention based, and are payable in common shares or cash in certain circumstances at a time determined by the Compensation Committee at its discretion. Most restricted stock units that were granted in 2021, 2020 and 2019 cliff vest over three years on December 31, 2023, December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively.
Stock Options
The following table summarizes the stock option activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
| Outstanding at beginning of year | 2,485,808 | | | $ | 11.60 | | | 563,230 | | | $ | 10.42 | | | 563,230 | | | $ | 10.42 | |
| Granted - replacement awards | — | | | — | | | 2,010,277 | | | 11.86 | | | — | | | — | |
| Exercised | (1,457,495) | | | 10.36 | | | (79,973) | | | 7.01 | | | — | | | — | |
| Forfeited/canceled | (26,253) | | | 36.48 | | | (7,726) | | | 41.04 | | | — | | | — | |
| Outstanding at end of year | 1,002,060 | | | $ | 12.75 | | | 2,485,808 | | | $ | 11.60 | | | 563,230 | | | $ | 10.42 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exercisable at end of year | 904,574 | | | $ | 13.35 | | | 2,172,052 | | | $ | 11.86 | | | 563,230 | | | $ | 10.42 | |
Stock options granted to date generally vest over a period from one to three years with an expiration date at ten years from the date of grant. On March 13, 2020, we granted 2.0 million options as AK Steel replacement awards. The weighted average fair value of the converted options was $0.51 per share and was calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. Qualifying termination events resulted in vest date accelerations and reductions to the option expiration date from ten years to three years.
The total intrinsic value of options exercised in 2021 was $13 million and the amount in 2020 was immaterial. For options outstanding at December 31, 2021, the weighted-average remaining contractual life was 3.0 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was $10 million. For options exercisable at December 31, 2021, the weighted-average remaining contractual life was 2.6 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was $8 million.
Nonemployee Directors
Our nonemployee directors are entitled to receive restricted share awards under the Directors’ Plan. For 2021, 2020 and 2019, nonemployee directors were granted a specified number of restricted shares, with a value equal to $120,000, $100,000 and $100,000, respectively. The number of shares is based on the closing price of our common shares on the date of the Annual Meeting. The restricted share awards issued under the Directors' Plan generally vest 12 months from the grant date. The awards are subject to any deferral election and the terms of the Directors’ Plan and an award agreement.
On March 13, 2020, 0.3 million restricted stock units previously awarded to the members of the AK Steel board of directors were distributed per the terms of the AK Steel Merger Agreement.
For the last three years, grants of restricted and/or deferred shares have been awarded to elected or re-elected nonemployee directors as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year of Grant | | Restricted Shares | | Deferred Shares |
| 2021 | | 58,851 | | | 13,078 | |
| 2020 | | 253,809 | | | 54,794 | |
| 2019 | | 86,477 | | | 23,659 | |
NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES
Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes includes the following components:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| United States | | $ | 3,827 | | | $ | (201) | | | $ | 313 | |
| Foreign | | (24) | | | 8 | | | — | |
| | $ | 3,803 | | | $ | (193) | | | $ | 313 | |
The components of the income tax provision (benefit) on continuing operations consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Current provision (benefit): | | | | | | |
| United States federal | | $ | 14 | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | (1) | |
| United States state & local | | 55 | | | — | | | — | |
| Foreign | | — | | | (1) | | | — | |
| | 69 | | | (3) | | | (1) | |
| Deferred provision (benefit): | | | | | | |
| United States federal | | 683 | | | (95) | | | 19 | |
| United States state & local | | 31 | | | (11) | | | — | |
| Foreign | | (10) | | | (2) | | | — | |
| Total income tax provision (benefit) from continuing operations | | $ | 773 | | | $ | (111) | | | $ | 18 | |
Reconciliation of our income tax attributable to continuing operations computed at the U.S. federal statutory rate is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Tax at U.S. statutory rate | | $ | 799 | | | 21 | % | | $ | (41) | | | 21 | % | | $ | 66 | | | 21 | % |
| Increase (decrease) due to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percentage depletion in excess of cost depletion | | (99) | | | (3) | | | (42) | | | 22 | | | (49) | | | (16) | |
| Non-taxable income related to noncontrolling interests | | (9) | | | — | | | (9) | | | 4 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Luxembourg legal entity reduction | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 846 | | | 271 | |
| Valuation allowance release: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Luxembourg legal entity reduction | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (846) | | | (271) | |
| State taxes, net | | 86 | | | 2 | | | (11) | | | 6 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other items, net | | (4) | | | — | | | (8) | | | 4 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Provision for income tax expense (benefit) and effective income tax rate including discrete items | | $ | 773 | | | 20 | % | | $ | (111) | | | 57 | % | | $ | 18 | | | 6 | % |
The increase in income tax expense in 2021 from income tax benefit in 2020 is directly correlated to the increase in pre-tax book income from the prior period for both federal and state income tax purposes.
The increase in income tax benefit from 2019 to 2020 is directly correlated to the decrease in pre-tax book income from the prior period for both federal and state income tax purposes. The Luxembourg legal entity reduction relates to initiatives resulting in the dissolution of certain entities and settlement of related financial instruments in 2019. The 2019 NOL deferred tax asset reduction resulted in tax expense of $846 million, which was fully offset by a decrease in the respective valuation allowance.
The components of income taxes for other than continuing operations consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | |
| Pension and OPEB | | $ | (206) | | | $ | (52) | | | $ | 11 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | (21) | | | (1) | | | — | |
| Total | | $ | (227) | | | $ | (53) | | | $ | 11 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Operating loss and other carryforwards | $ | 379 | | | $ | 1,236 | |
| Pension and OPEB liabilities | 584 | | | 228 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| State and local | 109 | | | 132 | |
| | | |
| Other liabilities | 287 | | | 190 | |
| Total deferred tax assets before valuation allowance | 1,359 | | | 1,786 | |
| Deferred tax asset valuation allowance | (409) | | | (836) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | 950 | | | 950 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| Investment in partnerships | (191) | | | (144) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Property, plant and equipment and mineral rights | (641) | | | (246) | |
| Other assets | (216) | | | (68) | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (1,048) | | | (458) | |
| Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) | $ | (98) | | | $ | 492 | |
We had gross domestic (including states) and foreign NOLs of $2,081 million and $1,407 million, respectively, at December 31, 2021. We had gross domestic and foreign NOLs of $7,444 million and $1,592 million, respectively, at December 31, 2020. The U.S. federal NOLs will begin to expire in 2034 and state NOLs will begin to expire in 2022. The foreign NOLs can be carried forward indefinitely. We had gross interest expense limitation carryforwards of $18 million and $80 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. This interest expense can be carried forward indefinitely.
The changes in the valuation allowance are presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 836 | | | $ | 441 | | | $ | 1,287 | |
| Change in valuation allowance: | | | | | |
| Included in income tax benefit | (82) | | | (3) | | | (846) | |
| | | | | |
| Increase (decrease) from acquisitions | (345) | | | 398 | | | — | |
| Balance at end of year | $ | 409 | | | $ | 836 | | | $ | 441 | |
During 2021, we recorded a decrease to the valuation allowance of $345 million related to the election filed with our 2020 federal tax return to waive the pre-acquisition NOLs that are limited under Section 382 of the IRC. An offsetting decrease is recorded in the NOL deferred tax asset in the same period. These amounts relate to a portion of the $398 million valuation allowance recorded during 2020 through opening balance sheet adjustments to reflect the portion of federal and state NOLs that are limited under Section 382 of the IRC acquired through the AK Steel Merger.
During 2019, a legal entity reduction initiative was completed in Luxembourg resulting in the dissolution of certain entities and settlement of related financial instruments, triggering the utilization of $1.3 billion of NOL deferred tax asset and reversal of the intercompany notes deferred tax liability of $447 million. The total net deferred tax reduction resulted in an expense of $846 million, which was fully offset by a decrease in the valuation allowance. Our losses in Luxembourg in recent periods represent sufficient negative evidence to require a full valuation allowance against the remaining deferred tax assets in that jurisdiction. We intend to maintain a valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets related to these operating losses until sufficient positive evidence exists to support the realization of such assets.
We also have a valuation allowance recorded against certain state NOLs, which are expected to expire before utilization. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, we had a valuation allowance recorded against certain state NOLs of $70 million and $98 million, respectively.
At December 31, 2021 and 2020, we had no cumulative undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries included in retained earnings. Accordingly, no provision has been made for U.S. deferred taxes related to future repatriation of earnings.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Unrecognized tax benefits balance as of January 1 | | $ | 107 | | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 29 | |
| | | | | | |
| Increase for tax positions in current year | | 4 | | | 7 | | | — | |
| | | | | | |
| Decrease for tax positions of prior year | | (66) | | | (4) | | | — | |
| Lapses in statutes of limitations | | (10) | | | — | | | — | |
| Increases from acquisitions | | — | | | 75 | | | — | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits balance as of December 31 | | $ | 35 | | | $ | 107 | | | $ | 29 | |
At December 31, 2021 and 2020, we had $35 million and $107 million, respectively, of unrecognized tax benefits recorded. Of this amount, $1 million was recorded in Other current liabilities for the year ended December 31, 2021. Additionally, $34 million and $2 million, were recorded in Other non-current liabilities for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. An additional $96 million was recorded in Other non-current assets for the year ended December 31, 2020. If the unrecognized tax benefits were recognized, $30 million would impact the effective tax rate. We do not expect that the amount of unrecognized benefits will change significantly within the next 12 months.
Tax years 2016 and forward remain subject to examination for the U.S., and tax years 2008 and forward remain subject to examination for Canada.
NOTE 13 - LEASE OBLIGATIONS
Our operating leases consist primarily of leases for office space, iron ore vessels, rail cars and processing equipment. Our finance leases consist primarily of processing equipment and mining equipment. We use our incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate to determine the present value of the lease payments, as our leases do not have readily determinable implicit discount rates. Our incremental borrowing rate is the rate of interest that we would have to borrow on a collateralized basis over a similar term and amount in a similar economic environment to pay our lease obligations. We determine the incremental borrowing rates for our leases by adjusting the local risk-free interest rate with a credit risk premium corresponding to our credit rating. From time to time, we may enter into arrangements for the construction or purchase of an asset and then enter into a financing arrangement to lease the asset. We recognize leased assets and liabilities under these arrangements when we obtain control of the asset.
Lease costs are presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Operating leases | $ | 70 | | | $ | 43 | |
| Finance leases: | | | |
| Amortization of lease cost | 94 | | | 15 | |
| Interest on lease liabilities | 9 | | | 4 | |
| Short-term leases | 66 | | | 13 | |
| | | |
| Total | $ | 239 | | | $ | 75 | |
Other information related to leases was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Cash paid for amounts included in measurement of lease liabilities: | | | |
| Operating leases within cash flows from operating activities | $ | 70 | | | $ | 43 | |
| Finance leases within cash flows from operating activities | $ | 9 | | | $ | 4 | |
| Finance leases within cash flows from financing activities | $ | 94 | | | $ | 15 | |
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new finance lease liabilities1 | $ | 50 | | | $ | 44 | |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term - operating leases (in years) | 8 | | 8 |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term - finance leases (in years) | 5 | | 5 |
| Weighted-average discount rate - operating leases | 7 | % | | 8 | % |
| Weighted-average discount rate - finance leases | 4 | % | | 4 | % |
| | | |
1 Right-of-use assets obtained in acquisitions are not included in this figure. |
Future minimum lease payments under noncancellable finance and operating leases as of December 31, 2021 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Finance Leases | | Operating Leases |
| 2022 | $ | 105 | | | $ | 68 | |
| 2023 | 96 | | | 56 | |
| 2024 | 31 | | | 47 | |
| 2025 | 28 | | | 39 | |
| 2026 | 19 | | | 35 | |
| Thereafter | 66 | | | 133 | |
| Total future minimum lease payments | 345 | | | 378 | |
| Less: imputed interest | 54 | | | 108 | |
| Total lease payments | 291 | | | 270 | |
| Less: current portion of lease liabilities | 97 | | | 50 | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | $ | 194 | | | $ | 220 | |
The current and long-term portions of our finance and operating lease liabilities are included in Other current liabilities and Other non-current liabilities, respectively.
NOTE 14 - ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS
The following is a summary of our asset retirement obligations:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
Asset retirement obligations1 | $ | 449 | | | $ | 342 | |
| Less: current portion | 35 | | | 7 | |
| Long-term asset retirement obligations | $ | 414 | | | $ | 335 | |
| | | |
1 Includes $293 million and $190 million related to our active operations as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. |
The accrued closure obligation provides for contractual and legal obligations related to our indefinitely idled and closed operations and for the eventual closure of our active operations. We performed a detailed assessment of our asset retirement obligations related to our active operations most recently in 2020 in accordance with our accounting policy, which requires us to perform an in-depth evaluation of the liability every three years in addition to
routine annual assessments. In 2020, we employed third-party specialists to assist in the evaluation.
The closure date for each of our active mine sites was determined based on the exhaustion date of the remaining mineral reserves, and the amortization of the related asset and accretion of the liability is recognized over the estimated mine lives. The closure date and expected timing of the capital requirements to meet our obligations for our indefinitely idled or closed mines is determined based on the unique circumstances of each property. For indefinitely idled or closed mines, the accretion of the liability is recognized over the anticipated timing of remediation. As the majority of our asset retirement obligations at our steelmaking operations have indeterminate settlement dates, asset retirement obligations have been recorded at present values using estimated ranges of the economic lives of the underlying assets.
The following is a roll-forward of our asset retirement obligation liability:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) | |
| 2021 | | 2020 | |
| Asset retirement obligation as of January 1 | $ | 342 | | | $ | 165 | | |
| Increase from acquisitions | 116 | | | 172 | | |
| Accretion expense | 18 | | | 14 | | |
| Remediation payments | (29) | | | (9) | | |
| Revision in estimated cash flows | 2 | | | — | | |
| Asset retirement obligation as of December 31 | $ | 449 | | | $ | 342 | | |
The increase from acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2021 relates to measurement period adjustments as a result of the final purchase price allocation of the AM USA Transaction.
NOTE 15 - CAPITAL STOCK
Underwritten Public Offering
On February 11, 2021, we sold 20 million of our common shares and 40 million common shares were sold by an affiliate of ArcelorMittal in an underwritten public offering. In each case, shares were sold at a price per share of $16.12. Prior to this sale, ArcelorMittal held approximately 78 million of our common shares, which were issued as a part of the consideration in connection with the AM USA Transaction. We did not receive any proceeds from the sale of the 40 million common shares sold on behalf of ArcelorMittal. We used the net proceeds from the offering, plus cash on hand, to redeem $322 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes.
Acquisition of AK Steel
As more fully described in NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS, we acquired AK Steel on March 13, 2020. At the effective time of the AK Steel Merger, each share of AK Steel common stock issued and outstanding prior to the effective time of the AK Steel Merger was converted into, and became exchangeable for, 0.400 Cliffs common shares, par value $0.125 per share. We issued a total of 127 million common shares in connection with the AK Steel Merger at a fair value of $618 million. Following the closing of the AK Steel Merger, AK Steel's common stock was de-listed from the NYSE.
Acquisition of ArcelorMittal USA
As more fully described in NOTE 3 - ACQUISITIONS, we acquired ArcelorMittal USA on December 9, 2020. Pursuant to the terms of the AM USA Transaction Agreement, we issued 78,186,671 common shares and 583,273 shares of a new series of our Serial Preferred Stock, Class B, without par value, designated as the “Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock,” in each case to an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of ArcelorMittal as part of the consideration paid by us in connection with the closing of the AM USA Transaction.
Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock Redemption
We had 583,273 shares of our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020. During the third quarter of 2021, we redeemed all 583,273 shares of our Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock at a redemption price of $1.3 billion using borrowings under our ABL Facility.
Amendment to Articles of Incorporation
On April 29, 2021, we filed a Certificate of Amendment to our Fourth Amended Articles of Incorporation, as amended, to increase the total number of authorized common shares from 600,000,000 to 1,200,000,000.
Preferred Stock
We have 3,000,000 shares of Serial Preferred Stock, Class A, without par value, authorized, of which, none are issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2021. We also have 4,000,000 shares of Serial Preferred Stock, Class B, without par value, authorized, of which, none are issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2021.
Dividends
The below table summarizes our recent dividend activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Declaration Date | | Record Date | | Payment Date | | Dividend Declared per Common Share |
| 2/18/2020 | | 4/3/2020 | | 4/15/2020 | | $ | 0.06 | |
| 12/2/2019 | | 1/3/2020 | | 1/15/2020 | | 0.06 | |
Subsequent to the dividend paid on April 15, 2020, our Board suspended future dividends.
Share Repurchase Program
In 2018, our Board of Directors authorized a program to repurchase outstanding common shares in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. The share repurchase program was effective until December 31, 2019. During 2019, we repurchased 24 million common shares at a cost of $253 million in the aggregate, including commissions and fees.
NOTE 16 - ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
The components of Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) within Cliffs shareholders’ equity and related tax effects allocated to each are shown below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Pre-tax
Amount | | Tax Benefit
(Expense) | | After-tax
Amount |
| As of December 31, 2021: | | | | | |
| Pension and OPEB | $ | 669 | | | $ | (120) | | | $ | 549 | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 1 | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | 89 | | | (21) | | | 68 | |
| $ | 759 | | | $ | (141) | | | $ | 618 | |
| As of December 31, 2020: | | | | | |
| Pension and OPEB | $ | (221) | | | $ | 86 | | | $ | (135) | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 3 | | | — | | | 3 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | (1) | | | — | | | (1) | |
| $ | (219) | | | $ | 86 | | | $ | (133) | |
| As of December 31, 2019: | | | | | |
| Pension and OPEB | $ | (454) | | | $ | 138 | | | $ | (316) | |
| Derivative financial instruments | (4) | | | 1 | | | (3) | |
| $ | (458) | | | $ | 139 | | | $ | (319) | |
The following table reflects the changes in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to Cliffs shareholders’ equity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Postretirement Benefit Liability,
net of tax | | Foreign Currency Translation | | Derivative Financial Instruments,
net of tax | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
| December 31, 2018 | $ | (281) | | | $ | — | | | $ | (3) | | | $ | (284) | |
| Other comprehensive loss before reclassifications | (57) | | | — | | | (2) | | | (59) | |
| Net loss reclassified from AOCI | 22 | | | — | | | 2 | | | 24 | |
| December 31, 2019 | (316) | | | — | | | (3) | | | (319) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 163 | | | 3 | | | (6) | | | 160 | |
| Net loss reclassified from AOCI | 18 | | | — | | | 8 | | | 26 | |
| December 31, 2020 | (135) | | | 3 | | | (1) | | | (133) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 675 | | | (2) | | | 117 | | | 790 | |
| Net loss (gain) reclassified from AOCI | 9 | | | — | | | (48) | | | (39) | |
| December 31, 2021 | $ | 549 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 68 | | | $ | 618 | |
The following table reflects the details about Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) components reclassified from Cliffs shareholders’ equity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) | | |
| Details about Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) Components | | Amount of (Gain)/Loss
Reclassified into Income,
Net of Tax | | Affected Line Item in the Statement of Consolidated Operations |
| Year Ended December 31, | |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | |
| Changes in pension and OPEB: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service costs1 | | $ | (1) | | | $ | (1) | | | $ | (1) | | | Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component |
Net actuarial loss1 | | 35 | | | 30 | | | 29 | | | Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component |
Settlements1 | | (22) | | | (6) | | | — | | | Net periodic benefit credits (costs) other than service cost component |
| Total before taxes | | 12 | | | 23 | | | 28 | | | |
| Income tax benefit | | (3) | | | (5) | | | (6) | | | Income tax benefit (expense) |
| Net of taxes | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 22 | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Changes in derivative financial instruments: | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity contracts | | $ | (61) | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 3 | | | Cost of goods sold |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | | 13 | | | (2) | | | (1) | | | Income tax benefit (expense) |
| Net of taxes | | $ | (48) | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 2 | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Total reclassifications for the period, net of tax | | $ | (39) | | | $ | 26 | | | $ | 24 | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
1 See NOTE 10 - PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS for further information. |
NOTE 17 - RELATED PARTIES
We have certain co-owned joint ventures with companies from the steel and mining industries, including integrated steel companies, their subsidiaries and other downstream users of steel and iron ore products.
Hibbing is a co-owned joint venture with U.S. Steel, in which, as of both December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2021, we own 85.3% and U.S. Steel owns 14.7%. As a result of the AM USA Transaction, we acquired an additional 62.3% ownership stake in the Hibbing mine and became the majority owner and mine manager. Prior to the AM USA Transaction, ArcelorMittal was a related party due to its ownership interest in Hibbing. As such, certain long-term contracts with ArcelorMittal resulted in Revenues from related parties, and are included within the below.
Revenues from related parties were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Revenue from related parties | $ | 139 | | | $ | 893 | | | $ | 1,015 | |
| Revenues | $ | 20,444 | | | $ | 5,354 | | | $ | 1,990 | |
| Related party revenues as a percent of Revenues | 0.7 | % | | 16.7 | % | | 51.0 | % |
| Purchases from related parties | $ | 94 | | | $ | 16 | | | $ | — | |
The following table presents the classification of related party assets and liabilities in the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (In Millions) |
| | December 31, |
| Balance Sheet Location of Assets (Liabilities) | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| Accounts receivable, net | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 2 | |
| | | | |
| Accounts payable | | (7) | | | (6) | |
| | | | |
NOTE 18 - VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
SunCoke Middletown
We purchase all the coke and electrical power generated from SunCoke Middletown’s plant under long-term supply agreements and have committed to purchase all the expected production from the facility through 2032. We consolidate SunCoke Middletown as a VIE because we are the primary beneficiary despite having no ownership interest in SunCoke Middletown. SunCoke Middletown had income before income taxes of $52 million and $41 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, which was included in our consolidated Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes.
The assets of the consolidated VIE can only be used to settle the obligations of the consolidated VIE and not obligations of the Company. The creditors of SunCoke Middletown do not have recourse to the assets or general credit of the Company to satisfy liabilities of the VIE. The Statements of Consolidated Financial Position includes the following amounts for SunCoke Middletown:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | — | | | $ | 5 | |
| Inventories | 20 | | | 21 | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 300 | | | 308 | |
| Accounts payable | (12) | | | (15) | |
| Other assets (liabilities), net | (12) | | | (10) | |
| Noncontrolling interests | (296) | | | (309) | |
NOTE 19 - EARNINGS PER SHARE
The following table summarizes the computation of basic and diluted EPS:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | $ | 3,030 | | | $ | (82) | | | $ | 295 | |
| Income from continuing operations attributable to noncontrolling interest | (45) | | | (41) | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) from continuing operations attributable to Cliffs shareholders | 2,985 | | | (123) | | | 295 | |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | 3 | | | 1 | | | (2) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders | $ | 2,988 | | | $ | (122) | | | $ | 293 | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 498 | | | 379 | | | 277 | |
| Redeemable preferred shares | 33 | | | — | | | — | |
| Convertible senior notes | 22 | | | — | | | 4 | |
| Employee stock plans | 5 | | | — | | | 3 | |
| Diluted | 558 | | | 379 | | | 284 | |
| | | | | |
Earnings (loss) per common share attributable to Cliffs common shareholders - basic1: | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | $ | 5.62 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.07 | |
| Discontinued operations | 0.01 | | | — | | | (0.01) | |
| $ | 5.63 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.06 | |
Earnings (loss) per common share attributable to
Cliffs common shareholders - diluted: | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | $ | 5.35 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.04 | |
| Discontinued operations | 0.01 | | | — | | | (0.01) | |
| $ | 5.36 | | | $ | (0.32) | | | $ | 1.03 | |
| | | | | |
1 For the year ended December 31, 2021, basic earnings per share was calculated by dividing Net income (loss) attributable to Cliffs shareholders, less $187 million of earnings attributed to Series B Participating Redeemable Preferred Stock, by the weighted average number of basic common shares outstanding during the period presented. |
The following table summarizes the shares that have been excluded from the diluted earnings per share calculation for the year ended December 31, 2020, as they were anti-dilutive:
| | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| 2020 |
| Redeemable preferred shares | 4 | |
| Convertible senior notes | 2 | |
| Shares related to employee stock plans | 1 | |
NOTE 20 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Purchase Commitments
We purchase portions of the principal raw materials required for our steel manufacturing operations under annual and multi-year agreements, some of which have minimum quantity requirements. We also use large volumes of natural gas, electricity and industrial gases in our steel manufacturing operations. We negotiate most of our purchases of chrome, industrial gases and a portion of our electricity under multi-year agreements. Our purchases of
coke are made under annual or multi-year agreements with periodic price adjustments. We typically purchase coal under annual fixed-price agreements. We also purchase certain transportation services under multi-year contracts with minimum quantity requirements.
Contingencies
We are currently the subject of, or party to, various claims and legal proceedings incidental to our current and historical operations. These claims and legal proceedings are subject to inherent uncertainties and unfavorable rulings could occur. An unfavorable ruling could include monetary damages, additional funding requirements or an injunction. If an unfavorable ruling were to occur, there exists the possibility of a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations for the period in which the ruling occurs or future periods. However, based on currently available information we do not believe that any pending claims or legal proceedings will result in a material adverse effect in relation to our consolidated financial statements.
Environmental Contingencies
Although we believe our operating practices have been consistent with prevailing industry standards, hazardous materials may have been released at operating sites or third-party sites in the past, including operating sites that we no longer own. If we reasonably can, we estimate potential remediation expenditures for those sites where future remediation efforts are probable based on identified conditions, regulatory requirements, or contractual obligations arising from the sale of a business or facility. For sites involving government required investigations, we typically make an estimate of potential remediation expenditures only after the investigation is complete and when we better understand the nature and scope of the remediation. In general, the material factors in these estimates include the costs associated with investigations, delineations, risk assessments, remedial work, governmental response and oversight, site monitoring, and preparation of reports to the appropriate environmental agencies.
The following is a summary of our environmental obligations:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In Millions) |
| December 31,
2021 | | December 31,
2020 |
| Environmental obligations | $ | 207 | | | $ | 135 | |
| Less current portion | 20 | | | 18 | |
| Long-term environmental obligations | $ | 187 | | | $ | 117 | |
The increase in environmental obligations as of December 31, 2021, compared to December 31, 2020, related to measurement period adjustments as a result of the purchase price allocation of the AM USA Transaction and the preliminary purchase price allocation of the FPT Acquisition.
We cannot predict the ultimate costs for each site with certainty because of the evolving nature of the investigation and remediation process. Rather, to estimate the probable costs, we must make certain assumptions. The most significant of these assumptions is for the nature and scope of the work that will be necessary to investigate and remediate a particular site and the cost of that work. Other significant assumptions include the cleanup technology that will be used, whether and to what extent any other parties will participate in paying the investigation and remediation costs, reimbursement of past response costs and future oversight costs by governmental agencies, and the reaction of the governing environmental agencies to the proposed work plans. Costs for future investigation and remediation are not discounted to their present value, unless the amount and timing of the cash disbursements are readily known. To the extent that we have been able to reasonably estimate future liabilities, we do not believe that there is a reasonable possibility that we will incur a loss or losses that exceed the amounts we accrued for the environmental matters discussed below that would, either individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. However, since we recognize amounts in the consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP that exclude potential losses that are not probable or that may not be currently estimable, the ultimate costs of these environmental matters may be higher than the liabilities we currently have recorded in our consolidated financial statements.
Pursuant to RCRA, which governs the treatment, handling and disposal of hazardous waste, the EPA and authorized state environmental agencies may conduct inspections of RCRA-regulated facilities to identify areas where there have been releases of hazardous waste or hazardous constituents into the environment and may order the facilities to take corrective action to remediate such releases. Likewise, the EPA or the states may require closure or post-closure care of residual, industrial and hazardous waste management units. Environmental regulators have the
authority to inspect all of our facilities. While we cannot predict the future actions of these regulators, it is possible that they may identify conditions in future inspections of these facilities that they believe require corrective action.
Pursuant to CERCLA, the EPA and state environmental authorities have conducted site investigations at some of our facilities and other third-party facilities, portions of which previously may have been used for disposal of materials that are currently regulated. The results of these investigations are still pending, and we could be directed to spend funds for remedial activities at the former disposal areas. Because of the uncertain status of these investigations, however, we cannot reasonably predict whether or when such spending might be required or its magnitude.
On April 29, 2002, AK Steel entered a mutually agreed-upon administrative order with the consent of the EPA pursuant to Section 122 of CERCLA to perform a RI/FS of the Hamilton plant site located in New Miami, Ohio. The plant ceased operations in 1990 and all of its former structures have been demolished. AK Steel submitted the investigation portion of the RI/FS and completed supplemental studies. Until the RI/FS is complete, we cannot reasonably estimate the additional costs, if any, we may incur for potentially required remediation of the site or when we may incur them.
Burns Harbor Water Issues
In August 2019, ArcelorMittal Burns Harbor LLC (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Burns Harbor LLC) suffered a loss of the blast furnace cooling water recycle system, which led to the discharge of cyanide and ammonia in excess of the Burns Harbor plant's NPDES permit limits. Since that time, the facility has taken numerous steps to prevent recurrence and maintain compliance with its NPDES permit. We engaged in settlement discussions with the U.S. Department of Justice, the EPA and the State of Indiana to resolve any alleged violations of environmental laws or regulations arising out of the August 2019 event. Later stages of the settlement discussions included the Environmental Law and Policy Center (ELPC) and Hoosier Environmental Council (HEC), which had filed a lawsuit on December 20, 2019 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Indiana alleging violations resulting from the August 2019 event and other Clean Water Act claims. We believe that a consent decree has been finalized and is currently pending final approvals, which requires specified enhancements to the mill's wastewater treatment systems and a $3 million civil penalty, along with other terms and conditions. ELPC and HEC are also proposed signatories to the consent decree. ArcelorMittal Burns Harbor LLC was served with a subpoena on December 5, 2019, from the United States District Court for the Northern District of Indiana, relating to the August 2019 event and has responded to the subpoena requests, including follow-up requests. With the resolution of monetary sanctions and injunctive relief requirements under the pending consent decree, we do not believe that the costs to resolve any other third-party claims, including potential natural resource damages claims, that may arise out of the August 2019 event are likely to have, individually or in the aggregate, a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
In addition to the foregoing matters, we are or may be involved in proceedings with various regulatory authorities that may require us to pay fines, comply with more rigorous standards or other requirements or incur capital and operating expenses for environmental compliance. We believe that the ultimate disposition of any such proceedings will not have, individually or in the aggregate, a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Tax Matters
The calculation of our tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax regulations. We recognize liabilities for anticipated tax audit issues based on our estimate of whether, and the extent to which, additional taxes will be due. If we ultimately determine that payment of these amounts is unnecessary, we reverse the liability and recognize a tax benefit during the period in which we determine that the liability is no longer necessary. We also recognize tax benefits to the extent that it is more likely than not that our positions will be sustained when challenged by the taxing authorities. To the extent we prevail in matters for which liabilities have been established, or are required to pay amounts in excess of our liabilities, our effective tax rate in a given period could be materially affected. An unfavorable tax settlement would require use of our cash and result in an increase in our effective tax rate in the year of resolution. A favorable tax settlement would be recognized as a reduction in our effective tax rate in the year of resolution. Refer to NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES for further information.
Other Contingencies
In addition to the matters discussed above, there are various pending and potential claims against us and our subsidiaries involving product liability, personal injury, commercial, employee benefits and other matters arising in the ordinary course of business. Because of the considerable uncertainties that exist for any claim, it is difficult to reliably
or accurately estimate what the amount of a loss would be if a claimant prevails. If material assumptions or factual understandings we rely on to evaluate exposure for these contingencies prove to be inaccurate or otherwise change, we may be required to record a liability for an adverse outcome. If, however, we have reasonably evaluated potential future liabilities for all of these contingencies, including those described more specifically above, it is our opinion, unless we otherwise noted, that the ultimate liability from these contingencies, individually or in the aggregate, should not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
NOTE 21 - SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On December 1, 2021, we issued a notice of redemption for all $294 million in aggregate principal amount outstanding of the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes. The 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes were redeemed on January 18, 2022, through a combination settlement, with the aggregate principal amount of $294 million paid in cash, and 24 million common shares, with a fair value of $499 million, delivered to noteholders in settlement of the premium due per the terms of the indenture, plus cash in respect of the accrued and unpaid interest on the 1.500% 2025 Convertible Senior Notes to, but not including, the redemption date per the terms of the indenture.
On February 10, 2022, our Board of Directors authorized a program to repurchase outstanding common shares in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions, which may include purchases pursuant to Rule 10b5-1 plans or accelerated share repurchases, up to a maximum of $1 billion. We are not obligated to make any purchases and the program may be suspended or discontinued at any time. The share repurchase program does not have a specific expiration date.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders and the Board of Directors of
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying statements of consolidated financial position of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the related statements of consolidated operations, comprehensive income, cash flows, and changes in equity, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 11, 2022, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Mineral Reserves — Asset Retirement Obligations, Valuation of Long-Lived Assets, Depreciation, Depletion and Amortization of Property, Plant and Equipment and Valuation in Acquisition Accounting — Refer to Notes 3, 5, 6 and 14 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
Iron ore mineral reserve estimates, combined with estimated annual production levels, are used to determine the iron ore mine closure dates utilized in recording the fair value liability for asset retirement obligations for active operating iron ore mines. Since the liability represents the present value of the expected future obligation, a significant change in iron ore mineral reserves or iron ore mine lives could have a substantial effect on the recorded obligation. Iron ore mineral reserve estimates are also used in evaluating potential impairments of iron ore mine asset groups as they are indicative of future cash flows and in determining maximum useful lives utilized to calculate depreciation, depletion and amortization of long-lived iron ore mine assets. Further, iron ore mineral reserve estimates are used in estimating the fair value of mineral reserves established through the purchase price allocation in a business combination.
The Company performs an in-depth evaluation of its iron ore mineral reserve estimates by iron ore mine on a periodic basis, in addition to routine annual assessments. The determination of iron ore mineral reserves requires management, with the support of management’s experts, to make significant estimates and assumptions related to key inputs including (1) the determination of the size and scope of the iron ore body through technical modeling, (2) the estimates of future iron ore prices recognizing that the price shall not exceed the three-year trailing average index price of iron ore adjusted to the Company’s realized price, production costs and capital expenditures, and (3) management’s mine plan for the proven and probable iron ore mineral reserves (collectively “the iron ore mineral reserve inputs”). Changes in any of the judgments or assumptions related to the iron ore mineral reserve inputs can have a significant impact with respect to the accrual for asset retirement obligations, the impairment of long-lived asset groups, the amount of depreciation, depletion and amortization expense and the estimated fair value of mineral reserves established through the purchase price allocation in a business combination. The consolidated asset retirement obligation balance was $449 million as of December 31, 2021, of which $208 million related to active iron ore mine operations. The total asset balance associated with the Company’s Steelmaking reportable segment was $18,326 million as of December 31, 2021, of which $1,622 million related to long-lived assets associated with the Company’s combined iron ore mine asset groups, and is inclusive of $231 million related to iron ore mineral reserves acquired through the AM USA Transaction. Depreciation, depletion and amortization expense for the Company’s combined iron ore mine asset groups was $172 million for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Given the significant judgments and assumptions made by management to estimate iron ore mineral reserves and the sensitivity of changes to iron ore mineral reserve estimates on the Company’s recorded asset retirement obligations, long-lived asset impairment considerations, calculated depreciation, depletion and amortization expense and estimated fair value of mineral reserves established through the purchase price allocation of a business combination, performing audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s judgments and estimates related to the iron ore mineral reserve inputs required a high degree of auditor judgment and an increased extent of effort.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to management’s significant judgments and assumptions related to iron ore mineral reserve quantities and the related iron ore mine closure dates included the following, among others:
•We tested the operating effectiveness of internal controls related to the Company’s estimation of iron ore mineral reserve quantities and the related iron ore mine closure dates.
•We evaluated the experience, qualifications and objectivity of management’s experts, including in-house iron ore mine engineers and the third-party Qualified Person.
•For an iron ore mine subject to the Company’s routine annual assessment we evaluated management’s assessment by:
◦Understanding the process used by management to survey and analyze the geological and operational status of current year iron ore mine production.
◦Evaluating the historical accuracy of management’s technical model as compared to actual iron ore mine production results.
◦Comparing the iron ore mine plan per the most recent Technical Report Summary, updated for current year depletion, to:
▪Presentations to the Audit Committee.
▪Information by asset group, asset retirement obligation valuation models, depreciation, depletion and amortization expense calculations and mineral reserve purchase price allocation valuation models.
•For an iron ore mine subject to the Company’s periodic in-depth evaluation of its iron ore mineral reserve estimate:
◦We evaluated management’s determination of the size and scope of the iron ore body, by:
▪Understanding the process used by management to complete research and exploration activities including mineralized resource drill samples.
▪Understanding the methodology utilized by management to apply the research and exploration data to the development of a technical model of the iron ore body.
▪Evaluating the historical accuracy of management’s technical model as compared to actual iron ore mine production results.
◦We evaluated management’s estimates of future iron ore prices, production costs and capital expenditures (the “financial assumptions”) as included in the Technical Report Summary, by:
▪Understanding and testing the methodology utilized by management for development of the future iron ore prices recognizing that the price shall not exceed the three-year trailing average index price of iron ore adjusted to the Company’s realized price.
▪Evaluated management’s ability to accurately forecast future iron ore prices, production costs and capital expenditures by comparing actual results to management’s historical forecasts.
▪Evaluated the reasonableness of management’s estimates of future iron ore prices to forecasted information included in analyst reports.
▪Evaluated the reasonableness of management’s forecast for production costs and capital expenditures by comparing the forecasts to: (1) historical results and (2) internal communications among management and to the Board of Directors.
◦We evaluated management’s iron ore mine plan for the proven and probable mineral reserves as included in the Technical Report Summary, by:
▪Understanding the process used by management to develop the iron ore mine plan for proven and probable iron ore mineral reserves applying key inputs such as the technical model of the iron ore body and the financial assumptions.
▪Comparing the iron ore mine plan to
•Presentations to the Audit Committee.
•Historical iron ore mine plan(s).
•Information by asset group, asset retirement obligation valuation models, depreciation, depletion and amortization expense calculations, and mineral reserve purchase price allocation valuation models.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Cleveland, Ohio
February 11, 2022
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2004.
| | | | | |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
| | | | | |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our Exchange Act reports is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure based solely on the definition of “disclosure controls and procedures” in Rule 13a-15(e) promulgated under the Exchange Act. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management necessarily was required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
As of the end of the period covered by this report, we carried out an evaluation under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on the foregoing, our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined under Rule 13a-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act.
Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the Company's consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit the preparation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with appropriate authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company's assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management conducted an assessment of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021 using the framework specified in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013), published by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. We have excluded from our assessment the internal control over financial reporting at FPT, which was acquired on November 18, 2021, and whose assets as of December 31, 2021 constituted 5% of the Company’s consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2021, and whose revenues for the period from November 18, 2021 through December 31, 2021, inclusive, constituted less than 1% of the Company’s consolidated revenues for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Based on such assessment, management has concluded that the Company's internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2021.
The effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021 has been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP (PCAOB ID No. 34), an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report that appears herein.
February 11, 2022
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting or in other factors that occurred during our last fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders and the Board of Directors of
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2021, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2021, of the Company and our report dated February 11, 2022, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
As described in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management excluded from its assessment the internal control over financial reporting at FPT, which was acquired on November 18, 2021, and whose assets as of December 31, 2021 constituted 5% of the Company’s consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2021, and whose revenues for the period from November 18, 2021 through December 31, 2021, inclusive, constituted less than 1% of the Company’s consolidated revenues for the year ended December 31, 2021. Accordingly, our audit did not include the internal control over financial reporting at FPT.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Cleveland, Ohio
February 11, 2022
| | | | | |
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
None.
| | | | | |
| Item 9C. | Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
Not applicable.
PART III
| | | | | |
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
The information required to be furnished by this Item will be set forth in the definitive proxy statement for our 2022 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (the "Proxy Statement") under the headings "Board Meetings and Committees — Audit Committee", "Code of Business Conduct and Ethics", "Independence and Related Party Transactions", and "Information Concerning Director Nominees”, and is incorporated herein by reference and made a part hereof from the Proxy Statement. The information regarding executive officers required by this Item is set forth in Part I - Item 1. Business hereof under the heading “Information About Our Executive Officers”, which information is incorporated herein by reference and made a part hereof.
| | | | | |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information required to be furnished by this Item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement under the headings “Director Compensation”, "Compensation Discussion and Analysis", “Compensation Committee Report”, “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation”, "Compensation-Related Risk Assessment" and “Executive Compensation” and is incorporated herein by reference and made a part hereof from the Proxy Statement.
| | | | | |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information required to be furnished by this Item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement under the headings "Ownership of Equity Securities of the Company" and "Equity Compensation Plan Information" and is incorporated herein by reference and made a part hereof from the Proxy Statement.
| | | | | |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information required to be furnished by this Item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Independence and Related Party Transactions” and is incorporated herein by reference and made a part hereof from the Proxy Statement.
| | | | | |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The information required to be furnished by this Item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Ratification of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” and is incorporated herein by reference and made a part hereof from the Proxy Statement.
PART IV
| | | | | |
Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
(a)(1) - List of Financial Statements
The following consolidated financial statements of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. are included at Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data above:
•Statements of Consolidated Financial Position - December 31, 2021 and 2020
•Statements of Consolidated Operations - Years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
•Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income - Years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
•Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows - Years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
•Statements of Consolidated Changes in Equity - Years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
•Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(a)(2) - Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulation of the SEC are not required under the related instructions or are inapplicable, and therefore have been omitted or are contained in the applicable financial statements or the notes thereto.
(a)(3) List of Exhibits
All documents referenced below have been filed pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., file number 1-09844, unless otherwise indicated.
| | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | Exhibit |
| Articles of Incorporation and Regulations of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. |
| Fourth Amended Articles of Incorporation of Cliffs, as filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Ohio on September 25, 2020 (filed as Exhibit 3.2 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on September 28, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Certificate of Amendment to Fourth Amended Articles of Incorporation of Cliffs, as filed with the Secretary of State of Ohio on December 7, 2020 (filed as Exhibit 3.1 to Cliffs' Form 8-K on December 9, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Certificate of Amendment to Fourth Amended Articles of Incorporation of Cliffs, as amended, as filed with the Secretary of State of Ohio on April 29, 2021 (filed as Exhibit 3.1 to Cliffs' Form 8-K on April 30, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Regulations of Cliffs (filed as Exhibit 3.2 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Instruments defining rights of security holders, including indentures |
| Indenture, dated as of March 17, 2010, between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.) and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.3 to Cliffs’ Registration Statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-186617) on February 12, 2013 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of September 20, 2010, between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.) and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee, including Form of 6.25% Notes due 2040 (filed as Exhibit 4.4 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on September 17, 2010 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 31, 2011, between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.) and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4(b) to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Seventh Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 7, 2013, between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (n/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.) and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Cliffs' Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2013 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | Exhibit |
| Eighth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 19, 2017, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee, including Form of 1.50% Convertible Senior Notes due 2025 (filed as Exhibit 4.2 to Cliffs' Form 8-K on December 19, 2017 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Indenture, dated as of May 13, 2019, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee, including Form of 5.875% Senior Notes due 2027 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Cliffs' Form 8-K on May 14, 2019 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 13, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.4 to Cliffs' Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 22, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.6 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 9, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.24 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 18, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.25 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 22, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantor party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed herewith). |
| Indenture, dated as of March 13, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent, including Form of 6.75% Senior Secured Notes due 2026 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 22, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.9 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 19, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent, including Form of 6.75% Senior Secured Notes due 2026 (filed as Exhibit 4.10 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 9, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.29 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 18, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.30 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 22, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantor party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed herewith). |
| Indenture, dated as of March 16, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee, including Form of 7.00% Senior Notes due 2027 (filed as Exhibit 4.7 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 22, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.7 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 9, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.38 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 18, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.39 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 22, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantor party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed herewith). |
| | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | Exhibit |
| Indenture, dated as of April 17, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent, including Form of 9.875% Senior Secured Notes due 2025 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of April 24, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent, including Form of 9.875% Senior Secured Notes due 2025 (filed as Exhibit 4.2 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 22, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.3 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 9, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.44 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference) |
| Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 18, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed as Exhibit 4.45 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 22, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantor party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee and first lien notes collateral agent (filed herewith). |
| Indenture, dated as of February 17, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee, including Forms of 4.625% Senior Guaranteed Notes due 2029 and 4.875% Senior Guaranteed Notes due 2031 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Cliffs' Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of December 22, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the Additional Guarantor party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (filed herewith). |
| Form of Common Share Certificate (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2019 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Description of Securities Registered under Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (filed herewith). |
| Material contracts |
| * Form of Change in Control Severance Agreement (covering newly hired officers) (filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K/A on September 16, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Form of 2016 Change in Control Severance Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. 2012 Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Plan (Amended and Restated effective October 26, 2021) (filed herewith). |
| * Form of Director and Officer Indemnification Agreement between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. and Directors and Officers (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2019 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. 2021 Nonemployee Directors’ Compensation Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on April 30, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| *Form of Restricted Shares Agreement for Nonemployee Directors (filed as Exhibit 10.3 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| *Form of Deferred Shares Agreement for Nonemployee Directors (filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Trust Agreement No. 1 (Amended and Restated effective June 1, 1997), dated June 12, 1997, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, with respect to the Cleveland-Cliffs Inc Supplemental Retirement Benefit Plan, Severance Pay Plan for Key Employees and certain executive agreements (filed as Exhibit 10.10 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Trust Agreement No. 1 Amendments to Exhibits, effective as of January 1, 2000, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, as Trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.11 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | Exhibit |
| * First Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 1, effective September 10, 2002, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, as Trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.12 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Second Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 1 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of December 31, 2008 (filed as Exhibit 10(y) to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2008 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Third Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 1 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of July 28, 2014 (filed as Exhibit 10.15 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Amended and Restated Trust Agreement No. 2, effective as of October 15, 2002, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, with respect to Executive Agreements and Indemnification Agreements with the Company’s Directors and certain Officers, the Company’s Severance Pay Plan for Key Employees, and the Retention Plan for Salaried Employees (filed as Exhibit 10.14 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Trust Agreement No. 2 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of December 31, 2008 (filed as Exhibit 10(aa) to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2008 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Third Amendment to Amended and Restated Trust Agreement No. 2 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of July 28, 2014 (filed as Exhibit 10.18 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Trust Agreement No. 7, dated as of April 9, 1991, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, with respect to the Cleveland-Cliffs Inc Supplemental Retirement Benefit Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.23 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * First Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 7, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, dated as of March 9, 1992 (filed as Exhibit 10.24 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Second Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 7, dated November 18, 1994, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.25 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Third Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 7, dated May 23, 1997, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.26 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Fourth Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 7, dated July 15, 1997, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.27 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Amendment to Exhibits to Trust Agreement No. 7, effective as of January 1, 2000, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee (filed as Exhibit 10.28 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Sixth Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 7 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of December 31, 2008 (filed as Exhibit 10(oo) to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2008 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Seventh Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 7 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of July 28, 2014 (filed as Exhibit 10.34 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Trust Agreement No. 10, dated as of November 20, 1996, by and between Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, with respect to the Cleveland-Cliffs Inc Nonemployee Directors’ Compensation Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.36 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| *First Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 10 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of December 31, 2008 (filed as Exhibit 10(ww) to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended February 26, 2009 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | Exhibit |
| * Second Amendment to Trust Agreement No. 10 between Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. (f/k/a Cleveland-Cliffs Inc) and KeyBank National Association, Trustee, entered into and effective as of July 28, 2014 (filed as Exhibit 10.45 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Letter Agreement, by and between Lourenco Goncalves and Cliffs Natural Resources Inc., signed as of September 11, 2014 (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K/A on September 16, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cleveland-Cliffs Inc and Subsidiaries Management Performance Incentive Plan Summary, effective January 1, 2004 (filed as Exhibit 10.47 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. 2017 Executive Management Performance Incentive Plan effective January 1, 2017 (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Cliffs' Form 8-K on April 27, 2017 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. Amended and Restated 2012 Incentive Equity Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on August 4, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Form of Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. Amended and Restated 2012 Incentive Equity Plan Non-Qualified Stock Option Award Memorandum (3-Year Vesting – January 2015 Grant) and Stock Option Award Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.69 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. 2015 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on May 21, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cliffs Natural Resources Inc. Amended and Restated 2015 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on April 27, 2017 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Form of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. Amended and Restated 2015 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan Restricted Stock Unit Award Memorandum and Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2018 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Form of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. Amended and Restated 2015 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan Performance Share Award Memorandum and Performance Share Award Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.3 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2018 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Form of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. Amended and Restated 2015 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan Cash Incentive Award Memorandum (TSR) and Cash Incentive Award Agreement (TSR) (filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2018 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. 2021 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on April 30, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| * Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. Supplemental Retirement Benefit Plan (as Amended and Restated effective October 26, 2021) (filed herewith). |
| Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of March 13, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| First Amendment to Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of March 27, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Cliffs’ Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Second Amendment to Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of December 9, 2020, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent (filed as Exhibit 10.42 to Cliffs’ Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2020 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Third Amendment to Asset-Based Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of December 17, 2021, among Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., the lenders party thereto from time to time and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on December 23, 2021 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Subsidiaries of the Registrant (filed herewith). |
| Schedule of the obligated group, including the parent and issuer and the subsidiary guarantors that have guaranteed the obligations under the 6.750% 2026 Senior Secured Notes, the 5.875% 2027 Senior Notes, the 7.000% 2027 Senior Notes, the 9.875% 2025 Senior Secured Notes, the 4.625% 2029 Senior Notes and the 4.875% 2031 Senior Notes issued by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. (filed herewith). |
| Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (filed herewith). |
| | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | Exhibit |
| Consent of SLR International Corporation regarding Hibbing Taconite Property, Minnesota, USA (filed as Exhibit 23.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Consent of SLR International Corporation regarding Minorca Property, Minnesota, USA (filed as Exhibit 23.2 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Consent of SLR International Corporation regarding Northshore Property, Minnesota, USA (filed as Exhibit 23.3 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Consent of SLR International Corporation regarding United Taconite Property, Minnesota, USA (filed as Exhibit 23.4 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Consent of SLR International Corporation regarding Tilden Property, Michigan, USA (filed herewith). |
| Power of Attorney (filed herewith). |
| Certification Pursuant to 15 U.S.C. Section 7241, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, signed and dated by Lourenco Goncalves as of February 11, 2022 (filed herewith). |
| Certification Pursuant to 15 U.S.C. Section 7241, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, signed and dated by Celso L. Goncalves Jr. as of February 11, 2022 (filed herewith). |
| Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, signed and dated by Lourenco Goncalves, Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., as of February 11, 2022 (filed herewith). |
| Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, signed and dated by Celso L. Goncalves Jr., Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer of Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., as of February 11, 2022 (filed herewith). |
| Mine Safety Disclosures (filed herewith). |
| Technical Report Summary on the Hibbing Taconite Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by SLR International Corporation with an effective date of December 31, 2021 (filed as Exhibit 96.1 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Technical Report Summary on the Minorca Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by SLR International Corporation with an effective date of December 31, 2021 (filed as Exhibit 96.2 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Technical Report Summary on the Northshore Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by SLR International Corporation with an effective date of December 31, 2021 (filed as Exhibit 96.3 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Technical Report Summary on the United Taconite Property, Minnesota, USA, prepared for the Company by SLR International Corporation with an effective date of December 31, 2021 (filed as Exhibit 96.4 to Cliffs’ Form 8-K on February 11, 2022 and incorporated herein by reference). |
| Technical Report Summary on the Tilden Property, Michigan, USA, prepared for the Company by SLR International Corporation with an effective date of December 31, 2021 (filed herewith). |
| 101 | The following financial information from Cleveland-Cliffs Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021 formatted in Inline XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language) includes: (i) the Statements of Consolidated Financial Position, (ii) the Statements of Consolidated Operations, (iii) the Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income, (iv) the Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows, (v) the Statements of Consolidated Changes in Equity, and (vi) Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| 104 | The cover page from this Annual Report on Form 10-K, formatted in Inline XBRL. |
_______________
* Indicates management contract or other compensatory arrangement.
| | | | | |
Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary |
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | CLEVELAND-CLIFFS INC. |
| | | | |
| | | By: | | /s/ K. A. Floriani |
| | | | | Name: | Kimberly A. Floriani |
| | | | | Title: | Senior Vice President, Controller &
Chief Accounting Officer |
| Date: | February 11, 2022 | | | | | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signatures | Title | Date |
| | |
| /s/ C. L. Goncalves | Chairman, President and
Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer) | February 11, 2022 |
| C. L. Goncalves |
|
| /s/ C. L. Goncalves Jr. | Executive Vice President,
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer) | February 11, 2022 |
| C. L. Goncalves Jr. |
|
| /s/ K. A. Floriani | Senior Vice President, Controller
& Chief Accounting Officer
(Principal Accounting Officer) | February 11, 2022 |
| K. A. Floriani |
|
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| J. T. Baldwin |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| R. P. Fisher, Jr. |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| W. K. Gerber |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| S. M. Green |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| R. S. Michael, III |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| J. L. Miller |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| G. Stoliar |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| D. C. Taylor |
| * | Director | February 11, 2022 |
| A. M. Yocum |
* The undersigned, by signing his name hereto, does sign and execute this Annual Report on Form 10-K pursuant to a Power of Attorney executed on behalf of the above-indicated directors of the registrant and filed herewith as Exhibit 24 on behalf of the registrant.
| | | | | |
| By: | /s/ C. L. Goncalves Jr. |
| (C. L. Goncalves Jr., as Attorney-in-Fact) |